Disc Couplings
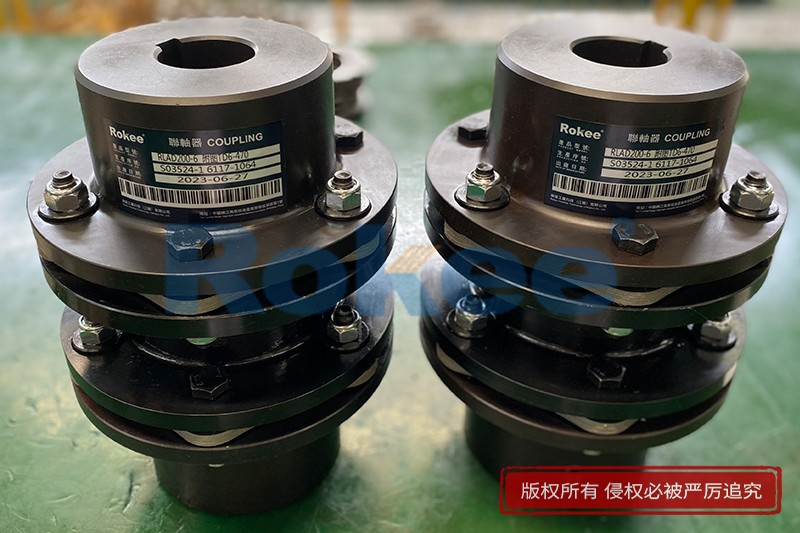

Rokee® is Disc Couplings Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® Disc Couplings have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
Disc Coupling is an efficient flexible coupling with no back clearance and free from maintenance. Due to its unique structural design, it can achieve the perfect delivery of torque. Meanwhile, Disc Coupling has excellent performances, including large axial and radial compensation ability, low reply feedback force and wide thermal adaptability, etc. With different change design, Disc Coupling can be applied at most power transmission sites.
-

JMI Diaphragm Coupling
JMI metal diaphragm coupling adopts the single-piece design, suitable for short distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMII Diaphragm Coupling
JMII metal diaphragm coupling also adopts the single-piece design but has no counterbore, suitable for short distance transmission, with more compact structure. -

JMIIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at both ends have no counterbore. -
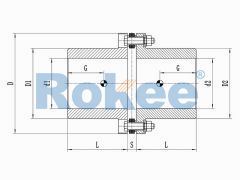
RLA Standard Single Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications, but cannot compensate for radial deviation. -
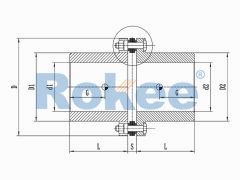
RLM Small Single Diaphragm Coupling
The RLM standard single section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working situations with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm, and cannot compensate for radial errors. -
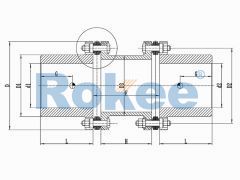
RLMD Small Double Diaphragm Coupling
The RLMD standard double section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working occasions with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm. -
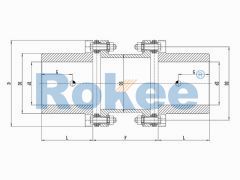
RLAD Standard Double Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications. -
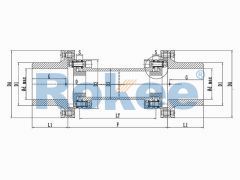
RLAT Super Long Wheelbase Diaphragm Coupling
Adopting an intermediate shaft design, suitable for ultra long shaft spacing power transmission applications. -
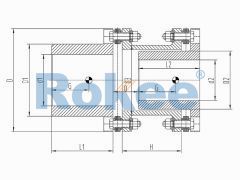
RLAR Single Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
Single side shaft sleeve reverse installation design, suitable for occasions with limited shaft head distance. -
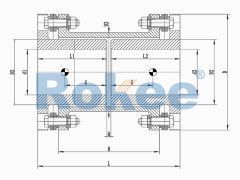
RLARD Double Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
The double-sided shaft sleeve reverse installation design is also applicable in situations where the distance from the shaft head is limited or the additional bending moment is smaller. -
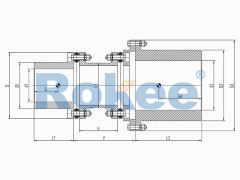
RLAF Large & Small Shaft Mounted Diaphragm Coupling
The size difference design of the bilateral shaft sleeve is suitable for situations where the diameter difference between the two ends of the shaft is significant. -
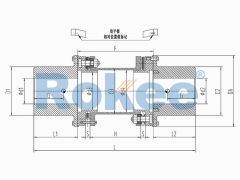
RLQA No Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for various industrial process pumps, fans, and other medium to low speed applications, with a maximum speed generally not exceeding 25000 rpm. It meets the requirements of API610/ISO14691 and is one of the first products for API applications. -
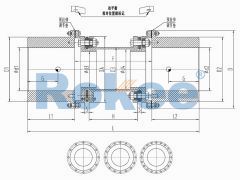
RLQF Flange Type Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications, with a maximum speed of up to 35000rpm. -
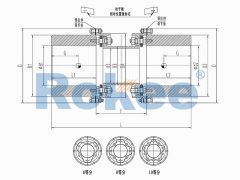
RLQU Improved Flange Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
The improved RLQF has smaller additional bending moments and better performance. Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications. -
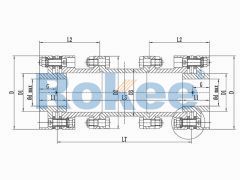
RLHD High Speed Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for higher speed applications, it also adopts a flexible component integrated assembly design, with a maximum speed of up to 42000rpm.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, the efficient and reliable transfer of torque between rotating shafts is a fundamental requirement across numerous industries. Among the various coupling devices designed to fulfill this role, disc couplings have emerged as a preferred choice for applications demanding high precision, durability, and the ability to accommodate misalignments without compromising performance. Unlike flexible couplings that rely on elastomeric components, disc couplings utilize thin, rigid discs or diaphragms to transmit torque while compensating for axial, radial, and angular misalignments. This unique design not only enhances their mechanical integrity but also makes them suitable for use in harsh operating environments where temperature extremes, chemical exposure, or high rotational speeds would degrade other coupling types.
1. Fundamental Principles of Disc Couplings
At its core, a disc coupling functions by transmitting torque through a series of thin, flat discs (or diaphragms) that are bolted to the input and output hubs of the coupling. The discs are typically arranged in pairs or stacks, with each disc designed to flex slightly under load, allowing for the accommodation of misalignments between the connected shafts. Unlike gear couplings, which rely on meshing teeth, or jaw couplings, which use rubber inserts, disc couplings transmit torque through pure tension and compression forces within the discs. When torque is applied to the input shaft, the discs stretch on one side and compress on the other, transferring the rotational force to the output shaft with minimal energy loss.
A key principle underlying the operation of disc couplings is their ability to handle misalignments without introducing additional stresses into the shaft system. Axial misalignment, which occurs when the shafts are displaced along their central axis, is compensated for by the axial flexibility of the discs. Radial misalignment, where the shafts are offset parallel to each other, is accommodated by the bending flexibility of the disc petals. Angular misalignment, caused by the shafts being inclined at an angle to one another, is addressed by the combined bending and twisting of the discs. Importantly, this misalignment compensation is achieved without any sliding or rolling contact between components, which eliminates wear and reduces the need for lubrication—a significant advantage over many other coupling designs.
Another critical principle is the balance and precision of disc couplings. Due to their rigid disc design and lack of loose components, disc couplings can be manufactured to very tight tolerances, ensuring high rotational balance. This balance is essential for applications involving high rotational speeds, as unbalanced couplings can generate excessive vibration, leading to premature wear of bearings, shafts, and other system components. The absence of lubrication also means that disc couplings do not suffer from lubricant degradation or contamination, further enhancing their reliability in long-term operation.
2. Structural Components of Disc Couplings
Disc couplings consist of several key components that work together to ensure efficient torque transmission and misalignment compensation. While designs may vary slightly depending on the application, the basic structure typically includes hubs, discs (or diaphragms), spacers (in some configurations), and fasteners.
Hubs are the connecting elements that attach the coupling to the input and output shafts. They are usually machined from solid metal and feature a bore that is either keyed, splined, or interference-fit to the shaft, ensuring a secure connection that can transmit high torques without slipping. The design of the hub is critical, as it must withstand the torque loads and transfer them evenly to the discs. Hubs may also include flanges or mounting surfaces for attaching the discs, with precise machining to ensure alignment between the hub and the discs.
The discs (or diaphragms) are the heart of the coupling, responsible for torque transmission and misalignment compensation. Discs are typically thin, circular plates with a series of holes around their perimeter for fasteners. They may be single discs or stacked in multiples to increase torque capacity and flexibility. Diaphragms, a variation of discs, are often conical or bell-shaped, providing enhanced flexibility and torque transmission capabilities. The shape and thickness of the discs are carefully engineered to balance torque capacity with the ability to flex under misalignment. Common disc configurations include single-disc, double-disc, and multi-disc designs, with each offering specific advantages in terms of misalignment range and torque rating.
Spacers are optional components used in "spacer-type" disc couplings to separate the two sets of discs and provide additional axial length. Spacers can be solid or hollow and are typically used when the shafts are separated by a significant distance or when there is a need to accommodate thermal expansion. Fasteners, such as bolts and nuts, are used to secure the discs to the hubs and spacers. These fasteners must be torqued to precise specifications to ensure a uniform transfer of force across the discs and prevent loosening during operation.
3. Key Advantages of Disc Couplings
Disc couplings offer a range of advantages over other types of couplings, making them ideal for a wide variety of industrial applications. One of the most significant advantages is their high torque capacity relative to their size. Due to the rigid nature of the discs and the efficient transfer of torque through tension and compression, disc couplings can transmit large amounts of torque without the need for large, bulky designs. This compact size makes them suitable for applications where space is limited, such as in automotive transmissions, aerospace engines, and industrial gearboxes.
Another major advantage is their ability to accommodate multiple types of misalignments without performance degradation. As previously noted, disc couplings can handle axial, radial, and angular misalignments, reducing the need for precise shaft alignment during installation and minimizing stresses on the shaft and bearings. This flexibility is particularly valuable in applications where thermal expansion or contraction of components can cause dynamic misalignments, such as in high-temperature industrial processes.
The absence of lubrication is another key benefit of disc couplings. Unlike gear couplings, which require regular lubrication to prevent wear and corrosion, disc couplings have no moving parts that require lubrication. This eliminates the need for lubrication maintenance, reduces the risk of lubricant contamination (which can damage other system components), and makes disc couplings suitable for use in clean environments, such as food processing plants, pharmaceutical facilities, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Disc couplings also exhibit excellent high-speed performance. Due to their balanced design and lack of loose components, they can operate at very high rotational speeds without generating excessive vibration. This makes them ideal for applications such as centrifuges, turbochargers, and high-speed electric motors, where vibration control is critical for reliability and performance.
Additionally, disc couplings are highly durable and have a long service life. The discs are typically made from high-strength materials that can withstand fatigue and wear, even under continuous operation. Unlike elastomeric couplings, which degrade over time due to heat, ozone, or chemical exposure, disc couplings are resistant to environmental factors, making them suitable for use in harsh conditions such as chemical plants, offshore platforms, and high-temperature industrial furnaces.
4. Diverse Applications of Disc Couplings
The unique combination of advantages offered by disc couplings has made them indispensable in a wide range of industries and applications. One of the primary application areas is the automotive industry, where disc couplings are used in transmissions, drivelines, and electric vehicle powertrains. In these applications, their compact size, high torque capacity, and ability to handle misalignments make them ideal for transmitting power from the engine or electric motor to the wheels.
The aerospace industry also relies heavily on disc couplings for use in jet engines, helicopter transmissions, and satellite systems. In aerospace applications, weight and reliability are critical, and disc couplings offer a lightweight, durable solution for torque transmission. Their ability to operate in high-temperature and high-vibration environments makes them suitable for use in engine components, where they must withstand extreme conditions while maintaining performance.
Industrial machinery is another major application area for disc couplings. They are commonly used in pumps, compressors, fans, and conveyors, where they ensure efficient power transmission and compensate for misalignments between the motor and the driven equipment. In pumping applications, for example, disc couplings help to reduce vibration and extend the life of the pump bearings, while their lubrication-free design makes them suitable for use in clean water or chemical pumping systems.
The energy sector, including power generation and renewable energy, also utilizes disc couplings extensively. In power plants, they are used in steam turbines, gas turbines, and generators, where they transmit high torques at high speeds. In renewable energy applications, such as wind turbines and solar thermal systems, disc couplings are used to connect the turbine or collector to the generator, ensuring reliable power transmission even in variable wind or temperature conditions.
Other applications of disc couplings include marine propulsion systems, where they transmit power from the engine to the propeller; machine tools, where they ensure precise torque transmission for cutting and machining operations; and medical equipment, such as centrifuges and MRI machines, where high precision and low vibration are essential.
5. Material Considerations for Disc Couplings
The performance and durability of disc couplings are heavily dependent on the materials used in their construction. The choice of material is determined by the application requirements, including torque capacity, operating temperature, environmental conditions, and corrosion resistance. The most common materials used for disc coupling components are stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and titanium.
Stainless steel is widely used for disc diaphragms due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It is particularly suitable for applications in chemical plants, marine environments, and food processing facilities, where corrosion is a major concern. Stainless steel discs also exhibit good fatigue resistance, making them ideal for high-cycle applications.
Carbon steel is commonly used for hubs and spacers due to its high torque capacity and low cost. It is suitable for applications where high strength is required but corrosion resistance is not a primary concern. Carbon steel components may be coated with paint or other protective finishes to enhance their corrosion resistance in moderate environments.
Aluminum is used in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace and automotive components. Aluminum couplings are lightweight and offer good thermal conductivity, making them suitable for high-temperature applications. However, aluminum has lower torque capacity than steel, so it is typically used in low to medium torque applications.
Titanium is a high-performance material used in specialized applications where extreme strength, lightweight, and corrosion resistance are required. It is commonly used in aerospace and marine applications, where the cost of titanium is justified by its superior performance. Titanium discs and hubs offer excellent fatigue resistance and can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments.
In addition to the base materials, the choice of fasteners is also critical. Fasteners are typically made from high-strength steel or stainless steel, with corrosion-resistant coatings where necessary. The selection of fasteners must ensure that they can withstand the torque loads and environmental conditions of the application, as loose or failed fasteners can lead to coupling failure.
6. Maintenance Practices for Disc Couplings
While disc couplings are known for their low maintenance requirements, regular inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure their long-term reliability and performance. The primary maintenance tasks for disc couplings include visual inspection, torque checking of fasteners, alignment verification, and replacement of worn or damaged components.
Visual inspection should be performed regularly to check for signs of disc damage, such as cracks, warping, or fatigue. Discs are the most critical component of the coupling, and any damage to the discs can compromise the coupling's ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments. Visual inspection should also check for signs of corrosion, wear on the hubs or spacers, and loose or missing fasteners.
Torque checking of fasteners is another important maintenance task. Over time, fasteners may loosen due to vibration or thermal cycling, which can lead to uneven torque distribution and disc damage. Fasteners should be torqued to the manufacturer's specifications using a calibrated torque wrench, and any loose fasteners should be tightened immediately. In some applications, lock washers or thread-locking compounds may be used to prevent fastener loosening.
Alignment verification is essential to ensure that the shafts are properly aligned. While disc couplings can accommodate misalignments, excessive misalignment can increase stress on the discs and reduce their service life. Shaft alignment should be checked during installation and periodically thereafter, particularly after any maintenance or equipment reconfiguration. Laser alignment tools are commonly used to ensure precise alignment, as they provide accurate measurements of axial, radial, and angular misalignments.
Replacement of worn or damaged components should be performed as soon as any issues are detected. Discs that are cracked, warped, or fatigued should be replaced immediately, as they can fail unexpectedly under load. Hubs or spacers that show signs of excessive wear or corrosion should also be replaced to ensure the integrity of the coupling. When replacing components, it is important to use parts that are compatible with the original coupling design, as non-standard parts can compromise performance and reliability.
In addition to these regular maintenance tasks, it is important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for operating conditions. Operating the coupling beyond its torque capacity, rotational speed, or temperature limits can lead to premature failure. Proper storage of spare components is also important, as exposure to moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures can damage the components before they are installed.
7. Conclusion
Disc couplings have established themselves as a reliable and efficient solution for torque transmission in a wide range of industrial, automotive, aerospace, and energy applications. Their unique design, which utilizes rigid discs to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments, offers numerous advantages over other coupling types, including high torque capacity, lubrication-free operation, high-speed performance, and durability in harsh environments. The selection of appropriate materials, based on application requirements, ensures that disc couplings can perform reliably in even the most demanding conditions.
Regular maintenance, including visual inspection, torque checking, alignment verification, and component replacement, is essential to maximize the service life of disc couplings and ensure their continued performance. By understanding the fundamental principles, structural components, and key advantages of disc couplings, engineers and maintenance professionals can select and maintain the appropriate coupling for their specific application, ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission.
As technology continues to advance, disc coupling designs are likely to evolve further, with improvements in material technology, manufacturing processes, and performance capabilities. These advancements will enable disc couplings to meet the growing demands of modern mechanical systems, including higher torque capacities, faster rotational speeds, and more extreme operating environments. In conclusion, disc couplings are a critical component in modern power transmission systems, and their importance is only set to increase as industries continue to seek more efficient, reliable, and durable mechanical solutions.
« Disc Couplings » Post Date: 2023/9/1
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/disc-couplings.html
- 2025-06-27Diaphragm Coupling Vs Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-22Exploded View of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-22Engineering Drawing of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-22Efficiency of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-22Disc Couplings Wholesale
- 2024-05-22Disc Couplings Supplier
- 2024-05-22Disc Couplings Manufacturer
- 2024-05-22Disc Couplings For Sale
- 2024-05-22Disc Couplings Factory
- 2024-05-22Disc Couplings Drawing
- 2024-05-22Disc Couplings Company
- 2024-05-22Disc Coupling Standard Sizes
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Sales
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Price
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Pictures
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Models
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Manufacturing
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Design
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Calculation
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Brands
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Assembly Drawing
- 2024-05-20Disc Coupling Advantages
- 2024-05-17Function of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-17Gap Chart of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-17Grease of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-17High Quality Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-17Installation of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-17Lubrication of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-17Machine Drawing of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-17Maintenance of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-17Material of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-17Misalignment Tolerance of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-13Disadvantages of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-13Customized Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-13Components of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-13Coaxiality of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-13Classification of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-13Catalogue of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-13Application of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-13Angle of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-13Alignment of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-133D Model of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-10Parts of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-10Procurement of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-10Purpose of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-10Schematic Diagram of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-10Size Calculation of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-10Size Chart of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-10Specifications of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-10Stiffness of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-10Structural Diagram of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-10Supply of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-10Tagging of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-10Torque of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-10Types of Disc Coupling
- 2024-05-10Uses of Disc Couplings
- 2024-05-10Working Principle of Disc Coupling
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Couplings Supply
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling Structural Diagram
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling Purpose
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling Parts
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling Make
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling For Sale
- 2023-11-10Metallic Disc Coupling Customized
- 2023-11-10Metallic Disc Coupling Function
- 2023-11-10Metallic Disc Coupling Size Calculation
- 2023-11-09Metallic Disc Coupling Specifications
- 2023-11-09Models Of Metallic Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-09Metallic Disc Coupling Working Principle
- 2023-11-09Metallic Disc Coupling Design
- 2023-11-08Types of Membrane Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-08Purpose of Membrane Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-08Models of Membrane Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Tagging
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Specifications
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Size Chart
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Parts
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Advantages
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Procurement
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Couplings Manufacturer
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Couplings For Sale
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Couplings Factory
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Couplings Catalogue
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Size Calculation
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Design
- 2023-11-08Disadvantages of Membrane Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Customized
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Manufacturing Enterprise
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Working Principle
- 2023-11-08Supply of Membrane Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Couplings Supplier
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Couplings Company
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Structural Diagram
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Price
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Function
- 2023-11-08Membrane Disc Coupling Applications
- 2023-11-08Types Of Metallic Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Factory
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Advantages
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Manufacturing Enterprise
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Manufacturer
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Catalogue
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Supplier
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Size Chart
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Company
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Price
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Applications
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-08Disadvantages Of Metallic Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-01Types of Metal Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Couplings Supply
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Couplings Supplier
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Diagram
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Specifications
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Size Chart
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Purpose
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Price
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Parts
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Couplings Model
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Couplings Manufacturer
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Make
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Couplings For Sale
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Couplings Factory
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Effect
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Disadvantages
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Design
- 2023-11-01Custom Metal Disc Coupling
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Company
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Catalogue
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Application
- 2023-11-01Metal Disc Coupling Advantages
- 2023-10-19Crane Drum Toothed Disc Coupling
- 2023-10-17Membrane Disc Couplings
- 2023-10-10Diaphragm Disc Couplings
- 2023-10-10Diaphragm Locking Disc Couplings
- 2023-10-10Claw Disc Couplings
- 2023-09-26Gear Brake Disc Coupling
- 2023-09-22Toothed Disc Coupling