Gear Tooth Coupling
Rokee® is a Gear Tooth Coupling Supplier from China, customized gear tooth coupling according to the drawings which provided by the customer, selling chinese national standard gear tooth coupling, support export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® industrial coupling have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
The Drum Gear Coupling is a specially designed advanced Gear Coupling. Its outer teeth are made into a sphere, with the center of the sphere on the axis of the gear. The teeth clearance is slightly larger than the general products and can transfer a greater torque and allow greater angular displacement, enjoying excellent performance and longer life.
ROD Curved-tooth Gear Coupling is one of the transmission products with core technology independently developed by Rokee and has established and reported corporate technical standards in the country. By combining with the standard coupling technology of advanced countries such as Japan and Germany, we optimized many detailed dimensions, and adopted the toothed design with a large pressure angle and short shaft design for the shaft hole, which reduces the length-diameter ratio, and has a more compact structure and excellent speed performance.
The bolts of similar types are standardized and the parts are universal. Compared with the national standard couplings, our Toothed Couplings can transfer more torque, with greatly reduced mass and small moment of inertia. It meets the European explosion-proof requirements and the comprehensive performance is greatly advanced. We highly recommend you to choose our Crown Gear Couplings for better transmission performance.
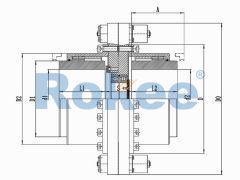
RODA Drum Gear Coupling
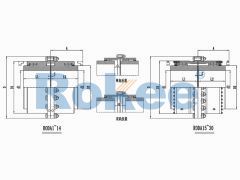
The RODA Drum Gear Coupling is the basic type of ROD series coupling, suitable for most situations where the compensation of transmission distance and motion position does not require special increase.RODT Indirect Tube Drum Gear Coupling
The RODT Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling, suitable for increasing transmission distance.RODX Intermediate Shaft Drum Gear Coupling
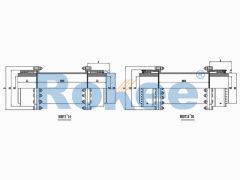
RODX Drum Gear Coupling is an extended type of ROD series coupling with a floating shaft design in the middle, suitable for increasing transmission distance.RODP Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
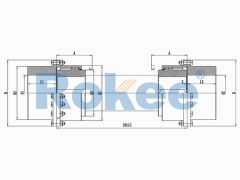
The RODP Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with a brake disc, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with disc brakes.RODF Split Brake Disc Drum Gear Coupling
The RODF Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with split brake discs, suitable for transmission situations where there is braking demand and the braking position changes when used in conjunction with disc brakes.RODW Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODW Drum Gear Coupling is a type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes.RODU Brake Wheel Drum Gear Coupling
The RODU Drum Gear Coupling is another type of ROD series coupling with brake wheels, suitable for transmission situations where braking needs to be used in conjunction with wheel brakes and applied to one end of the axle, achieving smoother and more reliable braking performance.RODV Vertical Installation Drum Gear Coupling
The RODV Drum Gear Coupling is a vertical installation type of the ROD series coupling, suitable for transmission situations that require vertical transmission torque.RODM Torsion Protection Drum Gear Coupling
The RODM Drum Gear Coupling is a torque setting form of the ROD series coupling. By adjusting relevant components, the maximum transmission torque can be easily set within a certain range. Suitable for shafting transmission situations that require safe torque operation to protect important machine components from excessive damage.
GICL Drum Gear Coupling
GICL drum gear coupling has larger inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for larger axial displacement.GICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement.GIICL Drum Gear Coupling
GIICL drum gear coupling has small inner teeth width, which can transfer torque while compensating for small axial displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.GIICLZ Drum Gear Coupling
Half of the GIICLZ drum gear coupling adopts a non-toothed semi-coupling sleeve structure, which is usually connected in pairs or used in occasions with small angular displacement. Also, its structure is compact and the moment of inertia is low.GCLD Drum Gear Coupling
GCLD drum gear coupling is generally used for direct connection with the motor, so it generally has a higher speed and compact structure.NGCL Drum Gear Coupling
NGCL drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.NGCLZ Drum Gear Coupling
NGCLZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required. Half of its structure adopts a semi-coupling sleeve design, with smaller angular displacement compensation but more stable braking.WG Drum Gear Coupling
The overall characteristics of WG drum gear coupling are similar to those of other drum gear couplings, but with a larger modulus design, which can generally transmit greater torque.WGZ Drum Gear Coupling
WGZ drum gear coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for shoe type braking.WGP Drum Gear Coupling
WGP drum gear coupling is designed with a brake disc, suitable for disc type braking.WGT Drum Gear Coupling
WGT drum gear coupling is designed with indirect tube, suitable for long distance torque transfer.WGC Drum Gear Coupling
WGC drum gear coupling is specially designed for situations where vertical transmission is required, suitable for some vertical transmission systems.WGJ Drum Gear Coupling
WGJ drum gear coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance torque transmission, and some are equipped with axial buffers.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, the ability to efficiently transfer torque between rotating shafts while accommodating misalignments is paramount to the performance and longevity of industrial machinery. Among the various coupling solutions available, gear tooth couplings stand out as a robust and reliable option, widely employed in heavy-duty applications where high torque, speed, and durability are non-negotiable requirements.
At its core, a gear tooth coupling is a mechanical device designed to connect two rotating shafts, enabling the transfer of rotational power from a driver (such as an electric motor or internal combustion engine) to a driven component (like a pump, compressor, or conveyor). What distinguishes gear tooth couplings from other types of couplings—such as flexible disc, jaw, or universal couplings—is their utilization of meshing gear teeth to transmit torque. This gear-based design not only allows for high torque capacity but also provides a degree of flexibility to compensate for axial, radial, and angular misalignments between the connected shafts, which is essential in real-world industrial settings where perfect alignment is often difficult to achieve and maintain.
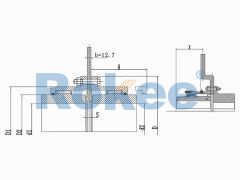
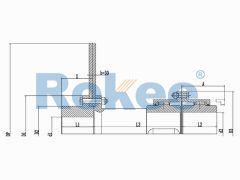
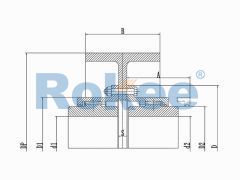
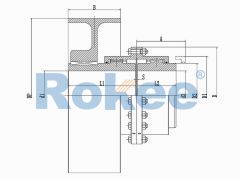
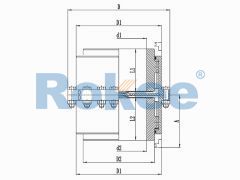
The basic structure of a gear tooth coupling typically consists of four main components: two gear hubs, two outer sleeves (also known as gear rings), and a lubrication system. The gear hubs are precision-machined to feature external gear teeth and are designed to be mounted directly onto the ends of the shafts via keyways, set screws, or hydraulic fitting methods. The outer sleeves, on the other hand, have internal gear teeth that mesh with the external teeth of the gear hubs. When assembled, the two gear hubs (one on each shaft) are enclosed within the outer sleeves, creating a meshed gear system that facilitates torque transmission. The lubrication system, which may include grease fittings or oil channels, is critical for reducing friction between the meshing teeth, minimizing wear, and dissipating heat generated during operation.
There are two primary types of gear tooth couplings based on their design configuration: straight-tooth (spur) and curved-tooth (helical) couplings. Straight-tooth gear couplings feature gear teeth that are cut parallel to the axis of the shaft. This design offers simplicity in manufacturing and assembly, making them a cost-effective option for certain applications. However, straight-tooth couplings have limitations when it comes to accommodating angular misalignments, as the meshing of straight teeth can result in higher contact stresses and increased wear under misaligned conditions. Curved-tooth gear couplings, by contrast, have teeth that are cut at an angle to the shaft axis, similar to helical gears. This curved tooth design allows for smoother meshing, even when the shafts are angularly misaligned, as the contact between the teeth is distributed over a larger surface area. This not only reduces contact stresses but also enables curved-tooth couplings to handle greater misalignments and operate more quietly than their straight-tooth counterparts. As a result, curved-tooth gear couplings are more commonly used in heavy-duty and high-speed applications where performance and reliability are critical.
The operational principle of gear tooth couplings revolves around the meshing of the gear teeth on the hubs and outer sleeves. When the driver shaft rotates, it imparts rotational motion to the attached gear hub. The external teeth of this hub mesh with the internal teeth of the outer sleeve, causing the sleeve to rotate in synchronization. The outer sleeve then transfers this rotational motion to the second gear hub (connected to the driven shaft) via its meshed teeth, thereby transmitting torque from the driver to the driven component. The flexibility of the coupling is achieved through the slight movement of the meshed teeth, which allows for small amounts of axial (end-to-end) movement, radial (side-to-side) displacement, and angular (tilting) misalignment between the two shafts. This flexibility is crucial for absorbing shocks and vibrations, reducing the stress on the shafts and other connected components, and preventing premature failure of the machinery.
One of the most significant advantages of gear tooth couplings is their high torque capacity. The meshing gear teeth provide a large contact area, allowing them to transmit significantly higher levels of torque compared to many other coupling types. This makes gear tooth couplings ideal for use in heavy-duty industrial applications, such as steel mills, mining equipment, and large-scale manufacturing machinery, where substantial power transfer is required. Additionally, gear tooth couplings are capable of operating at high rotational speeds, further expanding their applicability in high-performance systems.
Another key benefit of gear tooth couplings is their ability to accommodate multiple types of misalignments. In industrial environments, shafts can become misaligned due to a variety of factors, including thermal expansion and contraction, foundation settlement, bearing wear, and installation errors. Gear tooth couplings can compensate for axial misalignment (which occurs when the shafts move toward or away from each other), radial misalignment (where the shafts are offset parallel to each other), and angular misalignment (when the shafts are tilted relative to each other). This versatility ensures that the coupling remains functional and efficient even under less-than-ideal alignment conditions, reducing the need for frequent realignment and minimizing downtime.
Durability and long service life are also hallmark characteristics of gear tooth couplings. Constructed from high-strength materials such as alloy steels, which are often heat-treated to enhance hardness and wear resistance, gear tooth couplings are capable of withstanding the harsh operating conditions commonly encountered in industrial settings, including high temperatures, heavy loads, and exposure to dust, dirt, and other contaminants. When properly lubricated and maintained, gear tooth couplings can provide reliable service for many years, making them a cost-effective long-term solution for power transmission.
The versatility of gear tooth couplings is further evidenced by their wide range of industrial applications. In the steel industry, for example, gear tooth couplings are used in rolling mills, where they transmit torque from large motors to the rolls that shape and form steel. The high torque capacity and ability to accommodate misalignments make them well-suited for this application, as rolling mills operate under extreme loads and can experience significant shaft misalignments due to thermal expansion.
In the mining industry, gear tooth couplings are employed in equipment such as crushers, conveyors, and pumps. Crushers, which are used to break down large rocks and ore, require couplings that can handle high torque and withstand the heavy impact loads generated during operation. Gear tooth couplings are able to absorb these shocks and vibrations, ensuring reliable power transmission and protecting the drive system components. Conveyors, which are used to transport materials over long distances, also benefit from the flexibility of gear tooth couplings, as they can accommodate misalignments caused by the stretching of conveyor belts or the settlement of the conveyor structure.
The oil and gas industry is another major user of gear tooth couplings. They are used in pumps, compressors, and drilling equipment, where they must operate in harsh environments characterized by high pressures, high temperatures, and exposure to corrosive fluids and gases. Gear tooth couplings constructed from corrosion-resistant materials and equipped with effective lubrication systems are able to withstand these conditions, ensuring the reliable operation of critical equipment in oil and gas exploration, production, and refining processes.
Other industrial applications of gear tooth couplings include power generation (in turbines and generators), marine propulsion systems, large-scale fans and blowers, and heavy-duty manufacturing machinery such as extruders and presses. In each of these applications, the unique combination of high torque capacity, flexibility, and durability makes gear tooth couplings an indispensable component of the power transmission system.
Despite their inherent durability and reliability, gear tooth couplings require proper maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The most critical maintenance task is regular lubrication. The meshing gear teeth generate friction during operation, which can lead to wear, heat buildup, and ultimately, component failure if not properly lubricated. Lubricants such as grease or oil not only reduce friction but also provide a protective barrier against corrosion and help to remove debris from the meshing surfaces. The type of lubricant used should be appropriate for the operating conditions, including temperature, load, and speed, and the coupling should be lubricated at regular intervals as recommended by the manufacturer.
Regular inspection is also essential for the proper maintenance of gear tooth couplings. Inspections should include checking for signs of wear on the gear teeth (such as pitting, scuffing, or tooth loss), damage to the hubs or outer sleeves, and leaks in the lubrication system. Additionally, the alignment of the connected shafts should be checked periodically, as excessive misalignment can place additional stress on the coupling and lead to premature wear. If any issues are detected during inspection, prompt repairs or replacements should be carried out to prevent further damage to the coupling and other components of the machinery.
Another important maintenance consideration is the proper installation of gear tooth couplings. Correct installation, including proper shaft alignment, secure mounting of the hubs, and proper assembly of the outer sleeves, is critical for ensuring the coupling operates efficiently and reliably. Improper installation can lead to excessive wear, increased vibration, and reduced service life. It is recommended that installation be carried out by qualified technicians following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
In recent years, advancements in manufacturing technology have led to improvements in the design and performance of gear tooth couplings. Precision machining techniques, such as computer numerical control (CNC) machining, have enabled the production of gear teeth with tighter tolerances, resulting in smoother meshing, reduced wear, and increased torque capacity. Additionally, the use of advanced materials, such as composite materials and surface-treated steels, has further enhanced the durability and corrosion resistance of gear tooth couplings, making them suitable for even more demanding applications.
Despite the availability of alternative coupling technologies, gear tooth couplings continue to be a preferred choice in many industrial applications due to their unique combination of high torque capacity, flexibility, durability, and versatility. Their ability to handle heavy loads, high speeds, and misalignments makes them indispensable in industries such as steel, mining, oil and gas, and power generation, where reliable power transmission is critical to operational efficiency and productivity.
In conclusion, gear tooth couplings play a vital role in modern mechanical power transmission systems. Their robust design, based on meshing gear teeth, enables them to transmit high levels of torque while accommodating axial, radial, and angular misalignments. With a wide range of industrial applications, from rolling mills and crushers to pumps and turbines, gear tooth couplings are a cornerstone of heavy-duty industrial machinery. Proper maintenance, including regular lubrication, inspection, and correct installation, is essential to ensure their optimal performance and long service life. As manufacturing technologies continue to advance, gear tooth couplings are likely to become even more efficient and reliable, further solidifying their position as a key component in industrial power transmission.
« Gear Tooth Coupling » Post Date: 2023/10/20
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/blog/gear-tooth-coupling.html
Tags: Curved Tooth Couplings, pu sandwich panel line
- Principle Of Half Tooth Coupling
- Dimensions Of Half Tooth Couplings
- Brake Disc Drum Tooth Coupling
- Supplier Of Multi Angle A-tooth Coupling
- Rotary Brake Wheel Drum Tooth Coupling
- Assembly Drawing Of Elastic Pin Tooth Coupling
- Design Of Elastic Pin Tooth Coupling
- Mill Tooth Coupling
- High-end Professional Tooth Couplings
- Non Standard Tooth Coupling