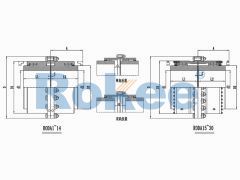
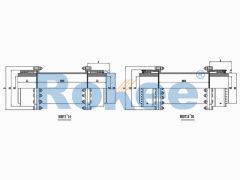
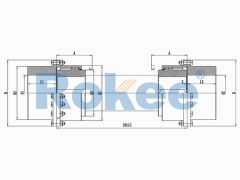
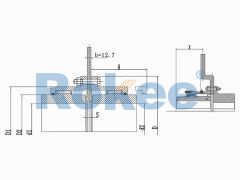
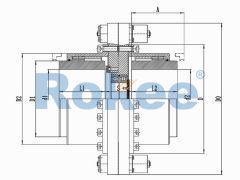
Crane Gear Coupling
Rokee® is a Crane Gear Coupling Supplier from China, customized crane gear coupling according to the drawings which provided by the customer, selling chinese national standard crane gear coupling, support export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® industrial coupling have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
The Drum Gear Coupling is a specially designed advanced Gear Coupling. Its outer teeth are made into a sphere, with the center of the sphere on the axis of the gear. The teeth clearance is slightly larger than the general products and can transfer a greater torque and allow greater angular displacement, enjoying excellent performance and longer life.
ROD Curved-tooth Gear Coupling is one of the transmission products with core technology independently developed by Rokee and has established and reported corporate technical standards in the country. By combining with the standard coupling technology of advanced countries such as Japan and Germany, we optimized many detailed dimensions, and adopted the toothed design with a large pressure angle and short shaft design for the shaft hole, which reduces the length-diameter ratio, and has a more compact structure and excellent speed performance.
The bolts of similar types are standardized and the parts are universal. Compared with the national standard couplings, our Toothed Couplings can transfer more torque, with greatly reduced mass and small moment of inertia. It meets the European explosion-proof requirements and the comprehensive performance is greatly advanced. We highly recommend you to choose our Crown Gear Couplings for better transmission performance.
RODA Drum Gear Coupling
The RODA Drum Gear Coupling is the basic type of ROD series coupling, suitable for most situations where the compensation of transmission distance and motion position does not require special increase.RODT Indirect Tube Drum Gear Coupling
The RODT Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling, suitable for increasing transmission distance.RODX Intermediate Shaft Drum Gear Coupling
RODX Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling with a floating shaft design in the middle, suitable for increasing transmission distance.RODP Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODP Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with a brake disc, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with disc brakes.RODF Split Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODF Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with split brake discs, suitable for transmission situations where there is braking demand and the braking position changes when used in conjunction with disc brakes.RODW Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODW Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes.RODU Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODU Drum Gear Coupling is another type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes and applied to one end of the axle, achieving smoother and more reliable braking performance.RODV Vertical Installation Drum Gear Coupling
The RODV Drum Gear Coupling is a vertical installation type of the ROD series coupling, suitable for transmission situations that require vertical transmission torque.RODM Torsion Protection Drum Gear Coupling
The RODM Drum Gear Coupling is a torque setting form of the ROD series coupling. By adjusting relevant components, the maximum transmission torque can be easily set within a certain range. Suitable for shafting transmission situations that require safe torque operation to protect important machine components from excessive damage.
GICL Drum Gear Coupling
GICL drum gear coupling has larger inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for larger axial displacement.GICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement.GIICL Drum Gear Coupling
GIICL drum gear coupling has small inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for small axial displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.GIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GIICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.GCLD Drum Gear Coupling
GCLD drum gear coupling is generally used for direct connection with the motor, so it generally has a higher speed and compact structure.NGCL Drum Gear Coupling
NGCL drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.NGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling
NGCLZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. Half of its structure adopts a semi-coupling sleeve design, with smaller angular displacement compensation but more stable braking.WG Drum Gear Coupling
The overall characteristics of WG drum gear coupling are similar to those of other drum gear couplings, but with a larger modulus design, which can generally transmit greater torque.WGZ Drum Gear Coupling
WGZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for shoe type braking.WGP Drum Gear Coupling
WGP drum gear coupling is designed with a brake disc, suitable for disc type braking.WGT Drum Gear Coupling
WGT drum gear coupling is designed with indirect tube, suitable for long distance torque transfer.WGC Drum Gear Coupling
WGC drum gear coupling is specially designed for situations where vertical transmission is required, suitable for some vertical transmission systems.WGJ Drum Gear Coupling
WGJ drum gear coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance torque transmission, and some are equipped with axial buffers.
In the realm of heavy machinery, cranes stand as indispensable workhorses, facilitating the lifting, moving, and positioning of massive loads across construction sites, ports, manufacturing facilities, and mining operations. The seamless functionality of a crane relies on the coordinated performance of numerous components, each playing a critical role in transmitting power, absorbing shocks, and accommodating misalignments. Among these essential parts, the crane gear coupling emerges as a vital element, serving as the connection between the crane's motor, reducer, and working mechanism.
A gear coupling is a type of mechanical coupling designed to transmit torque between two rotating shafts while accommodating certain amounts of misalignment, including angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. Specifically engineered for crane applications, crane gear couplings are tailored to withstand the unique operational demands of heavy-duty lifting, such as high torque loads, frequent start-stop cycles, and varying operating conditions. Unlike standard gear couplings used in general machinery, crane gear couplings are constructed with enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity to cope with the intermittent and intense stresses encountered during crane operations.
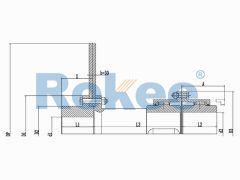
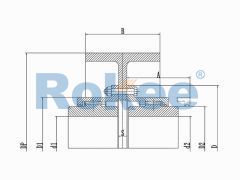
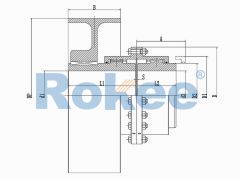
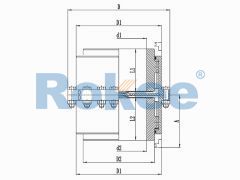
The basic structure of a crane gear coupling typically consists of four main components: two gear hubs, two outer sleeves, seals, and lubricants. The gear hubs are connected to the driving and driven shafts, respectively, and are equipped with external gear teeth. The outer sleeves feature internal gear teeth that mesh with the external teeth of the gear hubs, forming a rigid yet flexible connection. The seals are crucial for preventing the leakage of lubricants and the ingress of dust, moisture, and other contaminants, which can cause premature wear and damage to the gear teeth. Lubricants, on the other hand, reduce friction between the meshing gear teeth, dissipate heat generated during operation, and provide corrosion protection. Some advanced crane gear couplings may also incorporate additional components, such as flexible elements or damping devices, to further enhance their shock absorption and vibration reduction capabilities.
The working principle of a crane gear coupling revolves around the meshing of gear teeth to transmit torque. When the crane's motor starts, it generates rotational power that is transmitted to the gear hub connected to the motor shaft. The external teeth of this gear hub mesh with the internal teeth of the outer sleeve, causing the outer sleeve to rotate. The rotational motion of the outer sleeve is then transferred to the second gear hub, which is connected to the reducer or working mechanism shaft, thereby driving the crane's lifting, luffing, or slewing operations. During this process, the gear coupling accommodates misalignments between the two shafts by allowing a small amount of relative movement between the gear hubs and the outer sleeve. Angular misalignment is compensated by the tilting of the gear teeth meshing surfaces, while parallel misalignment is adjusted through the lateral movement of the gear hubs within the outer sleeve. Axial misalignment, caused by thermal expansion or contraction of the shafts, is absorbed by the axial play between the gear teeth.
The significance of crane gear couplings in crane operations cannot be overstated. First and foremost, they ensure efficient power transmission. By minimizing power loss during torque transfer, gear couplings enable the crane to utilize the motor's power effectively, ensuring that the required lifting capacity and operating speed are achieved. This is particularly important in heavy-duty applications where every unit of power counts, as inefficient power transmission can lead to increased energy consumption and reduced operational efficiency.
Secondly, crane gear couplings play a crucial role in protecting the crane's other components. The ability to absorb shocks and vibrations helps to reduce the impact of sudden load changes and start-stop cycles on the motor, reducer, and shafts. This shock absorption function prevents excessive stress from being transmitted to these critical components, thereby extending their service life and reducing the risk of unexpected failures. Additionally, by accommodating misalignments, gear couplings eliminate the additional forces that would otherwise be exerted on the shafts and bearings due to misalignment, further protecting the crane's drivetrain.
Thirdly, the reliability and durability of crane gear couplings contribute to the overall safety of crane operations. Cranes are often used in hazardous environments where equipment failures can have catastrophic consequences, including damage to property, injury to personnel, and disruption of operations. A well-designed and properly maintained gear coupling ensures stable and consistent performance, reducing the likelihood of sudden breakdowns during critical lifting operations. This reliability is essential for complying with safety regulations and standards in the heavy machinery industry.
When selecting a crane gear coupling, several key factors must be taken into consideration to ensure that it is compatible with the specific requirements of the crane and its operating conditions. The first and most important factor is the torque capacity. The gear coupling must be able to transmit the maximum torque generated by the motor without experiencing premature wear or failure. It is essential to calculate the maximum torque based on the crane's lifting capacity, operating speed, and other relevant parameters, and select a gear coupling with a torque rating that exceeds this maximum value to provide a safety margin.
Another critical factor is the misalignment capacity. Different crane applications may require the gear coupling to accommodate varying degrees of angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. It is important to assess the expected misalignment in the crane's drivetrain and select a gear coupling that can handle these misalignments without compromising performance or durability. Factors such as the installation accuracy of the shafts, the thermal expansion characteristics of the machinery, and the flexibility of the crane's structure can all affect the level of misalignment.
The operating environment is also an important consideration. Cranes may operate in harsh environments such as high temperatures, high humidity, dusty or corrosive conditions, or outdoor settings exposed to the elements. In such cases, the gear coupling must be constructed from materials that can withstand these environmental factors. For example, in corrosive environments, stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials may be used, while in high-temperature applications, heat-resistant alloys and lubricants may be required. Additionally, the seals and protective covers of the gear coupling should be designed to prevent the ingress of contaminants and ensure the integrity of the lubrication system.
The size and installation space of the gear coupling are also practical factors to consider. The gear coupling must fit within the available installation space in the crane's drivetrain, and its dimensions should be compatible with the shaft diameters of the motor and reducer. It is important to review the crane's technical specifications and dimensional constraints before selecting a gear coupling to avoid installation issues.
Proper maintenance of crane gear couplings is essential for ensuring their long-term performance, reliability, and safety. Regular maintenance practices can help to identify potential issues early, prevent premature wear and failure, and extend the service life of the gear coupling. One of the most important maintenance tasks is the regular inspection of the gear coupling. Inspections should include checking for signs of wear, such as excessive tooth wear, pitting, or scuffing on the gear teeth; checking for leaks in the seals; and inspecting the lubricant level and condition.
Lubrication is another critical aspect of gear coupling maintenance. The meshing gear teeth require a continuous supply of high-quality lubricant to reduce friction, dissipate heat, and prevent corrosion. The type of lubricant used should be appropriate for the operating conditions, such as temperature, load, and environment. It is important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for lubricant selection and replacement intervals. Regular lubricant analysis can also be performed to assess the condition of the lubricant and detect any contamination or degradation, which can indicate potential problems with the gear coupling.
Seal maintenance is also essential to ensure the integrity of the lubrication system. Damaged or worn seals can lead to lubricant leakage and the ingress of contaminants, which can cause rapid wear of the gear teeth and other components. Seals should be inspected regularly and replaced if any signs of damage or wear are detected. Additionally, the protective covers of the gear coupling should be checked to ensure that they are intact and properly secured, providing additional protection against contaminants and physical damage.
In the event of any abnormalities detected during inspection, such as excessive vibration, unusual noise, or reduced performance, immediate action should be taken to diagnose and resolve the issue. This may involve disassembling the gear coupling for a more detailed inspection, replacing worn or damaged components, or adjusting the alignment of the shafts. Delaying repairs can lead to more severe damage to the gear coupling and other components of the crane, resulting in costly downtime and potential safety hazards.
Looking to the future, the development of crane gear couplings is likely to be driven by several key trends in the heavy machinery industry, including the demand for higher efficiency, improved reliability, and enhanced safety. One of the main trends is the adoption of advanced materials and manufacturing technologies. The use of high-strength, lightweight materials, such as composite materials or advanced alloys, can help to reduce the weight of the gear coupling while maintaining or improving its load-bearing capacity and durability. This, in turn, can contribute to the overall efficiency of the crane by reducing energy consumption.
Another trend is the integration of smart technologies into crane gear couplings. The development of IoT (Internet of Things) and sensor technologies has made it possible to monitor the performance and condition of gear couplings in real-time. Sensors can be installed to measure parameters such as temperature, vibration, torque, and lubricant condition, providing valuable data that can be used to predict potential failures and optimize maintenance schedules. This predictive maintenance approach can help to reduce downtime, improve operational efficiency, and extend the service life of the gear coupling.
Additionally, there is a growing focus on environmental sustainability in the heavy machinery industry, which is likely to influence the development of crane gear couplings. Manufacturers may increasingly focus on developing gear couplings that are more energy-efficient, use environmentally friendly lubricants, and are easier to recycle at the end of their service life. This aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and minimize the environmental impact of industrial operations.
In conclusion, crane gear couplings are essential components that play a critical role in ensuring the reliable, efficient, and safe operation of cranes. Their ability to transmit torque efficiently, accommodate misalignments, and absorb shocks and vibrations makes them indispensable in heavy-duty lifting applications. When selecting a crane gear coupling, factors such as torque capacity, misalignment capacity, operating environment, and size must be carefully considered to ensure compatibility with the crane's requirements. Proper maintenance, including regular inspection, lubrication, and seal maintenance, is essential for extending the service life of the gear coupling and preventing unexpected failures. Looking ahead, the development of crane gear couplings is poised to benefit from advanced materials, smart technologies, and a focus on environmental sustainability, further enhancing their performance and value in the heavy machinery industry. As cranes continue to evolve to meet the growing demands of industrial operations, the importance of high-quality, reliable crane gear couplings will only continue to increase.
« Crane Gear Coupling » Post Date: 2023/9/23
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/blog/crane-gear-coupling.html
Tags: Internal Gear Couplings, Flexible Gear Couplings, Rubber Gear Coupling, Brake Drum Gear Coupling, Crown Gear Couplings, Curved-tooth Gear Couplings, Flange Gear Coupling, Face Gear Couplings, Crown Gear Coupling, pu sandwich panel line
- Elastic Shaft Pin Gear Coupling
- Heavy Machinery Gear Couplings
- Face Gear Coupling Design
- Calculation Method For Curved-tooth Gear Coupling
- Elastic Gear Coupling
- Main Oil Pump Gear Coupling
- Axial Compensation Of Curved-tooth Gear Coupling
- Drum Type Gear Coupling With Brake Wheel
- Heavy Duty Gear Coupling
- Assembly Tolerance Of Curved-tooth Gear Coupling