Curved Tooth Couplings
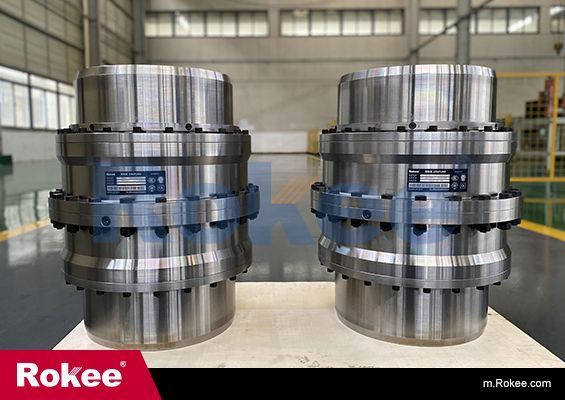

Rokee® is Curved Tooth Couplings Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® Curved Tooth Couplings have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
Curved Tooth Coupling has compact and reasonable structure, light weight, small hole-position fitting draw ratio, large pressure angle design, accurate centering and excellent speed performance. The bolt design has been standardized in series, the universality of parts is good and its service life far exceeds the one of domestic products.
-

GICL Drum Gear Coupling
GICL drum gear coupling has larger inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for larger axial displacement. -

GICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. -

GIICL Drum Gear Coupling
GIICL drum gear coupling has small inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for small axial displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low. -

GIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GIICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low. -

GCLD Drum Gear Coupling
GCLD drum gear coupling is generally used for direct connection with the motor, so it generally has a higher speed and compact structure. -

NGCL Drum Gear Coupling
NGCL drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. -

NGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling
NGCLZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. Half of its structure adopts a semi-coupling sleeve design, with smaller angular displacement compensation but more stable braking. -

WG Drum Gear Coupling
The overall characteristics of WG drum gear coupling are similar to those of other drum gear couplings, but with a larger modulus design, which can generally transmit greater torque. -

WGZ Drum Gear Coupling
WGZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for shoe type braking. -

WGP Drum Gear Coupling
WGP drum gear coupling is designed with a brake disc, suitable for disc type braking. -

WGT Drum Gear Coupling
WGT drum gear coupling is designed with indirect tube, suitable for long distance torque transfer. -

WGC Drum Gear Coupling
WGC drum gear coupling is specially designed for situations where vertical transmission is required, suitable for some vertical transmission systems. -

WGJ Drum Gear Coupling
WGJ drum gear coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance torque transmission, and some are equipped with axial buffers. -
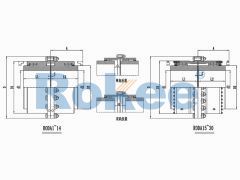
RODA Drum Gear Coupling
The RODA Drum Gear Coupling is the basic type of ROD series coupling, suitable for most situations where the compensation of transmission distance and motion position does not require special increase. -
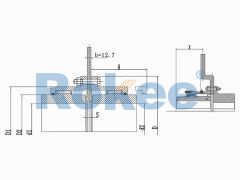
RODP Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODP Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with a brake disc, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with disc brakes. -
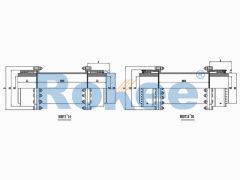
RODT Indirect Tube Drum Gear Coupling
The RODT Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling, suitable for increasing transmission distance. -
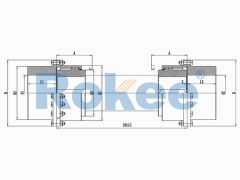
RODX Intermediate Shaft Drum Gear Coupling
RODX Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling with a floating shaft design in the middle, suitable for increasing transmission distance. -
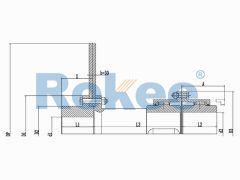
RODF Split Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODF Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with split brake discs, suitable for transmission situations where there is braking demand and the braking position changes when used in conjunction with disc brakes. -
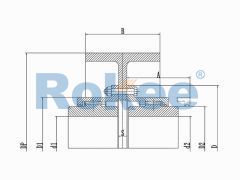
RODW Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODW Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes. -
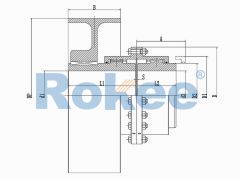
RODU Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODU Drum Gear Coupling is another type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes and applied to one end of the axle, achieving smoother and more reliable braking performance. -
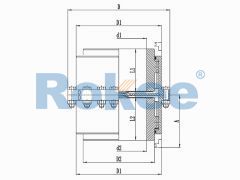
RODV Vertical Installation Drum Gear Coupling
The RODV Drum Gear Coupling is a vertical installation type of the ROD series coupling, suitable for transmission situations that require vertical transmission torque. -
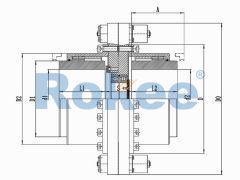
RODM Torsion Protection Drum Gear Coupling
The RODM Drum Gear Coupling is a torque setting form of the ROD series coupling. By adjusting relevant components, the maximum transmission torque can be easily set within a certain range. Suitable for shafting transmission situations that require safe torque operation to protect important machine components from excessive damage.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as critical components that connect two rotating shafts, enabling the seamless transfer of torque while accommodating various forms of misalignment. Among the diverse types of couplings available, curved tooth couplings stand out for their exceptional performance, durability, and versatility in handling high-torque applications. Unlike their straight-tooth counterparts, curved tooth couplings feature teeth with a curved profile, which fundamentally enhances their ability to absorb shock, reduce vibration, and tolerate misalignment.
The design of curved tooth couplings is a sophisticated blend of mechanical engineering principles, aimed at optimizing torque transmission efficiency while minimizing wear and tear. At the core of their structure, curved tooth couplings typically consist of two hubs with curved teeth, an outer sleeve (or flange) that meshes with the hub teeth, and in some cases, a flexible element or lubrication system. The most distinctive feature of these couplings is the curved profile of the teeth, which is carefully engineered to ensure continuous contact between the mating teeth during operation. This curved design differs significantly from straight-tooth couplings, where the teeth make linear contact, leading to higher stress concentrations and limited misalignment capacity.
The curvature of the teeth in curved tooth couplings is often designed to follow a circular arc or a logarithmic spiral, depending on the specific application requirements. Circular arc teeth are commonly used for general-purpose applications, as they provide a good balance between load-carrying capacity and misalignment tolerance. Logarithmic spiral teeth, on the other hand, offer even greater contact area and smoother torque transmission, making them suitable for high-speed and high-torque applications. Additionally, the number of teeth, module (tooth size), and pressure angle are key design parameters that influence the coupling’s performance. A higher number of teeth distributes the load more evenly, reducing the stress on individual teeth, while the module determines the coupling’s torque-carrying capacity—larger modules are capable of transmitting higher torques.
Another important design aspect of curved tooth couplings is the type of connection between the hubs and the shafts. Common connection methods include keyway connections, shrink-fit connections, and spline connections. Keyway connections are the most widely used due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, where a key is inserted into a groove (keyway) machined into both the shaft and the hub, ensuring a secure torque transfer. Shrink-fit connections involve heating the hub to expand its inner diameter, sliding it onto the shaft, and allowing it to cool and contract, creating an interference fit that eliminates the need for additional fasteners. Spline connections, which feature multiple grooves (splines) on both the shaft and the hub, provide a higher torque-carrying capacity and better alignment accuracy, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
The working principle of curved tooth couplings revolves around the meshing of the curved teeth on the hubs with the teeth on the outer sleeve, facilitating torque transmission while accommodating axial, radial, and angular misalignment. When torque is applied to one shaft, it is transferred to the corresponding hub, whose curved teeth engage with the teeth on the outer sleeve. The curved profile of the teeth allows for relative movement between the mating components, enabling the coupling to absorb misalignment between the two shafts. Axial misalignment occurs when the shafts are displaced along their axial direction, radial misalignment is caused by the shafts being offset parallel to each other, and angular misalignment happens when the shafts are inclined at an angle relative to each other. Curved tooth couplings are capable of accommodating all three types of misalignment simultaneously, which is a significant advantage over many other coupling types.
The continuous contact between the curved teeth also contributes to smoother torque transmission. Unlike straight-tooth couplings, where the teeth engage and disengage abruptly, the curved teeth gradually mesh and unmesh, reducing shock loads and vibration. This smooth engagement not only improves the overall performance of the mechanical system but also extends the lifespan of the coupling and other connected components, such as bearings and gears. Additionally, the curved tooth design minimizes friction between the mating teeth, especially when properly lubricated, further reducing wear and energy loss.
Curved tooth couplings offer a multitude of advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. One of the primary advantages is their high torque-carrying capacity. The curved tooth profile provides a larger contact area between the mating teeth compared to straight-tooth couplings, allowing them to transmit higher torques without excessive stress. This makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as industrial machinery, power generation, and marine propulsion systems, where large amounts of torque need to be transferred efficiently.
Another key advantage is their excellent misalignment tolerance. As mentioned earlier, curved tooth couplings can accommodate axial, radial, and angular misalignment, which is crucial in real-world applications where perfect alignment of shafts is often difficult to achieve due to manufacturing tolerances, thermal expansion, and structural deflection. By absorbing misalignment, these couplings reduce the stress on the shafts, bearings, and other components, preventing premature failure and minimizing maintenance costs.
Shock absorption and vibration damping are additional benefits of curved tooth couplings. The curved tooth profile acts as a buffer, absorbing shock loads that may occur during start-up, shutdown, or sudden changes in load. This is particularly important in applications such as mining equipment, construction machinery, and automotive transmissions, where shock loads are common. The reduction in vibration also improves the stability and reliability of the mechanical system, leading to better overall performance and a quieter operation environment.
Durability and long service life are also hallmarks of curved tooth couplings. The even distribution of load across the curved teeth reduces wear and tear, while the use of high-quality materials such as alloy steel, stainless steel, and cast iron further enhances their durability. When properly lubricated and maintained, curved tooth couplings can operate for extended periods without significant degradation, making them a cost-effective choice for long-term applications.
The versatility of curved tooth couplings is another factor that contributes to their widespread use. They can be customized to meet the specific requirements of different applications, including variations in size, torque capacity, misalignment range, and material selection. For example, in high-temperature applications, couplings made from heat-resistant materials can be used, while in corrosive environments, stainless steel or coated couplings are preferred. This adaptability makes curved tooth couplings suitable for a diverse range of industries and applications.
Curved tooth couplings find applications in a wide array of industries, spanning from heavy manufacturing to power generation and marine engineering. One of the most common applications is in industrial machinery, such as pumps, compressors, fans, and conveyors. In these applications, the couplings are used to connect the motor to the driven equipment, ensuring efficient torque transmission while accommodating misalignment caused by the operation of the machinery. For example, in a centrifugal pump system, the curved tooth coupling connects the electric motor to the pump shaft, absorbing any radial or angular misalignment that may occur due to the weight of the pump impeller or thermal expansion of the shaft.
Power generation is another major application area for curved tooth couplings. In thermal power plants, hydroelectric power plants, and wind farms, these couplings are used to connect turbines to generators, transmitting the high torque generated by the turbines to the generators for electricity production. The high torque-carrying capacity and misalignment tolerance of curved tooth couplings make them ideal for these applications, where reliable and efficient power transmission is critical. For instance, in a hydroelectric power plant, the curved tooth coupling connects the water turbine to the generator, accommodating any misalignment caused by the movement of the turbine shaft under varying water flow conditions.
Marine propulsion systems also rely heavily on curved tooth couplings. In ships and other marine vessels, the couplings are used to connect the main engine to the propeller shaft, transmitting the engine’s torque to the propeller to drive the vessel forward. The harsh marine environment, which includes saltwater corrosion, vibration, and shock loads, demands couplings that are durable and reliable. Curved tooth couplings, with their corrosion-resistant materials and excellent shock absorption capabilities, are well-suited for this application. Additionally, their ability to accommodate misalignment is crucial in marine systems, where the propeller shaft may experience deflection due to the vessel’s movement in the water.
Automotive and aerospace industries also utilize curved tooth couplings in specific applications. In automotive transmissions, for example, these couplings are used to connect different components of the transmission system, ensuring smooth torque transmission and absorbing shock loads during gear shifts. In aerospace applications, such as aircraft engines and auxiliary power units, curved tooth couplings are used for their high reliability, compact design, and ability to operate in high-temperature and high-speed environments.
Mining and construction machinery are other important application areas for curved tooth couplings. Equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, and mining trucks operate under harsh conditions with heavy loads, shock impacts, and significant misalignment. Curved tooth couplings are used in these machines to connect the engine to the transmission, axles, and other components, ensuring reliable power transmission and withstanding the demanding operating conditions. Their durability and shock absorption capabilities make them essential for minimizing downtime and maintenance costs in these industries.
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance and long service life of curved tooth couplings. One of the most critical maintenance tasks is regular lubrication. The meshing teeth of the coupling require a continuous supply of lubricant to reduce friction, prevent wear, and protect against corrosion. The type of lubricant used should be compatible with the coupling’s materials and the operating conditions, such as temperature and load. For high-temperature applications, high-temperature grease or oil is recommended, while in corrosive environments, lubricants with anti-corrosion additives are preferred. Lubrication intervals should be followed strictly, and the lubricant should be checked regularly for contamination and replaced when necessary.
Regular inspection is another important maintenance practice. Couplings should be inspected periodically for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Common signs of wear include excessive play between the teeth, uneven tooth wear, and the presence of metal particles in the lubricant. Damage to the coupling, such as cracked teeth or a bent outer sleeve, should be addressed immediately to prevent catastrophic failure. Misalignment should be checked using appropriate tools, such as dial indicators, and corrected if necessary. Additionally, the connection between the hub and the shaft should be inspected to ensure that it is secure, and any loose fasteners should be tightened.
Proper installation is also a key factor in the maintenance of curved tooth couplings. During installation, the shafts should be aligned as accurately as possible to minimize the load on the coupling. The coupling should be mounted correctly, ensuring that the teeth mesh properly and that there is no excessive interference or clearance. The use of proper installation tools and techniques is essential to avoid damaging the coupling or the shafts. Additionally, the coupling should be installed in a clean environment to prevent dirt and debris from entering the meshing teeth, which can cause premature wear.
In cases where the coupling is used in harsh environments, additional protective measures may be necessary. For example, in dusty or corrosive environments, the coupling can be enclosed in a protective cover to prevent the ingress of dirt, dust, or corrosive substances. In high-temperature environments, heat shields can be used to protect the coupling from excessive heat. These protective measures can significantly extend the service life of the coupling and reduce maintenance costs.
In conclusion, curved tooth couplings are essential components in modern mechanical power transmission systems, offering a unique combination of high torque-carrying capacity, excellent misalignment tolerance, shock absorption, and durability. Their sophisticated design, characterized by curved tooth profiles, enables them to perform reliably in a wide range of applications, from industrial machinery and power generation to marine propulsion and mining equipment. Proper design selection, installation, and maintenance are crucial to maximizing the performance and service life of curved tooth couplings, ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of the mechanical systems they support. As technology continues to advance, the design and materials of curved tooth couplings are likely to be further optimized, enhancing their performance and expanding their application range in the future.
« Curved Tooth Couplings » Post Date: 2023/9/1
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/curved-tooth-couplings.html
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Coupling Customized
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Couplings Manufacturing Enterprise
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-07Types Of Curved Tooth Couplings
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Couplings Supply
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Couplings Supplier
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Coupling Structural Diagram
- 2023-11-07Specifications Of Curved Tooth Couplings
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Coupling Size Chart
- 2023-11-07Purpose Of Curved Tooth Couplings
- 2023-11-07Parts Of Curved Tooth Couplings
- 2023-11-07Models Of Curved Tooth Couplings
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Coupling On Sales
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Couplings Factory
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-07Disadvantages Of Curved Tooth Couplings
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Coupling Design
- 2023-11-07Custom Curved Tooth Coupling
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Coupling Company
- 2023-11-07Catalogue Of Curved Tooth Couplings
- 2023-11-07Application Of Curved Tooth Couplings
- 2023-11-07Curved Tooth Coupling Advantages
- 2023-09-18Price Of Curved Tooth Coupling
- 2023-09-18Manufacturer Of Curved Tooth Coupling