Shim Pack Coupling
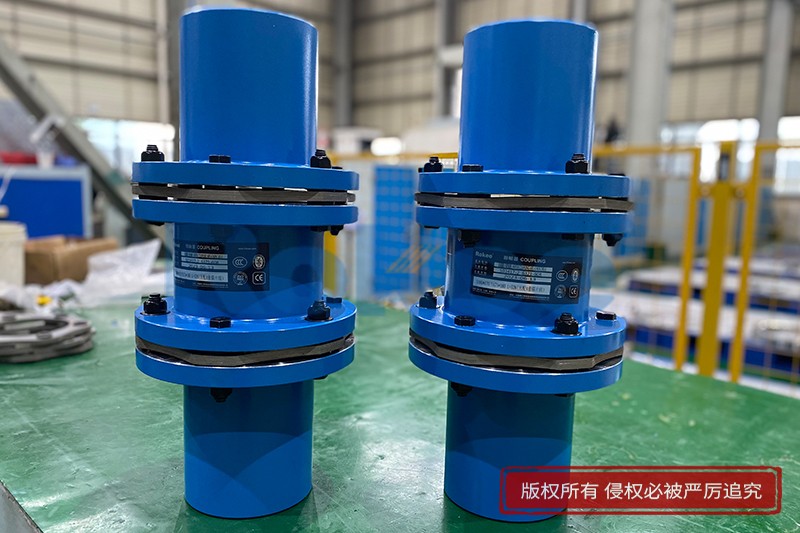

Rokee® is Shim Pack Coupling Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® Shim Pack Coupling have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
Shim Pack Coupling is an efficient flexible coupling with no back clearance and free from maintenance. Due to its unique structural design, Shim Pack Coupling can achieve the perfect delivery of torque. Meanwhile, Shim Pack Coupling has excellent performances, including large axial and radial compensation ability, low reply feedback force and wide thermal adaptability, etc. With different change design, Shim Pack Coupling can be applied at most power transmission sites.
-

JMI Diaphragm Coupling
JMI metal diaphragm coupling adopts the single-piece design, suitable for short distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMII Diaphragm Coupling
JMII metal diaphragm coupling also adopts the single-piece design but has no counterbore, suitable for short distance transmission, with more compact structure. -

JMIIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at both ends have no counterbore. -
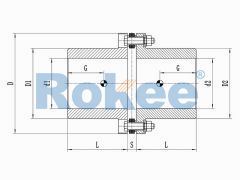
RLA Standard Single Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications, but cannot compensate for radial deviation. -
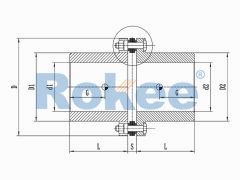
RLM Small Single Diaphragm Coupling
The RLM standard single section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working situations with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm, and cannot compensate for radial errors. -
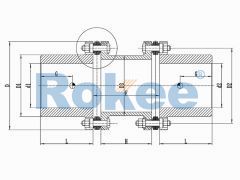
RLMD Small Double Diaphragm Coupling
The RLMD standard double section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working occasions with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm. -
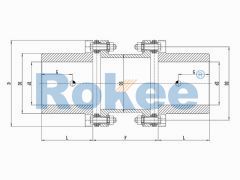
RLAD Standard Double Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications. -
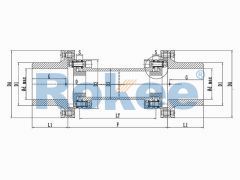
RLAT Super Long Wheelbase Diaphragm Coupling
Adopting an intermediate shaft design, suitable for ultra long shaft spacing power transmission applications. -
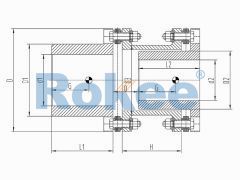
RLAR Single Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
Single side shaft sleeve reverse installation design, suitable for occasions with limited shaft head distance. -
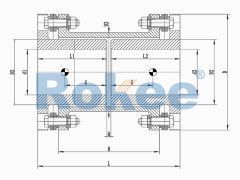
RLARD Double Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
The double-sided shaft sleeve reverse installation design is also applicable in situations where the distance from the shaft head is limited or the additional bending moment is smaller. -
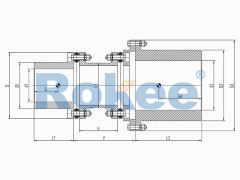
RLAF Large & Small Shaft Mounted Diaphragm Coupling
The size difference design of the bilateral shaft sleeve is suitable for situations where the diameter difference between the two ends of the shaft is significant. -
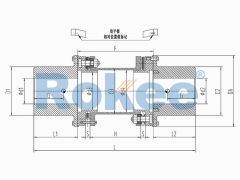
RLQA No Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for various industrial process pumps, fans, and other medium to low speed applications, with a maximum speed generally not exceeding 25000 rpm. It meets the requirements of API610/ISO14691 and is one of the first products for API applications. -
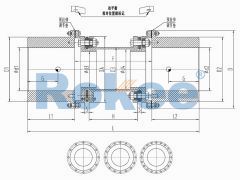
RLQF Flange Type Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications, with a maximum speed of up to 35000rpm. -
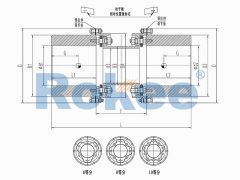
RLQU Improved Flange Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
The improved RLQF has smaller additional bending moments and better performance. Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications. -
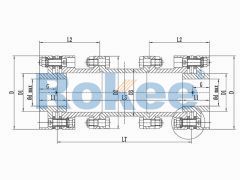
RLHD High Speed Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for higher speed applications, it also adopts a flexible component integrated assembly design, with a maximum speed of up to 42000rpm.
In the realm of industrial power transmission, the efficiency, reliability, and flexibility of coupling systems play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless operation across a wide range of machinery. Among the diverse types of couplings available, the shim pack coupling stands out as a versatile and robust solution, engineered to address the challenges of misalignment, torque transfer, and operational stability.
A shim pack coupling is a type of rigid-flexible coupling designed to transmit torque between two rotating shafts while accommodating limited amounts of misalignment. Unlike fully rigid couplings that require precise shaft alignment to avoid premature wear, or highly flexible couplings that may sacrifice torque capacity, shim pack couplings strike a balance between rigidity and flexibility through their unique structural configuration. The core component that defines this coupling type is the shim pack—a set of thin, precision-manufactured shims that are strategically placed to adjust the coupling’s alignment and compensate for axial, radial, and angular misalignments between the driving and driven shafts. This design not only enhances the coupling’s adaptability but also contributes to its durability and long service life in demanding industrial environments.
To understand the functionality of a shim pack coupling, it is essential to examine its key structural components. Typically, a shim pack coupling consists of four main parts: two hub assemblies, a shim pack, connecting bolts, and a protective cover. The hub assemblies are attached to the ends of the driving and driven shafts, usually via keyway connections or interference fits, ensuring a secure grip that prevents slippage during torque transmission. Each hub assembly features a flanged end with evenly spaced bolt holes, which are used to connect the two hubs through the shim pack. The shim pack itself is composed of multiple individual shims, often made from high-strength steel or other durable materials, with varying thicknesses. These shims are stacked between the flanges of the two hubs, and their arrangement and thickness determine the coupling’s ability to accommodate misalignment. The connecting bolts, which pass through the flanges and the shim pack, are tightened to create a clamping force that holds the entire assembly together, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Finally, the protective cover, though not always mandatory, is often installed to shield the coupling components from dust, debris, and external impacts, reducing the risk of contamination and damage.
The operational principle of a shim pack coupling revolves around the adjustability of the shim pack to correct misalignments and transmit torque effectively. When the coupling is installed, the shims are selected and arranged based on the measured misalignment between the two shafts. For angular misalignment—where the shafts are not colinear but intersect at a point—the shims are stacked unevenly, with thicker shims placed on one side of the flange to tilt the hub assembly and align the shafts. For parallel misalignment—where the shafts are parallel but offset—the shims are stacked uniformly on one side to shift the hub assembly horizontally, closing the offset gap. Axial misalignment, which involves the axial movement of one shaft relative to the other, is accommodated by the thickness of the shim pack, which can be adjusted to maintain the correct axial distance between the hubs. Once aligned, the coupling transmits torque from the driving shaft to the hub, through the clamping force of the bolts to the shim pack, and then to the driven hub and shaft. The shim pack, being rigid under clamping force, ensures that almost all the torque is transferred without significant loss, while its ability to be adjusted allows for precise alignment that minimizes stress on the shafts, bearings, and other related components.
One of the primary advantages of shim pack couplings is their exceptional adjustability, which simplifies installation and alignment processes. In industrial settings, shaft misalignment is a common issue that can arise due to factors such as foundation settlement, thermal expansion, or manufacturing tolerances. Traditional rigid couplings require complex and time-consuming alignment procedures, often involving specialized tools and skilled labor. In contrast, shim pack couplings allow for easy adjustment by adding, removing, or rearranging shims, making the alignment process faster and more efficient. This not only reduces installation time but also lowers labor costs, a significant benefit for industrial operations looking to minimize downtime.
Another key benefit of shim pack couplings is their high torque capacity. Due to their rigid construction when clamped, these couplings are capable of transmitting large amounts of torque without slipping or deformation. This makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications, such as those found in mining, steel production, and large-scale manufacturing, where high torque transfer is essential. Additionally, the use of high-strength materials in the shims and hubs ensures that the coupling can withstand the rigors of continuous operation under high loads, contributing to its long service life and reliability.
Shim pack couplings also offer excellent durability and resistance to wear. The shims, being made from hardened materials, are resistant to abrasion and deformation, even under high clamping forces and continuous torque transmission. Unlike flexible couplings that use rubber or elastomeric components which can degrade over time due to heat, oil, or chemical exposure, shim pack couplings have no such components, making them suitable for use in harsh environments where temperature extremes, oil contamination, or chemical exposure are common. This durability translates to lower maintenance costs and fewer replacements, further enhancing the economic efficiency of these couplings.
Furthermore, shim pack couplings provide good vibration damping properties. While they are not as flexible as some other coupling types, the slight flexibility offered by the shim pack helps to absorb minor vibrations generated during operation. This reduces the transmission of vibrations from the driving shaft to the driven shaft and other machinery components, minimizing noise and preventing premature wear on bearings, gears, and other critical parts. By reducing vibration-related stress, shim pack couplings contribute to the overall stability and longevity of the entire power transmission system.
The versatility of shim pack couplings is reflected in their wide range of industrial applications. They are commonly used in machinery where precise torque transmission and misalignment compensation are required, across various sectors including manufacturing, mining, oil and gas, power generation, and transportation. In the manufacturing industry, for example, shim pack couplings are used in conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and machine tools, where they ensure the smooth transfer of power between motors and driven components. In mining operations, they are employed in heavy-duty equipment such as crushers, grinders, and conveyor belts, where they withstand high torque loads and harsh environmental conditions. In the oil and gas sector, shim pack couplings are used in pumps, turbines, and drilling equipment, where their resistance to oil contamination and high temperatures makes them ideal for offshore and onshore applications. Additionally, they are used in power generation plants, where they connect turbines and generators, ensuring efficient power transmission with minimal downtime.
When selecting a shim pack coupling for a specific application, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. First and foremost, the torque capacity of the coupling must match or exceed the maximum torque generated by the driving shaft. Selecting a coupling with insufficient torque capacity can lead to slippage, deformation, or premature failure. It is also important to consider the maximum misalignment that the coupling will need to accommodate, as different shim pack configurations can handle varying levels of axial, radial, and angular misalignment. The operating speed of the shafts is another critical factor, as high-speed applications may require couplings with balanced components to avoid vibration and noise. The material of the coupling components should also be selected based on the operating environment—for example, in corrosive environments, stainless steel shims and hubs may be necessary to prevent rust and degradation. Additionally, the size of the coupling must be compatible with the shaft diameters of the driving and driven machinery, ensuring a proper fit that prevents slippage and ensures efficient torque transfer.
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the long-term performance and reliability of shim pack couplings. Regular inspection is the cornerstone of effective maintenance, and operators should periodically check the coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. This includes inspecting the shims for cracks, deformation, or excessive wear, checking the hub assemblies for looseness or damage, and verifying that the connecting bolts are properly tightened. If any signs of damage or misalignment are detected, immediate action should be taken—this may involve replacing worn shims, retightening bolts, or realigning the shafts. It is also important to keep the coupling clean and free from dust, debris, and contamination, as these can accelerate wear and damage to the components. In environments where the coupling is exposed to harsh conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive substances, more frequent inspections and maintenance may be necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Another important maintenance practice is the periodic retorquing of the connecting bolts. Over time, the clamping force of the bolts may decrease due to vibration, thermal cycling, or other operational factors, which can lead to slippage and reduced torque transmission. By retorquing the bolts at regular intervals, operators can maintain the required clamping force and ensure that the coupling remains secure. Additionally, when replacing shims, it is important to use precision-manufactured shims of the correct thickness and material to ensure proper alignment and torque transfer. Using low-quality or incorrect shims can lead to misalignment, increased stress on the shafts and bearings, and premature coupling failure.
Despite their many advantages, shim pack couplings are not suitable for all applications. They are not designed to accommodate large amounts of misalignment, and in applications where significant misalignment is unavoidable, more flexible coupling types may be more appropriate. Additionally, shim pack couplings are not ideal for applications that require damping of large vibrations, as their rigid construction limits their vibration absorption capabilities. It is therefore important to carefully evaluate the requirements of the application before selecting a shim pack coupling, ensuring that it is the most suitable solution for the specific operating conditions.
In conclusion, shim pack couplings are a versatile and reliable solution for power transmission in a wide range of industrial applications. Their unique design, featuring a precision-adjustable shim pack, allows for easy alignment and compensation of limited misalignments, while their rigid construction ensures high torque capacity and durability. The key advantages of these couplings—including adjustability, high torque capacity, durability, and vibration damping—make them an ideal choice for heavy-duty applications in sectors such as manufacturing, mining, oil and gas, and power generation. By following proper selection and maintenance practices, operators can ensure that shim pack couplings deliver optimal performance and longevity, contributing to the efficiency and reliability of industrial machinery. As industrial technology continues to evolve, the role of shim pack couplings is likely to remain prominent, as they continue to meet the growing demands for efficient and reliable power transmission in complex industrial environments.
« Shim Pack Coupling » Post Date: 2023/10/19
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/shim-pack-coupling.html
- 2024-06-12Material of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-06-12Maintenance of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-06-12Machine Drawing of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-06-12Lubrication of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-06-12Installation of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-06-12High Quality Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-06-07Misalignment Tolerance of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-06-07Parts of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-06-07Procurement of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-06-07Purpose of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-06-07Schematic Diagram of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-06-07Shim Pack Coupling Advantages
- 2024-06-07High Performance Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-06-04Grease of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-06-04Shim Pack Coupling Assembly Drawing
- 2024-05-29Shim Pack Coupling Brands
- 2024-05-29Shim Pack Coupling Calculation
- 2024-05-29Shim Pack Coupling Design
- 2024-05-29Shim Pack Coupling Manufacturing
- 2024-05-29Shim Pack Coupling Models
- 2024-05-29Shim Pack Coupling Pictures
- 2024-05-27Gap Chart of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-27Function of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-27Exploded View of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-27Engineering Drawing of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-27Efficiency of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-27Working Principle of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-27Uses of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-27Types of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-27Torque of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-27Tagging of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-27Supply of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-27Structural Diagram of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-27Stiffness of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-27Specifications of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-17Disadvantages of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-17Customized Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-17Components of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-17Coaxiality of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-17Classification of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-17Catalogue of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-17Application of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-17Angle of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-17Alignment of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-173D Model of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-10Size Chart of Shim Pack Couplings
- 2024-05-10Size Calculation of Shim Pack Coupling
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Coupling Price
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Coupling Sales
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Coupling Standard Sizes
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Couplings Company
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Couplings Drawing
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Couplings Factory
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Couplings For Sale
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Couplings Manufacturer
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Couplings Supplier
- 2024-05-10Shim Pack Couplings Wholesale