High Performance Disc Couplings
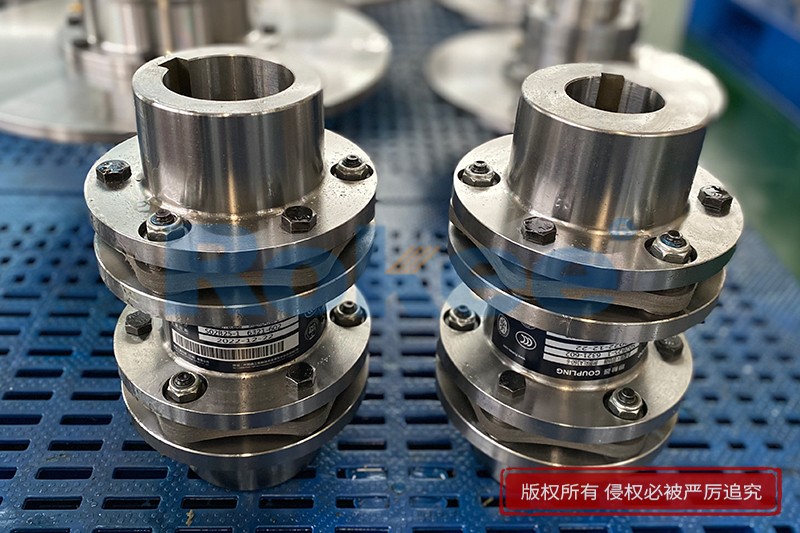

Rokee® is High Performance Disc Couplings Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® High Performance Disc Couplings have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
In the realm of industrial power transmission, the search for efficient, reliable, and durable coupling solutions has been a persistent pursuit. Among the various types of couplings available, high performance disc couplings have emerged as a preferred choice for a wide range of demanding applications. Unlike traditional coupling designs that rely on elastic elements or gear meshing, disc couplings utilize thin, flexible metal discs to transmit torque while accommodating misalignments. This unique design endows them with exceptional performance characteristics that make them indispensable in industries where precision, high speed, and reliability are non-negotiable.
-

JMI Diaphragm Coupling
JMI metal diaphragm coupling adopts the single-piece design, suitable for short distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMII Diaphragm Coupling
JMII metal diaphragm coupling also adopts the single-piece design but has no counterbore, suitable for short distance transmission, with more compact structure. -

JMIIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at both ends have no counterbore. -
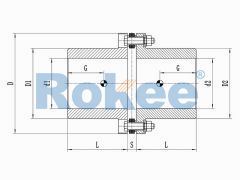
RLA Standard Single Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications, but cannot compensate for radial deviation. -
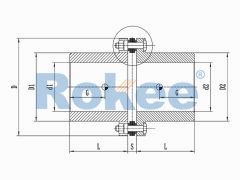
RLM Small Single Diaphragm Coupling
The RLM standard single section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working situations with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm, and cannot compensate for radial errors. -
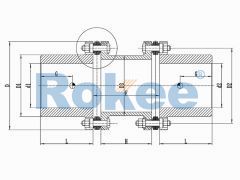
RLMD Small Double Diaphragm Coupling
The RLMD standard double section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working occasions with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm. -
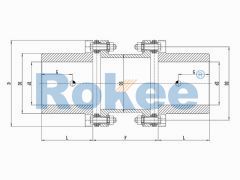
RLAD Standard Double Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications. -
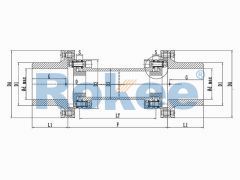
RLAT Super Long Wheelbase Diaphragm Coupling
Adopting an intermediate shaft design, suitable for ultra long shaft spacing power transmission applications. -
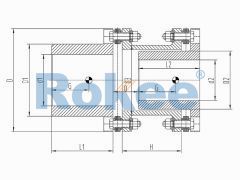
RLAR Single Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
Single side shaft sleeve reverse installation design, suitable for occasions with limited shaft head distance. -
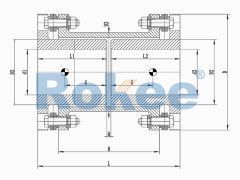
RLARD Double Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
The double-sided shaft sleeve reverse installation design is also applicable in situations where the distance from the shaft head is limited or the additional bending moment is smaller. -
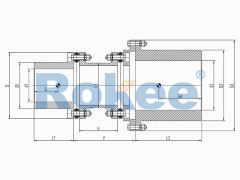
RLAF Large & Small Shaft Mounted Diaphragm Coupling
The size difference design of the bilateral shaft sleeve is suitable for situations where the diameter difference between the two ends of the shaft is significant. -
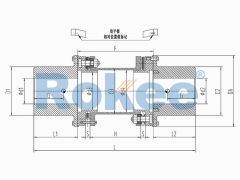
RLQA No Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for various industrial process pumps, fans, and other medium to low speed applications, with a maximum speed generally not exceeding 25000 rpm. It meets the requirements of API610/ISO14691 and is one of the first products for API applications. -
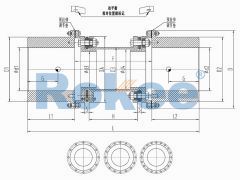
RLQF Flange Type Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications, with a maximum speed of up to 35000rpm. -
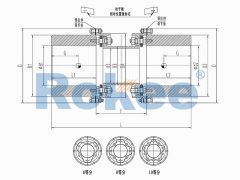
RLQU Improved Flange Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
The improved RLQF has smaller additional bending moments and better performance. Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications. -
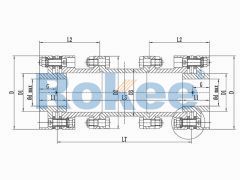
RLHD High Speed Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for higher speed applications, it also adopts a flexible component integrated assembly design, with a maximum speed of up to 42000rpm.
Working Principles of High Performance Disc Couplings
At the heart of a high performance disc coupling lies its disc pack, which is the primary component responsible for torque transmission and misalignment compensation. The disc pack consists of multiple thin, flat metal discs arranged in a stack, with each disc featuring precision-cut holes for bolt attachment. These discs are typically mounted between two hubs: one connected to the driving shaft (e.g., from a motor or turbine) and the other to the driven shaft (e.g., a pump, compressor, or gearbox). When torque is applied to the driving hub, it is transferred through the bolts to the disc pack, which then transmits the torque to the driven hub and ultimately to the driven shaft.
A key aspect of the disc coupling’s operation is its ability to accommodate three types of misalignment: angular, parallel, and axial. Angular misalignment occurs when the two shafts are not colinear but intersect at a point, while parallel misalignment refers to shafts that are parallel but offset from each other. Axial misalignment, on the other hand, involves linear displacement of one shaft relative to the other along the axial direction. The flexibility of the metal discs allows them to bend slightly under these misalignment conditions without causing excessive stress or wear. Unlike rigid couplings, which require near-perfect alignment, disc couplings can handle moderate levels of misalignment, reducing the need for precise shaft alignment during installation and minimizing the risk of premature failure due to misalignment-induced stress.
Another important principle of disc coupling operation is the absence of sliding or rolling contact between moving parts. Unlike gear couplings, which rely on meshing gear teeth, or jaw couplings, which use rubber or polyurethane spiders, disc couplings have no lubricated components or wearing surfaces that require constant maintenance. This design not only eliminates the risk of lubricant leakage and contamination but also ensures smooth, efficient torque transmission with minimal energy loss. The metal-to-metal contact in the disc pack is designed to be rigid under torque load, ensuring that there is no backlash or torsional deflection, which is critical for applications requiring precise motion control.
Core Advantages of High Performance Disc Couplings
High performance disc couplings offer a multitude of advantages over other coupling types, making them suitable for high-demand industrial applications. One of the most significant advantages is their high torque capacity relative to their size. The disc pack design allows for efficient torque transmission through a compact structure, making disc couplings ideal for applications where space is limited. This high power-to-weight ratio is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery, where lightweight and compact components are essential for optimizing overall system performance.
Another major advantage is their excellent torsional stiffness. Torsional stiffness refers to a coupling’s resistance to twisting under torque load. High torsional stiffness ensures that the coupling does not undergo excessive torsional deflection, which is crucial for maintaining precise speed and position control in applications such as machine tools, robotics, and precision conveyors. Unlike elastic couplings, which may introduce torsional backlash and reduce control precision, disc couplings provide near-zero backlash, ensuring that the driving and driven shafts move in perfect synchronization.
The maintenance-free nature of high performance disc couplings is another key benefit. As mentioned earlier, disc couplings have no lubricated components, sliding parts, or wearing elements that require regular inspection, lubrication, or replacement. This eliminates the need for frequent maintenance downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and improves overall system reliability. In contrast, gear couplings require regular lubrication to prevent wear and corrosion, while elastic couplings need periodic replacement of the elastic element due to fatigue and degradation. For industries operating 24/7, such as power generation and oil and gas, the maintenance-free operation of disc couplings translates to significant cost savings and increased productivity.
High performance disc couplings are also highly resistant to harsh operating conditions. The metal discs are typically made from high-strength alloys that can withstand extreme temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive environments. This makes them suitable for use in applications such as gas turbines, steam turbines, and chemical processing equipment, where traditional couplings may fail due to environmental stress. Additionally, the absence of lubricants means that disc couplings are not susceptible to lubricant breakdown at high temperatures, further enhancing their reliability in harsh conditions.
Vibration damping is another advantage of disc couplings, although it is often less pronounced than that of elastic couplings. The flexibility of the disc pack allows for some absorption of vibration and shock loads, reducing the transmission of vibrations from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. This helps to protect sensitive components in the system, such as bearings, gears, and electrical motors, from premature wear and failure. In applications where vibration is a concern, such as in high-speed rotating machinery, disc couplings can help to improve overall system stability and reduce noise levels.
Material Considerations for High Performance Disc Couplings
The performance and durability of a high performance disc coupling are largely dependent on the materials used in its construction, particularly for the disc pack. The choice of material for the discs is critical, as they must withstand high torque loads, bending stresses from misalignment, and potentially harsh environmental conditions. The most commonly used materials for disc pack construction are high-strength stainless steel, titanium alloys, and nickel-based superalloys.
Stainless steel is a popular choice for disc couplings due to its excellent combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Austenitic stainless steels, such as 316 and 304, are commonly used for general industrial applications where corrosion resistance is important. These materials have good ductility and can withstand moderate levels of stress and temperature. For applications requiring higher strength and temperature resistance, precipitation-hardened stainless steels, such as 17-4 PH, are preferred. These steels can be heat-treated to achieve high tensile strength, making them suitable for high-torque and high-speed applications.
Titanium alloys are used in high-performance applications where lightweight and extreme strength are critical, such as aerospace and racing. Titanium has a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and good fatigue strength. However, titanium alloys are more expensive than stainless steel, which limits their use to applications where the benefits outweigh the cost. Nickel-based superalloys, such as Inconel and Hastelloy, are used in applications involving extreme temperatures and corrosive environments, such as gas turbines and chemical processing. These alloys can withstand temperatures up to 1000°C or higher and are highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion.
In addition to the disc pack, the hubs and other structural components of the disc coupling are typically made from high-strength carbon steel or alloy steel. These materials provide the necessary rigidity and torque-carrying capacity for the coupling. The bolts used to attach the disc pack to the hubs are also critical components, and they are usually made from high-tensile steel or alloy steel to ensure that they can withstand the high clamping forces and torque loads. The choice of materials for the entire coupling assembly is based on the specific requirements of the application, including torque capacity, operating temperature, environmental conditions, and weight constraints.
Key Applications of High Performance Disc Couplings
High performance disc couplings are used in a wide range of industries and applications, thanks to their exceptional performance characteristics. One of the primary applications is in the power generation industry, where they are used to connect turbines (gas, steam, or hydro) to generators. In these applications, disc couplings must transmit high torque at high speeds while accommodating minor misalignments. The maintenance-free operation of disc couplings is particularly beneficial in power plants, where downtime can be extremely costly. Additionally, their ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments makes them suitable for use in turbine systems.
The aerospace industry is another major user of high performance disc couplings. They are used in aircraft engines, where they connect the turbine to the compressor and other components. In aerospace applications, lightweight and high strength are critical, and titanium or nickel-based disc couplings are often used to meet these requirements. Disc couplings in aircraft engines must also be highly reliable, as any failure can have catastrophic consequences. The absence of lubricants is a key advantage in aerospace applications, as it eliminates the risk of lubricant leakage, which can cause fires or other hazards.
In the industrial machinery sector, high performance disc couplings are used in a variety of applications, including machine tools, robotics, conveyors, and pumps. Machine tools require precise motion control, and the near-zero backlash of disc couplings ensures that the cutting tool moves accurately, resulting in high-quality machined parts. Robotics also benefit from the precise torque transmission and low backlash of disc couplings, as they enable smooth and accurate movement of robotic arms. Pumps and compressors, which often operate at high speeds and handle corrosive fluids, rely on disc couplings for their reliability and resistance to harsh conditions.
The automotive industry uses high performance disc couplings in high-performance vehicles, such as racing cars and luxury sports cars. These vehicles require efficient torque transmission from the engine to the transmission, and disc couplings provide the necessary high torque capacity and torsional stiffness. Additionally, the lightweight design of disc couplings helps to reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, improving performance and fuel efficiency. In electric vehicles, disc couplings are used to connect the electric motor to the drivetrain, as they can handle the high torque output of electric motors and provide precise control.
Other applications of high performance disc couplings include marine propulsion systems, where they connect the engine to the propeller shaft, and chemical processing equipment, where they are used in pumps, mixers, and reactors. Marine environments are highly corrosive, and the corrosion resistance of disc couplings makes them ideal for use in this industry. Chemical processing equipment often operates at high temperatures and handles corrosive chemicals, and disc couplings made from nickel-based superalloys can withstand these harsh conditions.
Maintenance and Inspection Practices for High Performance Disc Couplings
Although high performance disc couplings are maintenance-free in terms of lubrication and wear parts replacement, regular inspection is still necessary to ensure their continued reliability and performance. The primary goal of inspection is to detect any signs of damage or wear to the disc pack, hubs, bolts, or other components before they lead to failure. Regular inspection can also help to identify misalignment issues that may have developed over time, which can cause excessive stress on the coupling and other system components.
The frequency of inspection depends on the application and operating conditions. For general industrial applications, a visual inspection every six months to a year is recommended. For high-speed, high-torque, or harsh environment applications, more frequent inspections (e.g., every three months) may be necessary. During inspection, the coupling should be checked for signs of disc fatigue, such as cracks, tears, or deformation. The disc pack should also be inspected for any signs of corrosion, which can weaken the material and reduce the coupling’s torque capacity. The hubs and bolts should be checked for tightness, as loose bolts can cause excessive vibration and stress on the disc pack.
In addition to visual inspection, non-destructive testing (NDT) methods can be used to detect internal defects in the disc pack that may not be visible to the naked eye. Common NDT methods for disc couplings include ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and liquid penetrant testing. Ultrasonic testing uses high-frequency sound waves to detect cracks and other defects in the metal discs. Magnetic particle testing is used to detect surface and near-surface cracks in ferromagnetic materials, such as steel. Liquid penetrant testing is used to detect surface cracks in non-ferromagnetic materials, such as titanium and nickel alloys.
If any defects are detected during inspection, the affected components should be replaced immediately. The disc pack is a replaceable component, and it should be replaced as a whole rather than individual discs, as this ensures that the coupling’s performance characteristics are maintained. When replacing the disc pack, it is important to use components that are compatible with the original coupling design, as using non-standard components can compromise the coupling’s performance and reliability. The bolts should also be replaced when the disc pack is replaced, as they may have been subjected to fatigue stress.
Proper installation is also critical for the long-term performance of high performance disc couplings. During installation, the shafts should be aligned as accurately as possible to minimize the stress on the disc pack. Although disc couplings can accommodate moderate misalignment, excessive misalignment can lead to premature fatigue of the discs. The coupling should be mounted securely to the shafts, and the bolts should be tightened to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. It is also important to ensure that the coupling is not subjected to excessive axial or radial loads, which can cause damage to the hubs or disc pack.
Conclusion
High performance disc couplings have established themselves as a reliable and efficient solution for power transmission in a wide range of demanding applications. Their unique design, which utilizes flexible metal discs for torque transmission and misalignment compensation, endows them with exceptional characteristics such as high torque capacity, torsional stiffness, maintenance-free operation, and resistance to harsh conditions. The choice of materials for the disc pack and other components is critical to ensuring the coupling’s performance and durability, with stainless steel, titanium alloys, and nickel-based superalloys being the most commonly used materials.
From power generation and aerospace to industrial machinery and automotive applications, high performance disc couplings play a vital role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of modern industrial systems. Regular inspection and proper maintenance practices, although minimal compared to other coupling types, are essential to ensuring their continued performance and preventing premature failure.
As industrial technology continues to advance, the demand for high performance disc couplings is expected to grow, driven by the need for more efficient, reliable, and compact power transmission solutions. Ongoing research and development in materials science and coupling design are likely to further enhance the performance characteristics of disc couplings, making them suitable for even more demanding applications in the future. Whether in a gas turbine power plant, an aircraft engine, or a high-precision machine tool, high performance disc couplings are poised to remain a key component in the industrial power transmission landscape.
« High Performance Disc Couplings » Post Date: 2023/10/20
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/high-performance-disc-couplings.html