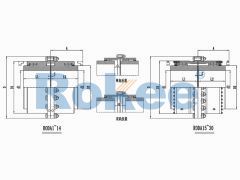
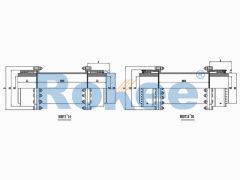
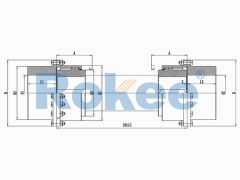
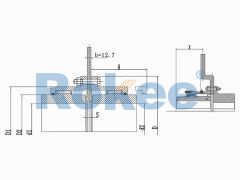
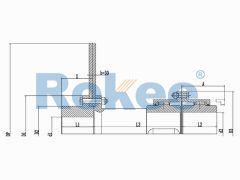
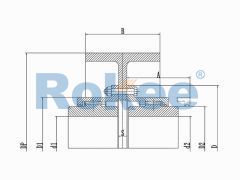
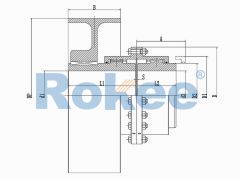
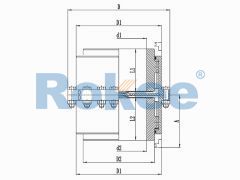
Barrel Gear Couplings
Rokee® is a Barrel Gear Couplings Supplier from China, customized barrel gear couplings according to the drawings which provided by the customer, selling chinese national standard barrel gear couplings, support export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® industrial coupling have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
The Drum Gear Coupling is a specially designed advanced Gear Coupling. Its outer teeth are made into a sphere, with the center of the sphere on the axis of the gear. The teeth clearance is slightly larger than the general products and can transfer a greater torque and allow greater angular displacement, enjoying excellent performance and longer life.
ROD Curved-tooth Gear Coupling is one of the transmission products with core technology independently developed by Rokee and has established and reported corporate technical standards in the country. By combining with the standard coupling technology of advanced countries such as Japan and Germany, we optimized many detailed dimensions, and adopted the toothed design with a large pressure angle and short shaft design for the shaft hole, which reduces the length-diameter ratio, and has a more compact structure and excellent speed performance.
The bolts of similar types are standardized and the parts are universal. Compared with the national standard couplings, our Toothed Couplings can transfer more torque, with greatly reduced mass and small moment of inertia. It meets the European explosion-proof requirements and the comprehensive performance is greatly advanced. We highly recommend you to choose our Crown Gear Couplings for better transmission performance.
RODA Drum Gear Coupling
The RODA Drum Gear Coupling is the basic type of ROD series coupling, suitable for most situations where the compensation of transmission distance and motion position does not require special increase.RODT Indirect Tube Drum Gear Coupling
The RODT Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling, suitable for increasing transmission distance.RODX Intermediate Shaft Drum Gear Coupling
RODX Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling with a floating shaft design in the middle, suitable for increasing transmission distance.RODP Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODP Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with a brake disc, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with disc brakes.RODF Split Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODF Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with split brake discs, suitable for transmission situations where there is braking demand and the braking position changes when used in conjunction with disc brakes.RODW Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODW Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes.RODU Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODU Drum Gear Coupling is another type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes and applied to one end of the axle, achieving smoother and more reliable braking performance.RODV Vertical Installation Drum Gear Coupling
The RODV Drum Gear Coupling is a vertical installation type of the ROD series coupling, suitable for transmission situations that require vertical transmission torque.RODM Torsion Protection Drum Gear Coupling
The RODM Drum Gear Coupling is a torque setting form of the ROD series coupling. By adjusting relevant components, the maximum transmission torque can be easily set within a certain range. Suitable for shafting transmission situations that require safe torque operation to protect important machine components from excessive damage.
GICL Drum Gear Coupling
GICL drum gear coupling has larger inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for larger axial displacement.GICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement.GIICL Drum Gear Coupling
GIICL drum gear coupling has small inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for small axial displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.GIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GIICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.GCLD Drum Gear Coupling
GCLD drum gear coupling is generally used for direct connection with the motor, so it generally has a higher speed and compact structure.NGCL Drum Gear Coupling
NGCL drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.NGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling
NGCLZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. Half of its structure adopts a semi-coupling sleeve design, with smaller angular displacement compensation but more stable braking.WG Drum Gear Coupling
The overall characteristics of WG drum gear coupling are similar to those of other drum gear couplings, but with a larger modulus design, which can generally transmit greater torque.WGZ Drum Gear Coupling
WGZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for shoe type braking.WGP Drum Gear Coupling
WGP drum gear coupling is designed with a brake disc, suitable for disc type braking.WGT Drum Gear Coupling
WGT drum gear coupling is designed with indirect tube, suitable for long distance torque transfer.WGC Drum Gear Coupling
WGC drum gear coupling is specially designed for situations where vertical transmission is required, suitable for some vertical transmission systems.WGJ Drum Gear Coupling
WGJ drum gear coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance torque transmission, and some are equipped with axial buffers.
In the realm of industrial power transmission, couplings serve as the critical link between rotating shafts, ensuring the seamless transfer of torque while accommodating misalignments and absorbing operational stresses. Among the diverse range of coupling types available, the barrel gear coupling stands out for its exceptional performance in heavy-duty and high-torque applications. Characterized by its robust construction, high load-bearing capacity, and ability to compensate for multiple forms of misalignment, this coupling has become an indispensable component in industries such as manufacturing, mining, energy, and transportation.
Understanding the Design of Barrel Gear Couplings
Barrel gear couplings are a type of flexible coupling that utilizes gear teeth to transmit torque between two shafts. Unlike rigid couplings, which require precise alignment and offer no flexibility, barrel gear couplings are engineered to accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for use in systems where perfect shaft alignment is difficult to achieve or maintain. The core design of a barrel gear coupling consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in its overall functionality.
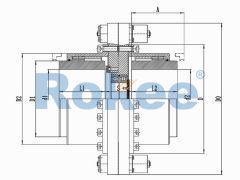
At the heart of the coupling are two gear hubs, each with external gear teeth that are cut in a barrel shape—this barrel-shaped tooth profile is the defining feature that gives the coupling its name. The gear hubs are typically mounted on the ends of the shafts that need to be connected, secured in place using keys, splines, or interference fits to ensure a tight and torque-resistant connection. Enclosing these gear hubs is a sleeve (also known as a gear case) with internal gear teeth that mesh perfectly with the external teeth of the hubs. The sleeve serves two primary purposes: it protects the meshing gears from external contaminants such as dust, dirt, and moisture, and it helps to distribute the load evenly across the gear teeth.
Another essential component of barrel gear couplings is the lubrication system. Given the high levels of friction and wear that occur between the meshing gear teeth during operation, proper lubrication is critical to ensuring the coupling’s longevity and performance. Most barrel gear couplings are equipped with lubrication fittings that allow for the injection of grease or oil into the sleeve, creating a film between the gear teeth that reduces friction, dissipates heat, and prevents premature wear. Some designs also include seals or gaskets to retain the lubricant and keep out contaminants, further enhancing the coupling’s reliability.
The materials used in the construction of barrel gear couplings are carefully selected to withstand the high torques, loads, and stresses encountered in industrial applications. The gear hubs and sleeves are typically made from high-strength alloy steels, such as 42CrMo or 35CrMo, which offer excellent mechanical properties including high tensile strength, toughness, and wear resistance. These materials are often heat-treated (e.g., quenched and tempered) to further enhance their durability and performance under extreme conditions. The choice of material may vary depending on the specific application requirements, such as the operating temperature, load capacity, and environmental conditions.
Operational Mechanics: How Barrel Gear Couplings Transmit Torque
The operational principle of barrel gear couplings revolves around the meshing of the barrel-shaped external gear teeth of the hubs with the internal gear teeth of the sleeve. When torque is applied to one of the shafts, it is transferred to the corresponding gear hub, which then transmits the torque to the sleeve via the meshing gear teeth. The sleeve subsequently transfers the torque to the second gear hub, which in turn drives the second shaft. This sequential transfer of torque ensures that power is transmitted efficiently from one shaft to the other, even in the presence of misalignments.
One of the key advantages of the barrel-shaped tooth profile is its ability to accommodate multiple types of misalignment. Angular misalignment occurs when the two shafts are not colinear but intersect at an angle. The barrel shape of the gear teeth allows for a greater contact area between the hub and sleeve gears when the shafts are angled, ensuring that torque transmission remains consistent. Parallel misalignment, on the other hand, occurs when the two shafts are parallel but offset from each other. In this case, the barrel gear teeth slide slightly against each other as the shafts rotate, allowing the coupling to compensate for the offset without compromising torque transfer.
Axial misalignment, which involves the movement of one shaft along its axial direction relative to the other, is also accommodated by barrel gear couplings. The length of the gear teeth and the design of the sleeve allow for a certain amount of axial movement, preventing binding or damage to the coupling or the connected equipment. This ability to compensate for all three types of misalignment makes barrel gear couplings highly versatile and suitable for use in a wide range of industrial applications where shaft alignment may be challenging.
In addition to torque transmission and misalignment compensation, barrel gear couplings also play a role in absorbing shock and vibration. The meshing of the gear teeth, combined with the flexibility provided by the barrel shape, helps to dampen sudden shocks and vibrations that may occur during operation, reducing the stress on the connected shafts, bearings, and other components. This shock absorption capability is particularly important in applications such as mining and construction, where heavy loads and sudden changes in torque are common.
Key Advantages of Barrel Gear Couplings
Barrel gear couplings offer a number of distinct advantages over other types of couplings, making them the preferred choice for many heavy-duty industrial applications. One of the most significant advantages is their high torque-carrying capacity. The meshing gear teeth provide a large contact area, allowing the coupling to transmit high levels of torque efficiently without slipping or failing. This makes barrel gear couplings ideal for use in applications such as large motors, pumps, compressors, and industrial gearboxes, where high torque transmission is essential.
Another major advantage is their ability to accommodate significant amounts of misalignment. As discussed earlier, barrel gear couplings can compensate for angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, making them suitable for use in systems where perfect alignment is difficult to achieve or maintain. This flexibility reduces the need for precise installation and alignment, saving time and labor costs. It also helps to extend the life of the connected equipment by reducing the stress on shafts, bearings, and seals.
Barrel gear couplings are also known for their robustness and durability. Constructed from high-strength alloy steels and heat-treated for enhanced wear resistance, these couplings are capable of withstanding harsh operating conditions, including high temperatures, heavy loads, and exposure to contaminants. Their simple and compact design also contributes to their durability, as there are fewer moving parts that can fail or require maintenance. This robustness makes barrel gear couplings suitable for use in industries such as mining, oil and gas, and steel production, where reliability is critical.
In addition to their high torque capacity and misalignment compensation, barrel gear couplings also offer excellent efficiency. The meshing of the gear teeth is designed to minimize friction, ensuring that most of the torque is transmitted from one shaft to the other without significant energy loss. This high efficiency helps to reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs, making barrel gear couplings an economical choice for long-term use.
Another advantage of barrel gear couplings is their ease of maintenance. While proper lubrication is essential, most barrel gear couplings are designed with lubrication fittings that allow for easy access and re-lubrication. The simple design also makes it easy to inspect the coupling for wear or damage, allowing for timely maintenance and replacement if necessary. This ease of maintenance helps to minimize downtime and ensure that the coupling remains in optimal condition for extended periods of time.
Industrial Applications of Barrel Gear Couplings
Due to their high torque capacity, flexibility, and durability, barrel gear couplings are used in a wide range of industrial applications across various sectors. One of the most common applications is in the mining industry. In mining operations, equipment such as conveyor belts, crushers, and grinding mills require the transmission of high levels of torque, and often operate in harsh conditions where misalignment is common. Barrel gear couplings are ideal for these applications, as they can transmit the required torque efficiently while accommodating the misalignment caused by the heavy loads and rough terrain.
The manufacturing industry also relies heavily on barrel gear couplings. In manufacturing plants, large motors, pumps, compressors, and industrial gearboxes are used to power various production processes. These machines require reliable torque transmission and often operate at high speeds, making barrel gear couplings the perfect choice. For example, in the automotive industry, barrel gear couplings are used in assembly line equipment and machining centers, where precision and reliability are essential.
The energy sector is another major user of barrel gear couplings. In power plants, both thermal and hydroelectric, large turbines and generators require the transmission of massive amounts of torque. Barrel gear couplings are used to connect these components, ensuring efficient power transmission and accommodating any misalignment that may occur due to thermal expansion or contraction. In wind energy applications, barrel gear couplings are also used in wind turbines, where they help to transmit torque from the rotor to the generator while compensating for the misalignment caused by wind loads.
The transportation industry also benefits from the use of barrel gear couplings. In heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks, buses, and trains, barrel gear couplings are used in the transmission systems to connect the engine to the drivetrain. They help to transmit the high torque generated by the engine efficiently while accommodating the misalignment caused by the movement of the vehicle. In marine applications, barrel gear couplings are used in ship propulsion systems, where they connect the engine to the propeller shaft, ensuring reliable power transmission in harsh marine environments.
Other applications of barrel gear couplings include construction equipment (such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes), agricultural machinery (such as tractors and harvesters), and oil and gas equipment (such as drilling rigs and pumps). In each of these applications, the unique combination of high torque capacity, misalignment compensation, and durability makes barrel gear couplings an essential component.
Maintenance Considerations for Barrel Gear Couplings
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of barrel gear couplings, proper maintenance is essential. The most critical maintenance task is regular lubrication. As mentioned earlier, the meshing gear teeth require a continuous film of lubricant to reduce friction, dissipate heat, and prevent wear. The frequency of lubrication depends on the operating conditions, such as the load, speed, and temperature. In general, barrel gear couplings should be lubricated every 6 to 12 months, or more frequently if they are operating in harsh conditions.
When lubricating a barrel gear coupling, it is important to use the correct type of lubricant. The lubricant should be compatible with the materials used in the coupling and should have the appropriate viscosity and temperature range for the operating conditions. Grease is the most common lubricant used for barrel gear couplings, as it provides excellent lubrication and stays in place better than oil. However, in some high-speed or high-temperature applications, oil may be preferred, as it dissipates heat more effectively.
Regular inspection is another important maintenance task. Inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. During an inspection, the coupling should be checked for worn or chipped gear teeth, loose fasteners, leaks in the lubrication system, and any signs of corrosion or damage to the sleeve. If any issues are detected, they should be addressed immediately to prevent further damage to the coupling or the connected equipment.
Alignment checks are also essential for the proper operation of barrel gear couplings. While these couplings can accommodate misalignment, excessive misalignment can lead to increased wear, reduced efficiency, and premature failure. Regular alignment checks should be conducted using precision tools such as laser alignment systems to ensure that the shafts are within the recommended alignment tolerances. If misalignment is detected, adjustments should be made to the connected equipment to correct it.
In addition to lubrication, inspection, and alignment, it is also important to replace worn or damaged components in a timely manner. If the gear teeth are severely worn or chipped, or if the sleeve is damaged, the affected components should be replaced to ensure the coupling’s performance and reliability. When replacing components, it is important to use parts that are compatible with the original coupling design to maintain its performance characteristics.
Conclusion
Barrel gear couplings are a critical component in modern industrial power transmission systems, offering a unique combination of high torque capacity, misalignment compensation, robustness, and efficiency. Their design, which features barrel-shaped gear teeth and a robust sleeve enclosure, allows them to transmit torque efficiently while accommodating angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for use in a wide range of heavy-duty applications across industries such as mining, manufacturing, energy, and transportation.
The key advantages of barrel gear couplings, including their high torque-carrying capacity, flexibility, durability, and ease of maintenance, make them the preferred choice for many industrial applications where reliability and performance are critical. By understanding the design principles, operational mechanics, and maintenance requirements of barrel gear couplings, industrial operators can ensure that these components perform optimally, extending their service life and reducing downtime.
As industrial systems continue to evolve and demand higher levels of performance and reliability, barrel gear couplings will remain an indispensable component, playing a vital role in ensuring the seamless transfer of power and the efficient operation of industrial equipment. Whether in mining, manufacturing, energy, or transportation, the versatility and performance of barrel gear couplings make them a cornerstone of modern industrial power transmission.
« Barrel Gear Couplings » Post Date: 2023/10/19
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/blog/barrel-gear-couplings.html
Tags: Internal Gear Couplings, Flexible Gear Couplings, Rubber Gear Coupling, Brake Drum Gear Coupling, Crown Gear Couplings, Curved-tooth Gear Couplings, Flange Gear Coupling, Face Gear Couplings, Crown Gear Coupling, pu sandwich panel line
- Process Standard For Curved-tooth Gear Coupling
- Components of Crown Gear Coupling
- Straight Gear Coupling
- External Gear Sleeve Of Drum Gear Coupling
- Nylon Sleeve Gear Couplings
- Flange Gear Coupling Machine Drawing
- Shaft End Dimensions Of Curved-tooth Gear Coupling
- Oil Pump Gear Coupling
- Failure Forms Of Drum Gear Couplings
- Curved-tooth Gear Coupling Structural Schematic Diagram