Pin Bush Couplings
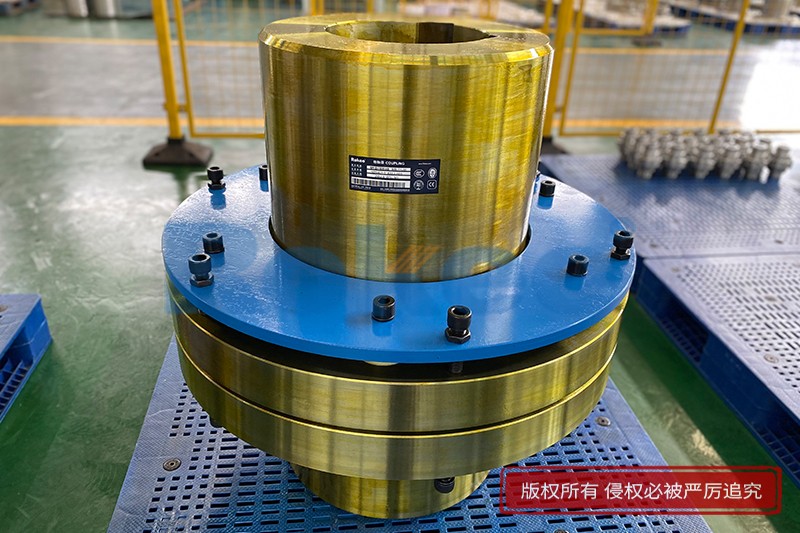
Rokee® is Pin Bush Couplings Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® Pin Bush Couplings have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
Pin Bush Coupling is simple and clever in design and has wide applicability. Pin Bush Coupling uses the pin with elastic sleeve to connect two semi-couplings with pin holes to realize torque transmission and larger angular compensation. At the same time, Pin Bush Coupling has good shock absorption and buffering performance, which can be used in high-speed occasions without lubrication and requiring easy pin sleeve replacement.
-

LT/TL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling
LT/TL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling is the basic form of this series of couplings. -

LTZ/TLL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling
LTZ/TLL Elastic Sleeve Pin Coupling is designed with a brake wheel, suitable for situations where braking is required.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings play an indispensable role as components that connect two shafts to transmit torque while accommodating various misalignments. Among the diverse types of couplings available, the pin bush coupling stands out for its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and versatility.
A pin bush coupling, also known as a rubber bush coupling or pin and sleeve coupling, is a flexible coupling designed to transmit rotational power between two coaxial shafts. Its core design revolves around a set of pins attached to one half of the coupling and corresponding bushes (or sleeves) mounted on the other half. The simplicity of this design is one of its key advantages, as it consists of relatively few components, making manufacturing and assembly straightforward. Unlike rigid couplings that require precise alignment and cannot accommodate misalignments, pin bush couplings incorporate a flexible element (the bush) that allows for a certain degree of angular, parallel, and axial misalignment between the connected shafts. This flexibility is crucial in mitigating the effects of shaft misalignment, which can arise from factors such as incorrect installation, thermal expansion, or wear of supporting bearings over time.
The basic structure of a pin bush coupling comprises four main components: two coupling halves, pins, and bushes. The coupling halves are typically cylindrical structures that are mounted on the ends of the two shafts to be connected. These halves are usually fabricated with flanges that contain holes for the insertion of pins. The pins are cylindrical fasteners that are secured to one of the coupling halves, either by threading, press-fitting, or using cotter pins. The bushes, which are the flexible elements of the coupling, are inserted into the corresponding holes in the other coupling half and act as sleeves that encase the pins. The interface between the pins and bushes is critical to the coupling's performance, as it is here that torque transmission occurs and misalignments are accommodated. In some designs, additional components such as washers or retaining rings may be used to secure the pins and bushes in place, preventing axial movement during operation.
The working principle of a pin bush coupling is based on the transfer of torque through the interaction between the pins and bushes. When one shaft rotates, it drives the coupling half to which the pins are attached. The pins then exert a force on the bushes, which in turn transmit the torque to the other coupling half and ultimately to the second shaft. The flexibility of the bushes allows for misalignment by deforming slightly as the shafts rotate. For example, in the case of angular misalignment (where the shafts are not perfectly coaxial but intersect at a small angle), the bushes flex as the pins rotate around the axis of the misaligned shafts, ensuring continuous torque transmission without excessive stress. Similarly, for parallel misalignment (where the shafts are offset but parallel), the bushes accommodate the offset by allowing the pins to move within the bush openings. Axial misalignment (where the shafts move along their axial direction) is also accommodated by the axial flexibility of the bushes.
Another important function of the pin bush coupling is its ability to dampen vibrations and absorb shock loads. The flexible bushes, often made from elastomeric materials, act as shock absorbers, reducing the transmission of vibrations from one shaft to the other. This vibration damping property is particularly beneficial in systems where the driving or driven machine generates significant vibrations, such as electric motors, pumps, or compressors. By reducing vibration transmission, pin bush couplings help minimize wear and tear on other components in the system, such as bearings, gears, and shafts, thereby extending the overall service life of the machinery.
Material selection for pin bush couplings is a critical factor that influences their performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. The choice of materials for each component is determined by factors such as the torque capacity required, operating temperature, environmental conditions (e.g., exposure to moisture, chemicals, or dust), and the level of misalignment expected. For the coupling halves, common materials include cast iron, steel, and aluminum. Cast iron is widely used due to its high strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for most general-purpose applications. Steel, particularly alloy steel, is preferred for high-torque applications or where higher strength and rigidity are required. Aluminum is used in applications where weight reduction is a priority, such as in some automotive or aerospace components, although it has lower torque capacity compared to cast iron and steel.
The pins are typically made from high-strength steel or stainless steel. High-strength steel is chosen for its ability to withstand the shear and tensile forces generated during torque transmission. Stainless steel is used in applications where corrosion resistance is essential, such as in marine environments or chemical processing plants. The bushes, being the flexible element, are usually made from elastomeric materials such as natural rubber, synthetic rubber (e.g., neoprene, nitrile rubber), or polyurethane. The selection of the bush material depends on the operating conditions: natural rubber offers good flexibility and vibration damping but has limited resistance to oil and high temperatures; neoprene is resistant to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for outdoor or industrial applications; nitrile rubber is highly resistant to oil and fuel, making it ideal for applications in the automotive or petroleum industries; polyurethane provides higher strength and durability than rubber and is resistant to abrasion, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pin bush couplings find applications across a wide range of industries due to their versatility, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. One of the most common applications is in the industrial sector, where they are used in machinery such as pumps, compressors, fans, blowers, and conveyors. In these applications, the coupling connects the electric motor (driving shaft) to the driven machine, transmitting torque while accommodating any misalignments that may occur. For example, in a centrifugal pump system, the pin bush coupling connects the motor shaft to the pump shaft, allowing for minor misalignments caused by thermal expansion of the pump casing or wear of the motor bearings.
The agricultural industry also relies heavily on pin bush couplings in various farm machinery. Tractors, for instance, use these couplings to connect the engine to auxiliary equipment such as harvesters, plows, and irrigation pumps. The ability of pin bush couplings to accommodate misalignments and dampen vibrations is particularly useful in agricultural settings, where machinery is often operated in rough terrain, leading to frequent shaft misalignments. Additionally, the cost-effectiveness of these couplings makes them a preferred choice for agricultural equipment, which often requires durable yet affordable components.
In the automotive industry, pin bush couplings are used in applications such as drive shafts, gearboxes, and auxiliary systems. For example, in some light commercial vehicles, pin bush couplings are used to connect the transmission output shaft to the drive shaft, transmitting torque from the engine to the wheels. The flexible nature of the coupling helps absorb shock loads generated during acceleration and deceleration, improving the smoothness of power transmission. In auxiliary systems such as power steering pumps or air conditioning compressors, pin bush couplings connect the engine's crankshaft to the auxiliary pump, allowing for misalignments between the two shafts.
Other industries where pin bush couplings are commonly used include the mining industry (in conveyors, crushers, and grinding mills), the construction industry (in concrete mixers, pumps, and excavators), and the marine industry (in ship propulsion systems and auxiliary machinery). In each of these industries, the coupling's ability to handle misalignments, dampen vibrations, and transmit torque reliably makes it an essential component.
Proper installation and maintenance of pin bush couplings are crucial to ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. Improper installation can lead to excessive wear, premature failure, and increased vibration, which can damage other components in the system. The first step in installation is to ensure that the shafts are properly aligned. While pin bush couplings can accommodate a certain degree of misalignment, excessive misalignment (beyond the coupling's rated capacity) can lead to increased stress on the pins and bushes, reducing their service life. Shaft alignment should be checked using tools such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems to ensure that angular, parallel, and axial misalignments are within the recommended limits specified by the coupling manufacturer.
The next step is to mount the coupling halves on the shafts. This typically involves using keyways and set screws or taper-lock bushings to secure the coupling halves to the shafts. It is important to ensure that the coupling halves are mounted tightly on the shafts to prevent slippage during operation, which can cause wear and reduce torque transmission efficiency. Once the coupling halves are mounted, the pins and bushes are installed. The bushes should be inserted into the holes in the coupling half with a snug fit, and the pins should be secured firmly to the other half. It is also important to check that all fasteners (such as cotter pins or retaining rings) are properly installed to prevent the pins or bushes from coming loose during operation.
Regular maintenance is essential to keep pin bush couplings in good working condition. Maintenance activities typically include periodic inspection, lubrication (if required), and replacement of worn components. Periodic inspection involves checking for signs of wear or damage to the pins, bushes, and coupling halves. Worn bushes may appear cracked, deformed, or worn down, while worn pins may show signs of corrosion, bending, or excessive wear on the contact surface with the bushes. Coupling halves should be checked for cracks, corrosion, or damage to the flanges or holes.
Lubrication is an important maintenance step for some types of pin bush couplings, particularly those with metal bushes or where the pins and bushes are subject to high levels of friction. Lubrication helps reduce friction between the pins and bushes, minimizing wear and extending their service life. The type of lubricant used should be compatible with the material of the bushes and the operating conditions (e.g., temperature, exposure to chemicals). It is important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the frequency and type of lubrication.
When worn components are detected, they should be replaced promptly to prevent further damage to the coupling or other components in the system. The replacement of pins and bushes is relatively straightforward, as these are the most commonly worn components. When replacing bushes, it is important to use bushes of the same material and dimensions as the original ones to ensure compatibility and maintain the coupling's performance characteristics. In some cases, it may be necessary to replace the entire coupling if the coupling halves are damaged beyond repair.
In recent years, advancements in materials science and manufacturing technology have led to improvements in the design and performance of pin bush couplings. One of the key trends is the development of high-performance elastomeric materials for bushes. These new materials offer enhanced properties such as higher temperature resistance, better chemical resistance, and increased durability compared to traditional rubber materials. For example, the use of polyurethane bushes has become more widespread due to their superior abrasion resistance and longer service life. Additionally, the development of composite materials for coupling halves has allowed for weight reduction while maintaining high strength, making these couplings suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor.
Another emerging trend is the integration of smart technologies into pin bush couplings for condition monitoring. Smart couplings are equipped with sensors that can measure parameters such as temperature, vibration, and torque, providing real-time data on the coupling's performance. This data can be transmitted to a central monitoring system, allowing maintenance professionals to detect potential issues such as excessive wear, misalignment, or overloading before they lead to coupling failure. This predictive maintenance approach helps reduce downtime, lower maintenance costs, and extend the service life of the coupling and the entire mechanical system.
Manufacturing processes for pin bush couplings have also evolved, with the adoption of advanced techniques such as computer numerical control (CNC) machining and 3D printing. CNC machining allows for greater precision in the manufacturing of coupling components, ensuring better fit and performance. 3D printing, on the other hand, enables the production of complex coupling designs that were previously difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods. This technology also allows for rapid prototyping, making it easier to test and refine new coupling designs.
Despite the emergence of new coupling technologies, pin bush couplings continue to be widely used due to their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliability. However, there are certain limitations that should be considered when selecting this type of coupling. One of the main limitations is their limited torque capacity compared to more heavy-duty couplings such as gear couplings or disc couplings. As a result, pin bush couplings are not suitable for applications requiring very high torque transmission. Another limitation is their relatively lower resistance to high temperatures, particularly when using rubber bushes, which can degrade at elevated temperatures. In such applications, couplings with metal or composite bushes may be more suitable.
In conclusion, the pin bush coupling is a versatile and cost-effective component that plays a vital role in mechanical power transmission systems. Its simple design, ability to accommodate misalignments, vibration damping properties, and wide range of material options make it suitable for applications across various industries, from industrial machinery to agriculture and automotive. Proper installation and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity, while advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies are driving improvements in its design and functionality. By understanding the characteristics and applications of pin bush couplings, engineers and maintenance professionals can leverage their advantages to enhance the efficiency and reliability of mechanical systems. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that pin bush couplings will remain a key component in power transmission, with further innovations aimed at improving their performance, durability, and adaptability to new applications.
« Pin Bush Couplings » Post Date: 2023/11/11
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/pin-bush-couplings.html
- 2025-12-02Pin Bush Coupling Types
- 2025-08-05Pin Bush Coupling Parts
- 2025-06-27Pin Bush Coupling Bolt Size Chart
- 2023-12-11Working Principle of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-12-11Uses of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-11Torque of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-12-11Tagging of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-12-11Supply of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-11Structural Diagram of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-11Stiffness of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-11Specifications of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-11Sales of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-12-11Purpose of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-11Price of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Couplings Supplier
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Size Calculation
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Procurement
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Misalignment Tolerance
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Grease
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Classification
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Catalogue
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Calculation
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Assembly Drawing
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Applications
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Alignment
- 2023-12-11Pin Bush Coupling Advantages
- 2023-12-06Pin Bush Coupling 3D Model
- 2023-12-06Parts of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-12-06Models of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-06Material of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-06Maintenance of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-06Machine Drawing of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-06Lubrication of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-06Installation of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-12-06Exploded View of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-06Engineering Drawing of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-06Efficiency of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-12-06Disadvantages of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-11-28Purpose of Flexible Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-11-28Models of Flexible Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Couplings Supply
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Couplings Manufacturer
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Couplings Factory
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Working Principle
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Structural Diagram
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Size Calculation
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Price
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Parts
- 2023-11-28Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Function
- 2023-11-28Disadvantages of Flexible Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-11-28Catalogue of Flexible Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-11-23Pin Bush Coupling Manufacturing Enterprise
- 2023-11-23Size Chart of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-11-23Types of Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-11-23Pin Bush Coupling Function
- 2023-11-23Pin Bush Coupling For Sale
- 2023-11-23Pin Bush Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-23Pin Bush Coupling Design
- 2023-11-23Pin Bush Coupling Customized
- 2023-11-16Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Applications
- 2023-11-11Pin Bush Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-11-11Pin Bush Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-11Pin Bush Coupling Factory
- 2023-11-11Pin Bush Coupling Company
- 2023-11-11Pin Bush Coupling Brands
- 2023-11-11Gap Chart of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-11-11Components of Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-11-10Types of Flexible Pin Bush Couplings
- 2023-11-10Flexible Pin Bush Couplings For Sale
- 2023-11-10Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Advantages
- 2023-11-10Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-10Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Size Chart
- 2023-11-09Flexible Pin Bush Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-09Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Specifications
- 2023-11-09Customized Flexible Pin Bush Coupling
- 2023-11-09Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Design
- 2023-11-09Flexible Pin Bush Couplings Supplier
- 2023-11-08Flexible Pin Bush Couplings Company
- 2023-11-08Flexible Pin Bush Coupling Manufacturing Enterprise
- 2023-10-20Pin Bush Couplings For Sale