Crown Gear Couplings
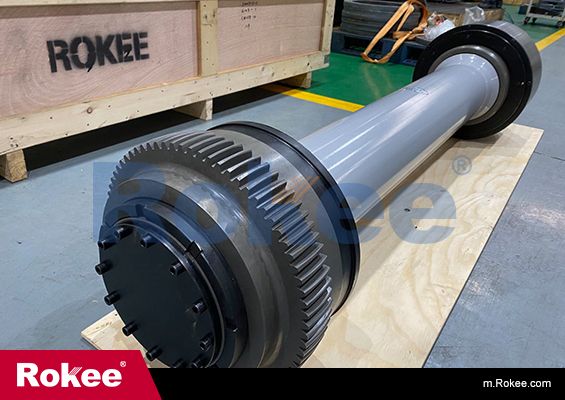

Rokee® is Crown Gear Couplings Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® Crown Gear Couplings have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
ROD Crown Gear Coupling is one of Rokee’s core technical products. It has compact and reasonable structure, light weight, small hole-position fitting draw ratio, large pressure angle design, accurate centering and excellent speed performance. The bolt design has been standardized in series, the universality of parts is good and its service life far exceeds the one of domestic products.
-

GICL Drum Gear Coupling
GICL drum gear coupling has larger inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for larger axial displacement. -

GICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. -

GIICL Drum Gear Coupling
GIICL drum gear coupling has small inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for small axial displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low. -

GIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GIICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low. -

GCLD Drum Gear Coupling
GCLD drum gear coupling is generally used for direct connection with the motor, so it generally has a higher speed and compact structure. -

NGCL Drum Gear Coupling
NGCL drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. -

NGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling
NGCLZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. Half of its structure adopts a semi-coupling sleeve design, with smaller angular displacement compensation but more stable braking. -

WG Drum Gear Coupling
The overall characteristics of WG drum gear coupling are similar to those of other drum gear couplings, but with a larger modulus design, which can generally transmit greater torque. -

WGZ Drum Gear Coupling
WGZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for shoe type braking. -

WGP Drum Gear Coupling
WGP drum gear coupling is designed with a brake disc, suitable for disc type braking. -

WGT Drum Gear Coupling
WGT drum gear coupling is designed with indirect tube, suitable for long distance torque transfer. -

WGC Drum Gear Coupling
WGC drum gear coupling is specially designed for situations where vertical transmission is required, suitable for some vertical transmission systems. -

WGJ Drum Gear Coupling
WGJ drum gear coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance torque transmission, and some are equipped with axial buffers. -
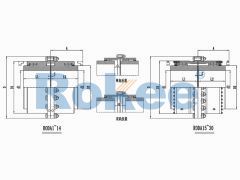
RODA Drum Gear Coupling
The RODA Drum Gear Coupling is the basic type of ROD series coupling, suitable for most situations where the compensation of transmission distance and motion position does not require special increase. -
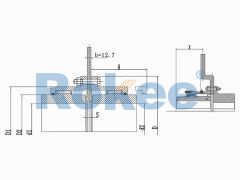
RODP Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODP Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with a brake disc, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with disc brakes. -
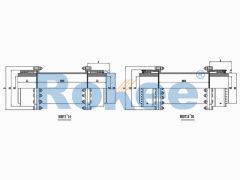
RODT Indirect Tube Drum Gear Coupling
The RODT Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling, suitable for increasing transmission distance. -
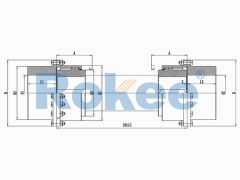
RODX Intermediate Shaft Drum Gear Coupling
RODX Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling with a floating shaft design in the middle, suitable for increasing transmission distance. -
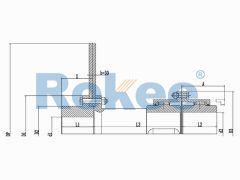
RODF Split Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODF Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with split brake discs, suitable for transmission situations where there is braking demand and the braking position changes when used in conjunction with disc brakes. -
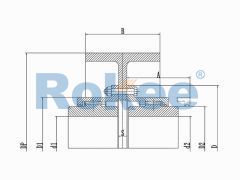
RODW Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODW Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes. -
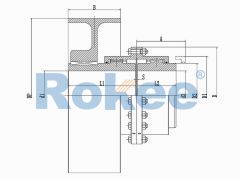
RODU Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODU Drum Gear Coupling is another type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes and applied to one end of the axle, achieving smoother and more reliable braking performance. -
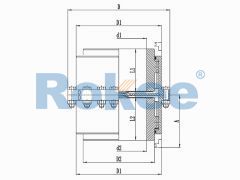
RODV Vertical Installation Drum Gear Coupling
The RODV Drum Gear Coupling is a vertical installation type of the ROD series coupling, suitable for transmission situations that require vertical transmission torque. -
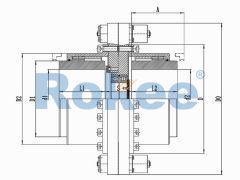
RODM Torsion Protection Drum Gear Coupling
The RODM Drum Gear Coupling is a torque setting form of the ROD series coupling. By adjusting relevant components, the maximum transmission torque can be easily set within a certain range. Suitable for shafting transmission situations that require safe torque operation to protect important machine components from excessive damage.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings play an indispensable role as components that connect two shafts to transmit torque while accommodating various forms of misalignment. Among the diverse types of couplings available, crown gear couplings stand out for their exceptional ability to handle high torque loads and significant misalignments, making them a preferred choice in numerous heavy-duty industrial applications.
The design of a crown gear coupling is a sophisticated integration of gear mechanics and coupling engineering, tailored to balance torque transmission efficiency with misalignment compensation. At its core, a standard crown gear coupling consists of two main components: a pair of crown gears (also referred to as crown wheel gears) and two hubs that attach to the respective shafts being connected. Each crown gear is mounted on a hub, and the gears mesh together to form the torque-transmitting interface. The defining feature of the crown gear is its curved tooth profile, where the teeth are cut on a conical surface, giving the gear a crown-like appearance—hence the name “crown gear coupling.”
The tooth profile of crown gears is meticulously engineered to enable smooth meshing even when the shafts are misaligned. Unlike straight-tooth gears, which require precise alignment to avoid excessive wear and stress, the curved teeth of crown gears provide a larger contact area, distributing the transmitted torque more evenly across the teeth. This design not only enhances the coupling’s load-bearing capacity but also allows it to accommodate three primary types of misalignment: angular misalignment (where the shafts intersect at an angle), parallel misalignment (where the shafts are offset parallel to each other), and axial misalignment (where the shafts move along their axial direction). Additionally, some crown gear coupling designs incorporate a sleeve or housing that encloses the meshing gears, serving to protect the gear teeth from contaminants and retain lubrication, which is critical for reducing friction and wear.
The dimensions of crown gear couplings vary widely to suit different application requirements, with parameters such as hub diameter, gear module, number of teeth, and overall coupling length being customized based on the torque rating, shaft size, and misalignment tolerance needed. The materials used in the construction of crown gear couplings are selected for their high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and fatigue. Common materials include alloy steels, which offer excellent tensile strength and toughness, making them suitable for heavy-duty torque transmission. In some cases, the gear teeth may undergo surface treatments such as carburizing, nitriding, or hardening to further enhance their wear resistance and extend the service life of the coupling.
The operational principle of a crown gear coupling revolves around the meshing of the crown gears to transmit torque from one shaft to another while compensating for misalignment. When torque is applied to the input shaft, the hub connected to this shaft rotates, causing the attached crown gear to turn. The meshing of the teeth between the two crown gears transfers this rotational force to the output shaft’s hub, thereby driving the output shaft. The curved tooth profile is crucial to the coupling’s ability to handle misalignment: as the shafts deviate from perfect alignment, the curved teeth slide against each other slightly, maintaining continuous contact and smooth torque transmission without creating excessive stress concentrations.
Lubrication plays a vital role in the operation of crown gear couplings, as it reduces friction between the meshing teeth, minimizes wear, and dissipates heat generated during operation. The type of lubricant used depends on factors such as the operating temperature, load conditions, and environmental factors. Common lubricants include mineral oils, synthetic oils, and greases, each offering specific advantages in terms of temperature resistance, viscosity, and lubrication longevity. The enclosed design of many crown gear couplings helps to keep the lubricant in place and prevents contamination by dust, dirt, and other debris, which can damage the gear teeth and reduce the coupling’s performance.
Crown gear couplings offer a range of key advantages that make them well-suited for heavy-duty industrial applications. One of the most significant advantages is their high torque capacity. The large contact area provided by the curved tooth profile allows crown gear couplings to transmit significantly higher torques compared to many other types of couplings, such as jaw couplings or sleeve couplings. This makes them ideal for use in applications where large amounts of power need to be transferred, such as in industrial machinery, turbines, and heavy equipment.
Another major advantage is their excellent misalignment compensation capability. Crown gear couplings can accommodate substantial angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, which is particularly important in applications where shaft alignment is difficult to maintain, such as in large rotating machinery or equipment subjected to vibration. The ability to handle misalignment without excessive wear or stress also contributes to the coupling’s long service life and reliability.
Crown gear couplings also exhibit good shock absorption and vibration damping properties. The meshing of the curved teeth helps to absorb sudden shocks and vibrations generated during operation, reducing the impact on the connected shafts and other components. This not only improves the overall stability of the mechanical system but also helps to prevent premature failure of other components, such as bearings and seals.
In addition, crown gear couplings are known for their compact design relative to their torque capacity. Despite their high load-bearing capability, they have a relatively small footprint, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. Their simple construction also facilitates easy installation and removal, which is beneficial for maintenance and repair operations.
The versatility of crown gear couplings is reflected in their wide range of applications across various industries. One of the most common applications is in the power generation industry, where they are used to connect turbines (such as steam turbines, gas turbines, and hydro turbines) to generators. In these applications, the coupling must transmit high torques efficiently while accommodating any misalignment between the turbine and generator shafts, which can occur due to thermal expansion, vibration, or installation tolerances. Crown gear couplings are well-suited for this role due to their high torque capacity and excellent misalignment compensation.
Another major application area is in the mining and mineral processing industry. Mining equipment such as crushers, conveyors, and mills operate under harsh conditions, requiring couplings that can handle high torques, heavy loads, and significant misalignments. Crown gear couplings are commonly used in these applications to connect the drive motors to the equipment shafts, ensuring reliable power transmission even in dusty, vibrating environments.
The steel and metalworking industry also relies heavily on crown gear couplings. Equipment such as rolling mills, extruders, and forging presses require couplings that can transmit large amounts of torque while accommodating the misalignments that occur due to the high forces and thermal stresses generated during the metalworking process. Crown gear couplings are ideal for these applications, as their robust design and wear-resistant materials can withstand the harsh operating conditions.
Other applications of crown gear couplings include marine propulsion systems, where they are used to connect the ship’s engine to the propeller shaft; heavy-duty pumps and compressors, which require reliable torque transmission and misalignment compensation; and industrial fans and blowers, where they help to maintain efficient operation despite vibration and misalignment.
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of crown gear couplings. Regular maintenance practices help to prevent premature wear, reduce the risk of unexpected failure, and minimize downtime. One of the most important maintenance tasks is regular lubrication. The lubricant should be checked periodically to ensure that it is clean and at the correct level. Contaminated or degraded lubricant can cause increased friction and wear between the gear teeth, leading to premature failure. Depending on the operating conditions, the lubricant should be replaced at regular intervals, as recommended by the coupling’s operating guidelines.
Regular inspection of the coupling components is also crucial. The crown gear teeth should be inspected for signs of wear, pitting, cracking, or deformation. Any damage to the teeth can compromise the coupling’s torque transmission capacity and lead to further damage if not addressed promptly. The hubs and other components should also be inspected for signs of corrosion, fatigue, or loose fasteners. In addition, the alignment of the connected shafts should be checked regularly, as excessive misalignment beyond the coupling’s tolerance can cause excessive stress on the gear teeth and other components.
When inspecting the coupling, it is important to follow proper safety procedures, such as shutting down the equipment and locking out the power source to prevent accidental startup. For couplings with an enclosed design, the housing may need to be removed to access the gear teeth and other internal components. If any damage or excessive wear is detected, the affected components should be repaired or replaced immediately to avoid further damage to the coupling or the connected equipment.
Another important maintenance practice is proper storage of spare coupling components. Spare crown gears, hubs, and other parts should be stored in a clean, dry environment to prevent corrosion and damage. They should also be protected from dust, dirt, and other contaminants that can affect their performance when installed.
Despite their robust design and reliability, crown gear couplings may encounter common issues such as gear tooth wear, lubrication failure, and misalignment-related damage. Gear tooth wear is often caused by inadequate lubrication, contaminated lubricant, or excessive misalignment. To prevent this, it is essential to maintain proper lubrication levels and ensure that the lubricant is clean and suitable for the operating conditions. Lubrication failure can occur due to leaks in the coupling housing, improper lubricant selection, or infrequent lubricant replacement. Regular inspection of the housing for leaks and proper lubricant management can help to avoid this issue.
Misalignment-related damage is typically caused by shafts that are misaligned beyond the coupling’s specified tolerance. This can lead to excessive stress on the gear teeth, resulting in cracking or deformation. To prevent this, regular shaft alignment checks should be performed, and any misalignment should be corrected promptly. In some cases, the use of alignment tools such as laser alignment systems can help to ensure precise shaft alignment.
In conclusion, crown gear couplings are essential components in modern mechanical power transmission systems, offering high torque capacity, excellent misalignment compensation, and reliable performance in harsh industrial environments. Their unique design, featuring curved tooth profiles that enable smooth meshing and torque transmission even under misaligned conditions, makes them well-suited for a wide range of applications across industries such as power generation, mining, steel production, and marine propulsion. Proper design selection, installation, and maintenance are critical to maximizing the performance and service life of crown gear couplings. By following recommended lubrication practices, conducting regular inspections, and ensuring proper shaft alignment, operators can ensure that crown gear couplings continue to operate efficiently and reliably, contributing to the overall productivity and stability of mechanical systems.
As industrial machinery continues to evolve toward higher power densities, greater efficiency, and more demanding operating conditions, the role of crown gear couplings is likely to remain crucial. Ongoing advancements in materials science and manufacturing technologies may lead to further improvements in the performance and durability of crown gear couplings, such as the development of new wear-resistant materials, more efficient lubrication systems, and optimized gear tooth profiles. These advancements will help to meet the evolving needs of industrial applications, ensuring that crown gear couplings remain a vital component in power transmission systems for years to come.
« Crown Gear Couplings » Post Date: 2023/8/19
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/crown-gear-couplings.html
- 2025-06-27Crown Gear Coupling Wholesale
- 2024-07-11Direct Sale Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-06-07Procurement of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-06-07Purpose of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-06-07Schematic Diagram of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-06-07Crown Gear Coupling Assembly Drawing
- 2024-06-07Crown Gear Coupling Brands
- 2024-06-07Crown Gear Coupling Calculation
- 2024-06-07Crown Gear Coupling Manufacturing
- 2024-06-07Crown Gear Coupling Models
- 2024-06-07Crown Gear Coupling Price
- 2024-06-04Parts of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-06-04Crown Gear Coupling Sales
- 2024-05-29Lubrication of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-29Installation of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-29High Quality Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-29High Performance Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-29Grease of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-29Crown Gear Coupling Standard Sizes
- 2024-05-29Crown Gear Couplings Drawing
- 2024-05-29Crown Gear Couplings Factory
- 2024-05-29Crown Gear Couplings For Sale
- 2024-05-27Material of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-27Maintenance of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-27Function of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-27Exploded View of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-27Engineering Drawing of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-27Efficiency of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-27Disadvantages of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-27Customized Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-27Components of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-27Classification of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-27Catalogue of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-27Application of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-27Angle of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-27Alignment of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-22Crown Gear Couplings Supplier
- 2024-05-22Size Calculation of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-22Size Chart of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-22Specifications of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-22Stiffness of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-22Structural Diagram of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-22Tagging of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-22Types of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-22Uses of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-22Working Principle of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-20Torque of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-20Crown Gear Couplings Manufacturer
- 2024-05-20Crown Gear Coupling Pictures
- 2024-05-20Crown Gear Coupling Advantages
- 2024-05-20Machine Drawing of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-203D Model of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-20Coaxiality of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-20Gap Chart of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-20Misalignment Tolerance of Crown Gear Coupling
- 2024-05-20Crown Gear Coupling Design
- 2024-05-20Crown Gear Couplings Company
- 2024-05-20Supply of Crown Gear Couplings
- 2024-05-20Crown Gear Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-09-23Crown Gear Coupling
- 2023-09-22Standard For Crown Gear Couplings