Diaphragm Couplings
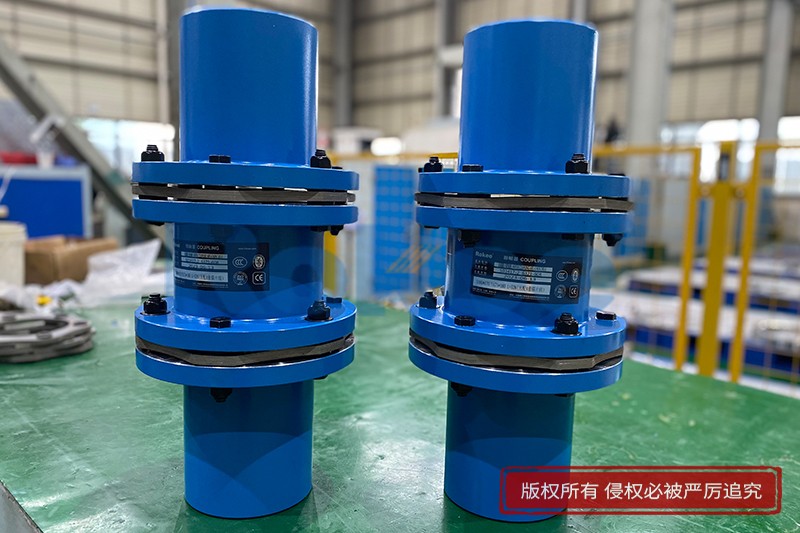

Rokee® is Diaphragm Couplings Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® Diaphragm Couplings have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
Diaphragm Coupling is an efficient flexible coupling with no back clearance and free from maintenance. Due to its unique structural design, diaphragm coupling can achieve the perfect delivery of torque. Meanwhile, diaphragm coupling has excellent performances, including large axial and radial compensation ability, low reply feedback force and wide thermal adaptability, etc. With different change design, diaphragm coupling can be applied at most power transmission sites.
-

JMI Diaphragm Coupling
JMI metal diaphragm coupling adopts the single-piece design, suitable for short distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMII Diaphragm Coupling
JMII metal diaphragm coupling also adopts the single-piece design but has no counterbore, suitable for short distance transmission, with more compact structure. -

JMIIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at both ends have no counterbore. -
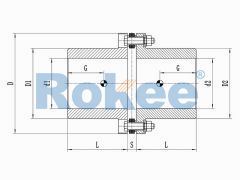
RLA Standard Single Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications, but cannot compensate for radial deviation. -
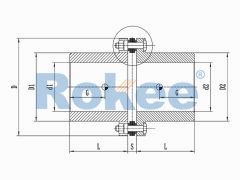
RLM Small Single Diaphragm Coupling
The RLM standard single section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working situations with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm, and cannot compensate for radial errors. -
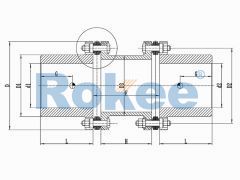
RLMD Small Double Diaphragm Coupling
The RLMD standard double section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working occasions with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm. -
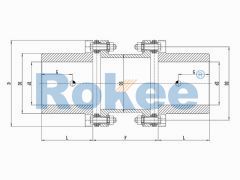
RLAD Standard Double Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications. -
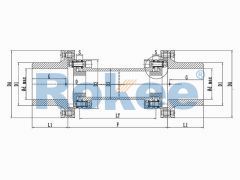
RLAT Super Long Wheelbase Diaphragm Coupling
Adopting an intermediate shaft design, suitable for ultra long shaft spacing power transmission applications. -
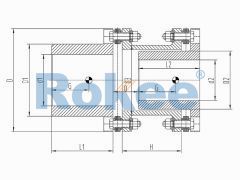
RLAR Single Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
Single side shaft sleeve reverse installation design, suitable for occasions with limited shaft head distance. -
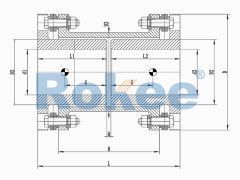
RLARD Double Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
The double-sided shaft sleeve reverse installation design is also applicable in situations where the distance from the shaft head is limited or the additional bending moment is smaller. -
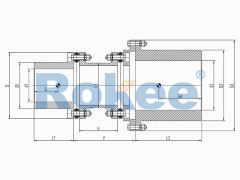
RLAF Large & Small Shaft Mounted Diaphragm Coupling
The size difference design of the bilateral shaft sleeve is suitable for situations where the diameter difference between the two ends of the shaft is significant. -
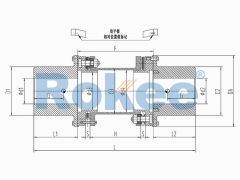
RLQA No Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for various industrial process pumps, fans, and other medium to low speed applications, with a maximum speed generally not exceeding 25000 rpm. It meets the requirements of API610/ISO14691 and is one of the first products for API applications. -
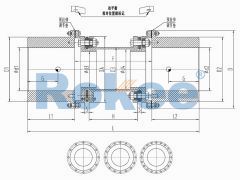
RLQF Flange Type Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications, with a maximum speed of up to 35000rpm. -
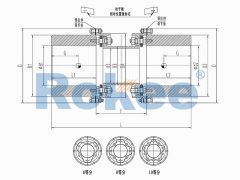
RLQU Improved Flange Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
The improved RLQF has smaller additional bending moments and better performance. Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications. -
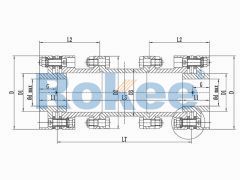
RLHD High Speed Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for higher speed applications, it also adopts a flexible component integrated assembly design, with a maximum speed of up to 42000rpm.
In the realm of power transmission systems, couplings play an indispensable role as the critical link between driving and driven components. Among the diverse array of coupling types available, diaphragm couplings have emerged as a preferred choice in numerous industrial applications due to their unique combination of high torque capacity, precision alignment capabilities, and resistance to harsh operating conditions. Unlike flexible couplings that rely on elastomeric elements for compensation, diaphragm couplings utilize thin, flexible metallic diaphragms to transmit torque while accommodating misalignments. This design not only ensures reliable power transfer but also eliminates the need for lubrication, reducing maintenance requirements and enhancing operational efficiency.
At the core of a diaphragm coupling's functionality lies its ability to transmit torque through flexible diaphragms while compensating for three primary types of misalignment: angular misalignment (the deviation in the axes of the driving and driven shafts), parallel misalignment (the offset between the two shafts), and axial displacement (the linear movement of one shaft relative to the other). The diaphragms, typically arranged in a series of thin, circular plates with a specific pattern of slots or holes, act as the flexible element that absorbs these misalignments without transferring excessive stress to the connected shafts or bearings. When torque is applied, the diaphragms undergo elastic deformation, allowing for relative movement between the input and output sides of the coupling while maintaining a consistent torque transfer. This elastic deformation is reversible, ensuring that the diaphragms return to their original shape once the load is removed, thus preventing permanent damage and ensuring long-term reliability.
The working principle of diaphragm couplings is rooted in the mechanical properties of the diaphragm material, which must exhibit high tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and flexibility. As torque is transmitted from the driving shaft to the coupling hub, the force is distributed evenly across the diaphragms. The slots or holes in the diaphragms are strategically designed to optimize flexibility in the directions required to compensate for misalignments, while maintaining rigidity in the torque-transmitting direction. This balance between flexibility and rigidity is crucial for minimizing power loss and ensuring precise torque transmission, making diaphragm couplings particularly suitable for high-speed and high-precision applications where even minor deviations can lead to significant performance issues.
Diaphragm couplings are available in several distinct structural configurations, each tailored to specific application requirements. The two most common types are single-diaphragm and double-diaphragm couplings. Single-diaphragm couplings consist of a single set of diaphragms attached to two hubs, one for the driving shaft and one for the driven shaft. This design offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for applications with moderate misalignment requirements and lower torque loads. However, single-diaphragm couplings tend to exert a certain amount of axial force on the connected shafts and bearings due to the unbalanced nature of the diaphragm deformation, which can limit their use in high-speed or long-term applications.
Double-diaphragm couplings, on the other hand, feature two sets of diaphragms separated by an intermediate shaft or spacer. This configuration eliminates the axial force generated by single-diaphragm designs by balancing the forces exerted by the two diaphragm sets. The intermediate spacer also provides additional flexibility, allowing for greater misalignment compensation and enabling the coupling to accommodate longer shaft distances. Double-diaphragm couplings are therefore more suitable for high-torque, high-speed applications, as well as those requiring precise alignment and minimal bearing loads. Another variation is the flexible-disc coupling, which uses a single flexible disc (a type of diaphragm) with a different slot pattern to achieve misalignment compensation, often used in light-duty to medium-duty applications where space is limited.
Material selection is a critical factor in determining the performance, reliability, and service life of diaphragm couplings. The diaphragms themselves are typically manufactured from high-performance metallic materials that offer a combination of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. The most commonly used materials include stainless steel, titanium alloys, and nickel-based superalloys. Stainless steel, particularly grades such as 304 and 316, is widely used due to its excellent corrosion resistance, good fatigue strength, and cost-effectiveness. It is suitable for most industrial applications operating in normal temperature ranges and moderate corrosive environments.
Titanium alloys are preferred for high-performance applications where weight reduction is critical, such as aerospace and marine propulsion systems. Titanium offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent fatigue resistance, and superior corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel, but comes with a higher cost. Nickel-based superalloys, such as Inconel, are used in extreme operating conditions, including high temperatures (exceeding 500°C) and highly corrosive environments. These alloys maintain their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for applications such as gas turbines, steam turbines, and industrial furnaces. The hubs and other structural components of diaphragm couplings are typically made from carbon steel or alloy steel, which provide high strength and rigidity to support the torque transmission process.
The unique characteristics of diaphragm couplings make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications across various sectors. One of the primary application areas is the power generation industry, where diaphragm couplings are used in gas turbines, steam turbines, and generators. In these applications, the high torque capacity, precision alignment, and lubrication-free design of diaphragm couplings ensure reliable power transmission, even at high speeds (up to 30,000 rpm) and high temperatures. The absence of lubrication also reduces the risk of contamination, which is critical in power generation systems where even minor impurities can cause significant damage to sensitive components.
Another major application area is the aerospace industry, where diaphragm couplings are used in aircraft engines, auxiliary power units (APUs), and flight control systems. The lightweight design, high strength-to-weight ratio, and resistance to extreme temperatures and vibrations make diaphragm couplings ideal for aerospace applications, where weight reduction and reliability are paramount. In addition, the lubrication-free operation eliminates the need for maintenance during flight, reducing operational costs and enhancing safety.
The automotive industry also utilizes diaphragm couplings in high-performance vehicles, such as racing cars and luxury sports cars, as well as in electric vehicle (EV) drivetrains. In EVs, diaphragm couplings are used to connect the electric motor to the transmission, providing efficient torque transmission and compensating for misalignments between the motor and transmission shafts. The lubrication-free design is particularly beneficial in EVs, as it reduces maintenance requirements and improves overall efficiency. Other application areas include industrial machinery (such as pumps, compressors, and conveyors), marine propulsion systems, and renewable energy systems (such as wind turbines and solar tracking systems).
Proper installation is essential to ensure the optimal performance and service life of diaphragm couplings. The first step in the installation process is to ensure that the shafts of the driving and driven components are properly aligned. Misalignment beyond the coupling's rated capacity can lead to excessive stress on the diaphragms, resulting in premature failure. Alignment should be performed using precision tools, such as laser alignment systems or dial indicators, to ensure that angular misalignment is within 0.1 to 0.5 degrees and parallel misalignment is within 0.1 to 0.3 mm, depending on the coupling size and application requirements.
Next, the coupling hubs should be securely attached to the shafts using the appropriate fasteners (such as keyways, set screws, or hydraulic shrink fits). It is important to follow the manufacturer's specifications for torque values when tightening the fasteners to ensure a secure connection without damaging the shafts or hubs. The diaphragms should then be installed between the hubs, ensuring that they are properly aligned and not subjected to any preload. In double-diaphragm couplings, the intermediate spacer should be centered between the two diaphragm sets to balance the axial forces.
After installation, a final check should be performed to verify the alignment and ensure that the coupling rotates freely without any binding or excessive vibration. Any issues identified during this check should be addressed immediately to prevent damage to the coupling or connected components. It is also important to ensure that the coupling is installed in a clean environment, free from dust, debris, and moisture, which can cause corrosion and premature wear.
One of the key advantages of diaphragm couplings is their low maintenance requirements, primarily due to the absence of lubrication. However, regular inspection and maintenance are still necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent unexpected failures. The primary maintenance tasks include periodic inspection of the diaphragms for signs of wear, fatigue, or damage (such as cracks, tears, or deformation). Inspections should be performed at regular intervals, depending on the application and operating conditions, typically every 6 to 12 months for normal operating conditions and more frequently for harsh environments.
During inspections, the diaphragms should be visually examined for any visible damage. If cracks or other signs of fatigue are detected, the diaphragms should be replaced immediately to prevent catastrophic failure. The hubs and fasteners should also be inspected for tightness, corrosion, and wear. Any loose fasteners should be tightened to the manufacturer's specifications, and corroded components should be cleaned or replaced as necessary. In addition, the alignment of the shafts should be checked periodically, as misalignment can develop over time due to thermal expansion, vibration, or component wear. Re-alignment should be performed if necessary to ensure that the coupling operates within its rated misalignment capacity.
In harsh environments, such as those with high humidity, corrosive gases, or abrasive particles, additional maintenance measures may be required. This can include the application of protective coatings to the coupling components, the installation of protective covers to prevent contamination, or more frequent inspection intervals. It is also important to ensure that the coupling is not subjected to excessive loads or speeds beyond its rated capacity, as this can significantly reduce its service life.
Looking ahead, the development of diaphragm couplings is expected to be driven by several key trends, including the increasing demand for high-performance and energy-efficient power transmission systems, the growing adoption of renewable energy sources, and the advancement of material science and manufacturing technologies. One of the primary trends is the development of lightweight and high-strength diaphragm couplings using advanced materials, such as carbon fiber composites. Carbon fiber composites offer a higher strength-to-weight ratio than traditional metallic materials, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as aerospace and electric vehicles. These materials also exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and fatigue strength, further enhancing the reliability and service life of the couplings.
Another trend is the integration of smart technologies into diaphragm couplings to enable condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. This includes the installation of sensors to measure temperature, vibration, and torque, which can be used to detect early signs of wear or damage. The data collected by these sensors can be analyzed using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to predict when maintenance or replacement is required, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. This is particularly beneficial in critical applications, such as power generation and aerospace, where unplanned downtime can result in significant economic losses or safety risks.
The growing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, is also expected to drive the demand for diaphragm couplings. Wind turbines, in particular, require reliable and efficient power transmission systems to convert the rotational energy of the blades into electrical energy. Diaphragm couplings are well-suited for this application due to their high torque capacity, ability to compensate for misalignments caused by wind loads, and lubrication-free design, which reduces maintenance requirements in remote and harsh environments. As the global focus on renewable energy intensifies, the demand for diaphragm couplings in this sector is expected to grow significantly.
In addition, advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), are enabling the production of more complex and optimized diaphragm designs. 3D printing allows for the creation of diaphragms with intricate slot patterns and geometries that are difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. This enables the design of diaphragms that offer improved flexibility, higher torque capacity, and better fatigue resistance, further enhancing the performance of diaphragm couplings. Additive manufacturing also allows for the production of custom-made couplings tailored to specific application requirements, reducing lead times and costs.
In conclusion, diaphragm couplings represent a critical component in modern power transmission systems, offering a unique combination of high torque capacity, precision alignment, lubrication-free operation, and resistance to harsh operating conditions. Their diverse structural configurations, coupled with the ability to select materials tailored to specific applications, make them suitable for a wide range of industries, from power generation and aerospace to automotive and renewable energy. Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential to ensure their optimal performance and service life, while ongoing advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies are expected to drive their continued evolution and adoption in the future. As industries continue to demand more efficient, reliable, and high-performance power transmission solutions, diaphragm couplings are poised to play an increasingly important role in meeting these needs.
« Diaphragm Couplings » Post Date: 2023/9/26
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/diaphragm-couplings.html
- 2025-06-27Diaphragm Coupling Vs Disc Coupling
- 2024-07-11High-end Multi-specification Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-05-05Lubrication of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-05-05Installation of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-05-05Custom Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-05-05Disadvantages of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Advantages
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Assembly Drawing
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Calculation
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Design
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Drawing
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Models
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Picture
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Sales
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Coupling Standard Sizes
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Couplings Company
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Couplings For Sale
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Couplings Supplier
- 2024-05-05Double Diaphragm Couplings Wholesale
- 2024-05-05Efficiency of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-05-05Engineering Drawing of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-05-05Exploded View of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-05-05Gap Chart of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-05-05Grease of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-04-02Procurement of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-04-02Purpose of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-04-02Size Calculation of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-04-02Size Chart of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-04-02Specifications of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-04-02Structural Diagram of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-04-02Tagging of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-04-02Torque of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-19Coaxiality of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-19Classification of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-03-19Catalogue of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-03-19Application of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-19Angle of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-19Alignment of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-04Types of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-04High Performance Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-03-04Parts of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-04Misalignment Tolerance of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-04Material of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-04Maintenance of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-04Uses of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-04Working Principle of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-03-02High Quality Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-01-17Supply of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-01-17Schematic Diagram of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-01-17Machine Drawing of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-01-17Function of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2024-01-17Double Diaphragm Coupling Brands
- 2024-01-17Double Diaphragm Couplings Factory
- 2024-01-173D Model of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-01-17Components of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2024-01-17Double Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturing
- 2023-12-14Two-way Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Stepped Style Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Steel Rolling Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Standard Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Small-scale Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-12-14Quick Fit Type Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14One-way Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Large & Small Axis Installation Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-12-14Intermediate Section Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Integrated Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Industry Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Hydraulic Pressure Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Heavy Load Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Heavy Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Gearbox Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Flexibility Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Flange Type Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-12-14Extra Long Wheelbase Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-12-14Expansion Sleeve Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-12-14Dilated Joint Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling With Single Shaft Sleeve
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling With Reverse Installation Of Shaft Sleeve
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling With Double Axis Sleeve
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Water Pumps
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Vacuum Pumps
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Support Seat
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Steam Turbine
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Pumps
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Paper Making Machinery
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Paper Making Equipment
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Induced Draft Fan
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Front Pumps
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Electrical Machinery
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Compressor
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Booster Fan
- 2023-12-14Diaphragm Coupling For Ball Mill
- 2023-12-14Currency Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-12-14Conical Sleeve Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-12-14Automation Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Uses of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Torque of Flexible Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-11-14Sales of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Size Chart of Flexible Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-11-14Parts of Flexible Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-11-14Material of Flexible Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Couplings Supplier
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Couplings For Sale
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Couplings Factory
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Working Principle
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Tagging
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Supply
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Structural Diagram
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Specifications
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Size Calculation
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Purpose
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Procurement
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Misalignment Tolerance
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturing Enterprise
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Maintenance
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Machine Drawing
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Installation
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Grease
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Gap Chart
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Function
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Engineering Drawing
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Components
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Calculation
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Assembly Drawing
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Applications
- 2023-11-14Exploded View of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Efficiency of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Disadvantages of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Customized Flexible Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-11-14Classification of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Types of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Stiffness of Flexible Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Couplings Company
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Lubrication
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Design
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Alignment
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Advantages
- 2023-11-14Flexible Diaphragm Coupling 3D Model
- 2023-11-14Catalogue of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-11-14Brands of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-28Short Type Double Diaphragm Coupling Model
- 2023-10-28Short Shaft Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-28Short Double Diaphragm Coupling Function
- 2023-10-28Split Diaphragm Coupling Processing
- 2023-10-28Steel Diaphragm Couplings Principle
- 2023-10-28Elastic Diaphragm Couplings Principle
- 2023-10-28Short Double Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-10-28Flange Type Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-10-28Fans Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-10-28Rigid Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-10-28Rigid Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-10-28Separate Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-28Separate Connecting Rod Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-28Sales Of Split Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-28Flange Diaphragm Coupling Specification
- 2023-10-28Split Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-10-28Square Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-28Steel Diaphragm Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-10-28High-precision Diaphragm Coupling Types
- 2023-10-28Standard For Rigid Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-28Steel Diaphragm Coupling Company
- 2023-10-28Guide Rail Diaphragm Coupling Types
- 2023-10-28Steel Diaphragm Couplings Supply
- 2023-10-28Steam Turbine Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-10-28Ball Mill Diaphragm Coupling Structure
- 2023-10-28Double Diaphragm Coupling Supply
- 2023-10-28Turbine Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-10-28Single Diaphragm Coupling Connection Diagram
- 2023-10-28Single Diaphragm Coupling Characteristics
- 2023-10-28Single Diaphragm Coupling Assembly Drawing
- 2023-10-28Single Diaphragm Coupling Application Scenarios
- 2023-10-28Single Diaphragm Coupling Anatomical Drawing
- 2023-10-28Single Diaphragm Coupling Advantages
- 2023-10-28Single Diaphragm Coupling Working Principle
- 2023-10-20Diaphragm Coupling Working Principle
- 2023-10-20Diaphragm Coupling Parts
- 2023-10-20Diaphragm Coupling In Turbo Machinery Industry
- 2023-10-18Torque Limiting Diaphragm Coupling Customization
- 2023-10-18Turbine Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-10-18Medium Speed Coal Mill Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Long Span Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Long Span High-precision Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Main Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Step Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-10-18Water Pump Diaphragm Coupling Model
- 2023-10-18Refrigeration Compressor Dual Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Screw Transmission Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Self Locking Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Servo Motor Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-18Spindle Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-18Expansion Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-10-18Supporting Seat Diaphragm Coupling Enterprise
- 2023-10-18Tensioning Large Shaft Sleeve Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Water Pump Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-10-18Double Diaphragm Couplings Types
- 2023-10-18Universal Diaphragm Coupling Enterprise
- 2023-10-18Water Pump Diaphragm Coupling Company
- 2023-10-18Diaphragm Couplings For Vertical Mill Reducers
- 2023-10-18Diaphragm Couplings For Centrifugal Compressors
- 2023-10-18Connecting Rod Type Metal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Metal Diaphragm Coupling Brand
- 2023-10-18Mechanical Seal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Metal Diaphragm Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-10-18Top Screw Fixed Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Steel Plate Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-18Flange Type Diaphragm Couplings Supply
- 2023-10-18Steel Single Key Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Top Mill Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Custom High-precision Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-18Guide Rail Diaphragm Coupling Design
- 2023-10-18Guide Rail Diaphragm Coupling For Sale
- 2023-10-18Flange Diaphragm Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-10-18High Sensitivity Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-18High-precision Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-18Wheel Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-18Tamping Machine Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Short Wheelbase Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Short Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Rigid Flexible Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-18Flange Diaphragm Coupling Principle
- 2023-10-18Multifunctional Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Power Plant Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-18Rigid Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-10-18Steel Diaphragm Couplings Production
- 2023-10-17Double Diaphragm Coupling Angle Deviation
- 2023-10-17Double Diaphragm Coupling Accuracy
- 2023-10-17Double Diaphragm Coupling Coaxiality
- 2023-10-17Dual Diaphragm Coupling Design
- 2023-10-17Double Diaphragm Coupling Sectional View
- 2023-10-17Double Diaphragm Couplings Instructions
- 2023-10-17Dual Diaphragm Coupling Radial Compensation
- 2023-10-17Single Key Groove Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Single Diaphragm Coupling Transmission Method
- 2023-10-17Short Type Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Single Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturing Company
- 2023-10-17Single Diaphragm Coupling Input & Output
- 2023-10-17Single Diaphragm Coupling Function
- 2023-10-17Large Diaphragm Couplings For Ball Mills
- 2023-10-17Impact Resistant Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Expansion Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Model
- 2023-10-17Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-10-17Stepped Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Special Diaphragm Coupling For Screw Rod
- 2023-10-17Small Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-17Low Torque Dual Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Keyless Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17High Quality Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Heavy Duty Diaphragm Coupling Factory
- 2023-10-17Expansion Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Double Ring Bolt Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Heavy Duty Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Diaphragm Coupling For Paper Making
- 2023-10-17Custom Expansion Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Cement Grinding Heavy Tooth Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Expansion Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling Brand
- 2023-10-17Brake Wheel High-speed Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-17Brake Wheel Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-13Conical Sleeve Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-13Conical Ring Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-13Compressor Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-13Combination Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-13Expanded Diaphragm Couplings Characteristics
- 2023-10-13Cement Vertical Mill Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-13Reducer Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-13Cement Mill Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-12Expansion Type Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-10-12Expansion Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling Structure Diagram
- 2023-10-12Step Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-12Stepped Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-12Heavy-duty Diaphragm Coupling Structural Diagram
- 2023-10-12Automated Diaphragm Couplings Supplier
- 2023-10-12Support Seat Diaphragm Coupling Specifications
- 2023-10-12Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-10-12Flexible Transmission Porous Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-12Inner Hole Keyway Equipment Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-12Flexible Diaphragm Coupling Principle
- 2023-10-12Corrosion-resistant Diaphragm Couplings Production
- 2023-10-12Special Diaphragm Coupling For Ball Mill
- 2023-10-12Double Diaphragm Coupling Specification
- 2023-10-12Flexible Diaphragm Couplings Standard Model
- 2023-10-12Torsional Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-12Torque Limiting Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-12Turbine Diaphragm Coupling Factory
- 2023-10-10Corrosion Resistant Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-10Double Cone Sleeve Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-10High Temperature Resistant Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-10Clamping Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-09Rigid Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-09Multi Section Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-09Low Speed Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-09High Precision Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-09High Elasticity Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-09Flange Type Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-09Flange Type Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-09Flange Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-09Dry Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-09Diaphragm Couplings For Fans
- 2023-10-08Engine Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-08Anticorrosive Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-08Brand Of Steel Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-08Customized Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-08Diaphragm Couplings For Power Plants
- 2023-10-08Manufacturing Of Single Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-08Wholesale Of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-08Characteristics Of Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-08Double Diaphragm Coupling Distributor
- 2023-10-08Double Diaphragm Coupling Enterprise
- 2023-10-08Double Diaphragm Coupling Type
- 2023-10-08Dual Diaphragm Coupling Brand
- 2023-10-08Double Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-10-07Rotary Kiln Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Rapid Feed Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Metal Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-10-07Locomotive Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Key Connected Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Extended Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Economical Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Drawing Of Metal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Connected To Intermediate Shaft Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Clamping Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Clamping Plate Bushing Type Metal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Adjustable Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Application Of Metal Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-07Buffer Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-10-07Centering Requirements For Diaphragm Couplings Of Pumps
- 2023-10-07Cooling Tower Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Connecting Rod Type Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Screw Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Track Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Refrigerator Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Connecting Rod Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Supplier Of Double Cone Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Types Of Automated Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-07Wholesale Of Small Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-10-07Stiffness Of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-10-07Durable Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-27High Temperature Resistant Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-27Durable Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-27Double Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-09-27Double Diaphragm Coupling For Sale
- 2023-09-27Diaphragm Couplings For Belt Conveyors
- 2023-09-27Diaphragm Couplings For Ball Mills
- 2023-09-27Customization Of Diaphragm Couplings For Steam Turbines
- 2023-09-27Corrosion Resistant Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-27Ball Mill Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Ball Mill Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Ball Mill Heavy-duty Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Clean Water Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26CNC Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Corrosion Resistant Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Customized Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Diaphragm Coupling For Grinding Machines
- 2023-09-26Diaphragm Coupling Of Coal Mill
- 2023-09-26Diaphragm Coupling Of Steam Pump
- 2023-09-26Double Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Double Stainless Steel Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Flexible Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Front Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26High Strength Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Inner Expansion Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Inner Tensioning Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Sintering Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Turbine Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Paper Cutter Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Mill Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Diaphragm Couplings For Machine Tools
- 2023-09-26Connected To Intermediate Section Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Clamping Plate Bushing Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Clamping Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Extended Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Insulated Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Laser Machine Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Machining Center Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Metal Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Metal Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Metal Laminated Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Metal Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Open Structure Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Piston Compressor Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Tight Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Stepped Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Reducer Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Precision Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Metering Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Mechanical Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Machine Tool Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Keyway Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Extension Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Extended Shaft Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Extended Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Double Diaphragm Couplings For Machine Tools
- 2023-09-26Diaphragm Couplings For Mining Machinery
- 2023-09-26Damping Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Compact Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Air Compressor Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Buffer Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Circular Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Pipeline Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Industrial Robot Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Industrial Diaphragm Coupling Brand
- 2023-09-26High Temperature Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26High Pressure Fan Motor Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26High Performance Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26High Performance & Low Price Dual Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Efficient Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26Diaphragm Coupling Of Water Supply Pump
- 2023-09-26Diaphragm Coupling For Roller Table
- 2023-09-26Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26High Performance Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26High Quality Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-26High Speed Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Low Speed Heavy-duty Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25High Sensitivity Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25High Precision Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Flange Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Elastic Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Diaphragm Couplings For Multi-stage Pumps
- 2023-09-25Electric Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Fan Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Flange Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Forged Steel Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Guide Rail Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Generator Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25High Rigidity Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Low Speed Metal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Motor Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Multilayer Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Powder Mill Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Rigid Metal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Split Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Spring Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-25Steel Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Vertical Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Vertical Grinding Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Six Hole Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Screw Compressor Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Screw Machine Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Keyless Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Hexagonal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Cooling Tower Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Connecting Rod Laminated Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Connecting Rod Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Chain Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Centrifugal Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Centrifugal Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Centrifugal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Water Pump Dual Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Tensioning Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Type Of Expansion Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-22Support Seat Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-09-22Supplier Of High-quality Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-21Stepped Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Tensioning Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Universal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Water Pump Motor Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Whole Piece Metal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Water Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Tensioning Sleeve Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Supporting Seat Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Step Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Servo Motor Dual Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Servo Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Rolling Steel Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Non Countersunk Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Locking Disc Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Long Shaft Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Long Span Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Kiln Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Intermediate Shaft Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Integral Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Hydraulic Sleeve Type Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Induced Draft Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Hydraulic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21High Quality Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Heavy Metal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Heavy Duty Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Expansion Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Drawing Of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Double Locking Disc Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Direct Spindle Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Double Cone Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Double Diaphragm Coupling Intermediate Gasket
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Couplings For Heavy-duty Machinery
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Couplings For Paper Machinery
- 2023-09-21Correction Of Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Customized Universal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Coupling For Circulating Pumps
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Coupling For Desulfurization Pump
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Couplings For Heavy-duty & Low-speed Applications
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Couplings For Turbine Fans
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Couplings For Servo Motors
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Couplings For Cement Mills
- 2023-09-21Design Of A New Type Of Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Diaphragm Coupling Of Wire Drawing Machine
- 2023-09-21Customization Of Small Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-21Conical Sleeve Type Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Conical Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Circular Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Automatic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Bi-directional Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Cam Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Booster Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Advantages Of Water Pump Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-21Gear Corrosion-resistant Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14How To Use A Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Drawing Of Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Dimensions Of Single Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Benefits Of Single Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Adjustment Of Single Expansion Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Adjustment Of One-way Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-143D Diagram Of Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Working Principle Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Which Is The Best Manufacturer For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Which Company Is Cheaper For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14What Is The Spacing Between Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14What Are The Types Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Types Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Stress Situation Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Specification Of Elastic Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Specification Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Selection Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Sectional View Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Scope Of Use Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Schematic Diagram Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Operation
- 2023-09-14Quotation For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Processing Standard For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Principles Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Model Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Material Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Installation Steps Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Installation Standard For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Installation Method Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14Installation Requirements For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-14Installation Drawing Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-14How To Remove The Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Wholesale Of High Torque Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-13Types Of High Torque Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-13Type Of Diaphragm Coupling For Transmission Seat
- 2023-09-13Structural Drawing Of Large Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Structural Diagram Of Large Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Standard For Diaphragm Couplings With Intermediate Sleeves
- 2023-09-13Standard For Diaphragm Couplings With Intermediate Shaft
- 2023-09-13Specification And Model Of Large Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Single Type Elastic Diaphragm Coupling With Cone Sleeve
- 2023-09-13Ship Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Production Process Of High Torque Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Material Of Large Diameter Diaphragm Coupling Diaphragm
- 2023-09-13Marine Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Manufacturer Of High Torque Step Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Large Unit Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Large Tube Mill Reducer Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Large Fan Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Large Diaphragm Coupling Structure
- 2023-09-13Large Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-09-13Large Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13Large Ball Mill Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13High Torque Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-09-13High Torque Diaphragm Coupling Factory
- 2023-09-13Extended Diaphragm Coupling With Intermediate Knot
- 2023-09-13Double Diaphragm Coupling With Extension Joint
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Couplings For Marine Diesel Engines
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Stop
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Spark Free Shield
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Partition
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Locking Disc
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Liner
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Keyway
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Intermediate Section
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Flywheel
- 2023-09-13Advantages Of Diaphragm Coupling With Intermediate Shaft
- 2023-09-13Alignment Of Double Diaphragm Couplings For Large Fans
- 2023-09-13Basic Diaphragm Coupling With Counterbore
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Expansion Sleeve
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Counterbore
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Brake Wheel
- 2023-09-13Diaphragm Coupling With Boss
- 2023-09-13Manufacturer Of High Torque Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-13What Are The Types Of Diaphragm Couplings For Transmission Seats
- 2023-09-13Transmission Seat Diaphragm Coupling Accessories
- 2023-09-06How Much Is The Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06How Long Is The Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Function Of Elastic Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Fault Analysis Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Engineering Drawing Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06End Face Clearance Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Elastic Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Elastic Metal Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling With or Without Top Screw
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling With Key
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling With Hinge
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Shaft Entry Length
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Parameters
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Material
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Jamming
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Hinge
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Function
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Flange
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Extension
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Diaphragm Material
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Cone Ring
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Column Penetration Method
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling And Shaft Installation
- 2023-09-06Elastic Diaphragm Coupling And Shaft Fit
- 2023-09-06Elastic Corrosion-resistant Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Efficiency Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Eccentricity Compensation For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-06Drawing Method For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-06Do Elastic Diaphragm Couplings Need To Be Locked
- 2023-09-06Disassembly Method Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-06Disadvantages Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-02Dimensions Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-02Correction Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-02Connection Diagram Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-02Concentricity Adjustment Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-09-02Clearance Standard For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-09-02Characteristics Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-31Centering Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-31Centering And Alignment Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-31Calculation Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Bolts
- 2023-08-31Boundary Dimensions Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-31Axial Clearance Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Assembly Drawing Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Alignment Standards For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-31Advantages Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-31Abnormal Noise Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Conical Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Diaphragm Coupling With Automatic Wheel
- 2023-08-31High Torque Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31High Torque Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31High Power Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Manufacturer Of Large Moment Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Diaphragm Coupling For High-power Motors
- 2023-08-31Which Is The Best Type Of Diaphragm Coupling For The Transmission Seat
- 2023-08-31Which Is The Best Manufacturer For The Diaphragm Coupling Of The Transmission Seat
- 2023-08-31Which Is The Cheapest Manufacturer For Transmission Seat Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-31Transmission Seat Diaphragm Coupling Type
- 2023-08-31Transmission Seat Diaphragm Coupling Price
- 2023-08-31Transmission Seat Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-08-31Supply Of Diaphragm Coupling For Transmission Seat
- 2023-08-31Customized Transmission Seat Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Customization Of Diaphragm Coupling For Transmission Seat
- 2023-08-31Transmission Seat Diaphragm Coupling Agent
- 2023-08-31Customized By The Manufacturer Of The Transmission Seat Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Standard For Diaphragm Couplings With Transmission Seats
- 2023-08-31Quotation For Diaphragm Coupling Of Transmission Seat
- 2023-08-31Transmission Seat Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Transmission Shaft Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-31Characteristics Of Transmission Double Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-31Transmission Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-28Applicable Fields Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-28Allowable Error Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-28Alignment Error Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-28Adjustment Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-28Compensation Amount Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-28Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Pin Shaft
- 2023-08-28Failure Analysis Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-28How To Install An Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-28What Is The Price Of A Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-28What Are The Types Of Single Section Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-28What Are The Brands Of Single Section Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Wholesale Of Single Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Unidirectional Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Unidirectional Precision Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Single Section Expansion Sleeve Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Single Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-08-24Single Diaphragm Coupling Processing
- 2023-08-24Single Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-08-24Single Diaphragm Coupling For Sale
- 2023-08-24Single Diaphragm Coupling Customization Factory
- 2023-08-24Single Diaphragm Coupling Agent
- 2023-08-24Non Standard Customization Of Single Section Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Manufacturer Of Single Section Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Customized Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Customization Of Single Section Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Customized Manufacturer Of Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Model Of Elastic Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Model Of Elastic Single Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Specification And Model Of Elastic Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Technical Standard For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Structural Drawing Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Schematic Diagram Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Structure
- 2023-08-24Radial Compensation Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Specification And Model Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Structural Diagram Of Elastic Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Usage Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Standard Model Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Service Life Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Production Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Installation Spacing Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24How To Apply Force To Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Elastic Double Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Supply
- 2023-08-24Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-08-24Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Adjustment Angle
- 2023-08-24Drawing Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-24Design Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Centering Requirements For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Applicable Occasions For Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-24Advantages And Disadvantages Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-19Wholesale Of Elastic Diaphragm Couplings
- 2023-08-19Manufacturer Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-19Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Supplier
- 2023-08-19Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Company
- 2023-08-19Brand Of Elastic Diaphragm Coupling
- 2023-08-18Elastic Diaphragm Coupling Factory