Metallic Disc Couplings
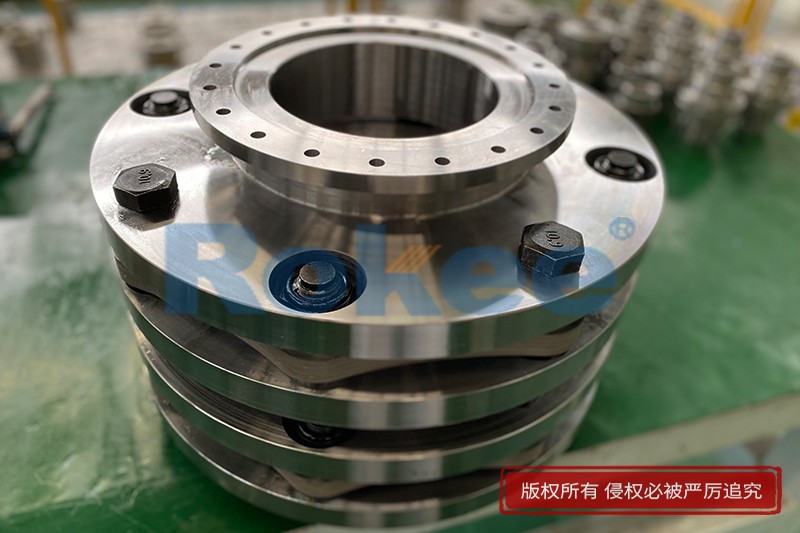

Rokee® is Metallic Disc Couplings Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® Metallic Disc Couplings have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
Metallic Disc Coupling is a kind of high-performance metal flexible coupling, which compensates axial and angular displacements by the deformation of elastic diaphragm while transferring torque. Metallic Disc Coupling features with compact structure, large transmission torque, long service life, maintenance-free, high temperature resistance, acid and alkali resistance, and corrosion resistance, suitable for shafting transmission in high temperature, high speed and corrosive environment.
-

JMI Diaphragm Coupling
JMI metal diaphragm coupling adopts the single-piece design, suitable for short distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMII Diaphragm Coupling
JMII metal diaphragm coupling also adopts the single-piece design but has no counterbore, suitable for short distance transmission, with more compact structure. -

JMIIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at both ends have no counterbore. -
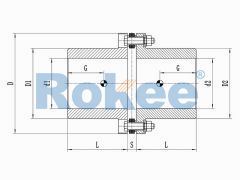
RLA Standard Single Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications, but cannot compensate for radial deviation. -
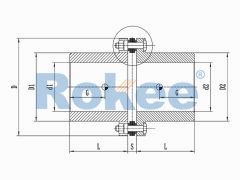
RLM Small Single Diaphragm Coupling
The RLM standard single section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working situations with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm, and cannot compensate for radial errors. -
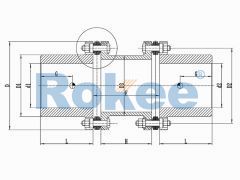
RLMD Small Double Diaphragm Coupling
The RLMD standard double section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working occasions with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm. -
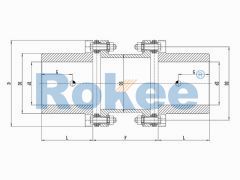
RLAD Standard Double Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications. -
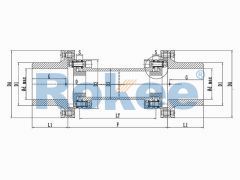
RLAT Super Long Wheelbase Diaphragm Coupling
Adopting an intermediate shaft design, suitable for ultra long shaft spacing power transmission applications. -
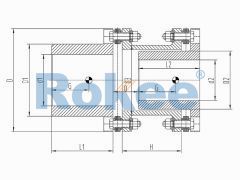
RLAR Single Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
Single side shaft sleeve reverse installation design, suitable for occasions with limited shaft head distance. -
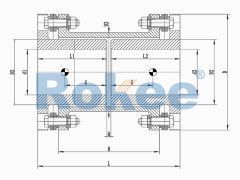
RLARD Double Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
The double-sided shaft sleeve reverse installation design is also applicable in situations where the distance from the shaft head is limited or the additional bending moment is smaller. -
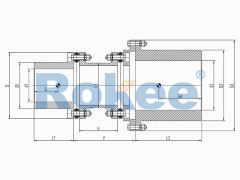
RLAF Large & Small Shaft Mounted Diaphragm Coupling
The size difference design of the bilateral shaft sleeve is suitable for situations where the diameter difference between the two ends of the shaft is significant. -
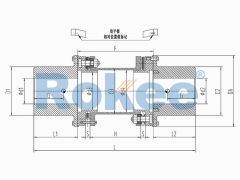
RLQA No Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for various industrial process pumps, fans, and other medium to low speed applications, with a maximum speed generally not exceeding 25000 rpm. It meets the requirements of API610/ISO14691 and is one of the first products for API applications. -
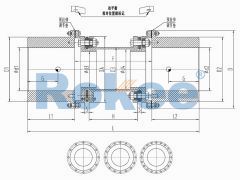
RLQF Flange Type Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications, with a maximum speed of up to 35000rpm. -
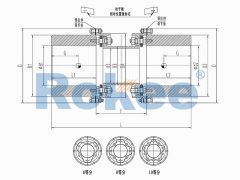
RLQU Improved Flange Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
The improved RLQF has smaller additional bending moments and better performance. Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications. -
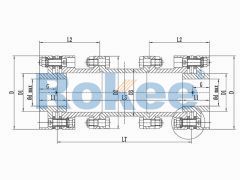
RLHD High Speed Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for higher speed applications, it also adopts a flexible component integrated assembly design, with a maximum speed of up to 42000rpm.
In the realm of industrial power transmission, the efficient and reliable transfer of torque between rotating shafts is paramount to the smooth operation of machinery. Among the various coupling solutions available, metallic disc couplings have emerged as a preferred choice for high-performance applications due to their unique combination of flexibility, durability, and precision. Unlike elastomeric or gear couplings, metallic disc couplings utilize thin, flexible metallic discs to accommodate misalignments while transmitting torque without the need for lubrication.
1. Understanding Metallic Disc Couplings: Definition and Core Components
A metallic disc coupling is a type of rigid-flexible coupling designed to transmit torque from a driving shaft to a driven shaft while compensating for three main types of misalignment: angular, parallel, and axial. The defining feature of this coupling is its use of metallic discs (or disc packs) as the flexible element, which replaces the rubber or plastic components found in elastomeric couplings and the gear teeth in gear couplings. This metallic construction imparts superior strength, temperature resistance, and longevity, making the coupling suitable for harsh and high-demand environments.
The core components of a typical metallic disc coupling include:
- Disc Packs: The heart of the coupling, disc packs are composed of multiple thin metallic discs arranged in a stack. Common materials used for these discs include stainless steel, titanium, and high-strength alloy steels. The discs are precision-manufactured with holes around their circumference to allow for bolting to the hubs. The number and thickness of the discs vary depending on the torque requirements and the level of flexibility needed.
- Hubs: These are cylindrical components that attach to the driving and driven shafts. Hubs are typically made of forged steel or aluminum alloy and are designed to fit the shaft diameter via interference fit, keyway, or clamping mechanisms. The hubs feature flanges that connect to the disc packs through bolts.
- Spacer (Optional): Some metallic disc couplings include a spacer between the two sets of disc packs. Spacers are used to accommodate longer shaft distances and can be solid or hollow. Hollow spacers are often preferred for lightweight applications or where reduced inertia is critical.
- Bolts and Fasteners: High-tensile bolts are used to secure the disc packs to the hubs and spacers (if present). These bolts must be torqued to precise specifications to ensure proper transmission of torque and to prevent premature failure of the disc packs.
Disc packs can be configured in two main designs: single-disc and multi-disc. Single-disc couplings are simpler but offer limited flexibility, while multi-disc couplings, with their stacked configuration, provide greater misalignment capacity and higher torque density. Additionally, disc packs may be designed with different shapes, such as circular, square, or hexagonal, to optimize flexibility and torque transmission.
2. Working Mechanism: How Metallic Disc Couplings Transmit Torque and Compensate Misalignment
The working principle of a metallic disc coupling revolves around the flexibility of the metallic disc packs. When torque is applied to the driving shaft, it is transferred to the driving hub, which in turn exerts a rotational force on the disc pack. The disc pack bends slightly to accommodate any misalignment between the driving and driven shafts and transmits the torque to the driven hub, ultimately rotating the driven shaft.
To understand the misalignment compensation, it is important to break down the three types of misalignment and how the disc packs address each:
1. Angular Misalignment: This occurs when the axes of the two shafts intersect at an angle. The metallic discs flex along their thickness to absorb the angular offset. The flexibility of the discs allows the coupling to maintain torque transmission without creating excessive stress on the shafts or bearings. The maximum angular misalignment capacity typically ranges from 0.5 to 3 degrees, depending on the design of the disc pack.
2. Parallel Misalignment: This happens when the axes of the two shafts are parallel but offset from each other. Parallel misalignment is compensated by the lateral flexibility of the disc packs. The amount of parallel misalignment that can be accommodated is generally smaller than angular misalignment, typically up to 0.5 mm per 100 mm of coupling length.
3. Axial Misalignment: Axial misalignment occurs when the shafts move toward or away from each other along their axes. The metallic disc packs can stretch or compress slightly to accommodate this movement, with axial displacement capacity ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters, depending on the coupling design.
A key advantage of the metallic disc design is that it transmits torque without slip, ensuring precise speed synchronization between the driving and driven shafts. Unlike gear couplings, which rely on meshing gears and require lubrication to reduce friction and wear, metallic disc couplings have no sliding or rotating contact between moving parts (other than the shaft-hub connection). This eliminates the need for regular lubrication, reducing maintenance requirements and the risk of lubricant contamination in sensitive applications.
3. Key Advantages of Metallic Disc Couplings
Metallic disc couplings offer a range of benefits that make them superior to other coupling types in many industrial applications. These advantages stem from their unique design and the properties of the metallic materials used:
3.1 High Torque Density and Load Capacity
Metallic materials such as stainless steel and alloy steels have high tensile strength and fatigue resistance, allowing metallic disc couplings to transmit high levels of torque relative to their size. This high torque density makes them ideal for compact machinery where space is limited, such as in automotive transmissions, industrial gearboxes, and turbomachinery.
3.2 Wide Temperature Range Tolerance
Unlike elastomeric couplings, which can degrade at high temperatures (typically above 120°C) and become brittle at low temperatures (below -40°C), metallic disc couplings can operate reliably over a wide temperature range. Depending on the material, they can withstand temperatures from -50°C to 350°C or higher, making them suitable for applications such as gas turbines, steam engines, and industrial ovens where extreme temperatures are common.
3.3 No Lubrication Required
The absence of sliding or meshing parts in the coupling mechanism eliminates the need for lubrication. This not only reduces maintenance costs and downtime but also makes metallic disc couplings suitable for clean environments, such as food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and semiconductor production, where lubricant contamination could compromise product quality.
3.4 Low Vibration and Noise
The flexible metallic disc packs absorb vibration and shock loads, reducing the transmission of vibrations from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. This helps to minimize machinery noise and extend the lifespan of bearings, gears, and other components. In contrast, gear couplings can generate significant noise due to gear meshing, especially when misaligned, and elastomeric couplings may harden over time, reducing their vibration-damping capabilities.
3.5 Long Service Life and High Reliability
Metallic disc couplings have a long service life due to the high fatigue resistance of the metallic discs and the absence of wear-prone components. When properly installed and maintained, they can operate for tens of thousands of hours without failure. This high reliability is critical in mission-critical applications where unplanned downtime can result in significant financial losses, such as in power generation, oil and gas exploration, and marine propulsion systems.
3.6 Precision Torque Transmission
Metallic disc couplings transmit torque with minimal backlash, ensuring precise speed and position control. This makes them ideal for applications that require high precision, such as robotics, CNC machines, and automated production lines. In contrast, gear couplings may have significant backlash due to gear tooth clearance, and elastomeric couplings can exhibit slight slip under high loads.
4. Industrial Applications of Metallic Disc Couplings
Due to their versatility and superior performance characteristics, metallic disc couplings are used in a wide range of industrial sectors. Below are some of the key applications where these couplings are commonly employed:
4.1 Power Generation
In power plants (thermal, nuclear, hydroelectric, and wind), metallic disc couplings are used to connect turbines to generators. These applications require high torque transmission, precise alignment, and resistance to extreme temperatures and harsh environments. The no-lubrication feature is particularly beneficial in nuclear power plants, where lubricant contamination is a major concern.
4.2 Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry relies on metallic disc couplings for various applications, including pumps, compressors, and drilling rigs. These couplings must withstand high pressures, corrosive environments (due to exposure to oil, gas, and saltwater), and high torque loads. The durability and low maintenance requirements of metallic disc couplings make them well-suited for offshore drilling platforms, where access for maintenance is limited.
4.3 Automotive and Aerospace
In the automotive industry, metallic disc couplings are used in high-performance vehicles, such as racing cars and electric vehicles, to connect the engine to the transmission. They offer precise torque transmission and high-speed capability, which is essential for these applications. In the aerospace sector, metallic disc couplings are used in aircraft engines and auxiliary power units (APUs), where lightweight design, high reliability, and temperature resistance are critical.
4.4 Industrial Machinery and Manufacturing
Metallic disc couplings are widely used in industrial machinery such as pumps, compressors, fans, conveyors, and CNC machines. In CNC machining, for example, the precision torque transmission and low backlash of these couplings ensure accurate cutting and positioning. In pumping applications, they accommodate misalignments between the motor and pump shafts, reducing wear on bearings and extending pump life.
4.5 Marine Propulsion
Marine vessels, including ships and submarines, use metallic disc couplings to connect the engine to the propeller shaft. These couplings must withstand high torque, corrosive saltwater environments, and significant misalignments caused by hull flexing. The no-lubrication feature is advantageous in marine applications, as it eliminates the risk of lubricant leakage into the ocean.
4.6 Renewable Energy
In renewable energy systems such as wind turbines and solar thermal plants, metallic disc couplings play a crucial role in transmitting torque from the rotor to the generator. Wind turbines, in particular, require couplings that can accommodate misalignments caused by wind-induced vibrations and shaft deflection, while also withstanding harsh outdoor environments. The high reliability and low maintenance requirements of metallic disc couplings make them ideal for these applications, where downtime for maintenance is costly and logistically challenging.
5. Selection Criteria for Metallic Disc Couplings
Selecting the right metallic disc coupling for a specific application requires careful consideration of several key factors. The following criteria should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and reliability:
5.1 Torque Requirement
The primary factor in coupling selection is the maximum torque that the coupling will need to transmit. This includes both the nominal operating torque and any peak torque loads (such as startup torque or shock loads). The coupling must be rated for a torque capacity that exceeds the maximum expected torque to ensure safety and prevent premature failure.
5.2 Shaft Misalignment
The type and magnitude of misalignment between the driving and driven shafts must be determined. This includes angular, parallel, and axial misalignment. The selected coupling must have a misalignment capacity that matches or exceeds the expected misalignment in the application. Failure to account for misalignment can result in excessive stress on the coupling discs, shafts, and bearings.
5.3 Operating Speed
The maximum operating speed (in RPM) of the shafts is another critical factor. Metallic disc couplings have a maximum allowable speed, which is determined by the centrifugal forces acting on the disc packs and other components. Exceeding this speed can lead to component failure due to fatigue or structural damage.
5.4 Environmental Conditions
The operating environment must be considered, including temperature, humidity, corrosive substances, and dust. For high-temperature applications, couplings made from heat-resistant materials (such as titanium or Inconel) should be selected. For corrosive environments, stainless steel or coated components may be necessary to prevent rust and degradation.
5.5 Shaft Diameter and Length
The coupling must be compatible with the diameter of the driving and driven shafts. Hubs are available in a range of sizes to fit different shaft diameters, and some hubs are adjustable (via clamping mechanisms) to accommodate multiple shaft sizes. The distance between the two shafts (shaft separation) will determine whether a spacer is needed and the length of the spacer.
5.6 Inertia Requirements
In high-speed applications or applications that require rapid acceleration and deceleration, the moment of inertia of the coupling is important. Lower inertia couplings (such as those with hollow spacers or lightweight materials) can help to reduce energy consumption and improve dynamic performance.
6. Maintenance and Inspection of Metallic Disc Couplings
While metallic disc couplings require less maintenance than gear or elastomeric couplings, regular inspection and maintenance are still essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent unexpected failure. The following maintenance practices are recommended:
6.1 Regular Visual Inspections
Visual inspections should be performed periodically to check for signs of damage, such as cracks in the disc packs, loose bolts, or corrosion. Cracks in the discs are a critical issue, as they can lead to sudden coupling failure. Any damaged components should be replaced immediately.
6.2 Bolt Torque Checks
The bolts that secure the disc packs to the hubs and spacers can loosen over time due to vibration. Regular torque checks should be performed using a torque wrench to ensure that the bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose bolts can cause misalignment, excessive stress on the discs, and eventual failure.
6.3 Shaft Alignment Checks
Shaft alignment should be checked periodically, especially after maintenance or when new machinery is installed. Misalignment can increase stress on the coupling and other components, reducing service life. Alignment can be checked using tools such as dial indicators, laser alignment systems, or optical alignment tools.
6.4 Cleaning
In dusty or corrosive environments, the coupling should be cleaned regularly to remove dirt, debris, and corrosive substances. This helps to prevent corrosion and ensures that moving parts (if any) operate smoothly. A mild detergent and water can be used for cleaning, followed by drying to prevent rust.
6.5 Replacement of Wear Components
While metallic disc couplings have a long service life, the disc packs will eventually wear out due to fatigue. The lifespan of the disc packs depends on the operating conditions, torque loads, and misalignment. Manufacturers typically provide guidelines for the replacement of disc packs based on operating hours or visual signs of wear. It is important to replace the disc packs before they fail to avoid damage to the shafts, bearings, or other machinery components.
7. Future Trends in Metallic Disc Coupling Technology
As industrial machinery becomes more advanced, the demand for high-performance, efficient, and reliable coupling solutions continues to grow. Several trends are shaping the future of metallic disc coupling technology:
7.1 Lightweight Materials and Design Optimization
Manufacturers are increasingly using lightweight materials such as titanium and carbon fiber composites to reduce the weight and moment of inertia of metallic disc couplings. This is particularly important for aerospace and automotive applications, where weight reduction improves fuel efficiency and performance. Additionally, advanced design techniques such as finite element analysis (FEA) are being used to optimize the shape and thickness of the disc packs, improving flexibility and torque capacity while reducing material usage.
7.2 Smart Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
The integration of sensors and monitoring systems into metallic disc couplings is becoming more common. These sensors can detect changes in vibration, temperature, and torque, providing real-time data on the coupling’s performance. This enables predictive maintenance, allowing operators to identify potential issues before they lead to failure. For example, vibration sensors can detect misalignment or disc damage, while temperature sensors can alert operators to overheating.
7.3 Increased Corrosion Resistance
With the growing use of metallic disc couplings in harsh and corrosive environments (such as offshore oil and gas platforms and chemical plants), there is a focus on improving corrosion resistance. This includes the use of advanced coatings, such as ceramic or polymer coatings, and the development of new alloys that offer superior resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
7.4 Customization for Specific Applications
As industrial applications become more specialized, there is a growing demand for custom metallic disc couplings tailored to specific requirements. Manufacturers are offering customized solutions, including custom hub designs, disc pack configurations, and spacer lengths, to meet the unique needs of applications such as large-scale wind turbines, high-speed turbomachinery, and precision robotics.
8. Conclusion
Metallic disc couplings have established themselves as a versatile and reliable solution for power transmission in a wide range of industrial applications. Their unique design, which utilizes flexible metallic disc packs, offers a combination of high torque density, wide temperature tolerance, no lubrication requirements, and precise torque transmission that is unmatched by other coupling types. From power generation and oil and gas to automotive and renewable energy, metallic disc couplings play a critical role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of machinery.
The selection of the right metallic disc coupling requires careful consideration of torque requirements, misalignment, operating speed, environmental conditions, and other factors. Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to maximize the coupling’s service life and prevent unexpected failure. As technology advances, the future of metallic disc couplings looks promising, with ongoing developments in lightweight materials, smart monitoring, and customization poised to further enhance their performance and expand their range of applications.
In an era where industrial efficiency and reliability are more important than ever, metallic disc couplings continue to be a key component in the drive toward more efficient, sustainable, and high-performance machinery. Their ability to withstand harsh conditions, transmit torque precisely, and require minimal maintenance makes them an indispensable part of modern industrial systems.
« Metallic Disc Couplings » Post Date: 2023/11/8
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/metallic-disc-couplings.html
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Couplings Supply
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling Structural Diagram
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling Purpose
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling Parts
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling Make
- 2023-11-14Metallic Disc Coupling For Sale
- 2023-11-10Metallic Disc Coupling Customized
- 2023-11-10Metallic Disc Coupling Function
- 2023-11-10Metallic Disc Coupling Size Calculation
- 2023-11-09Metallic Disc Coupling Specifications
- 2023-11-09Models Of Metallic Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-09Metallic Disc Coupling Working Principle
- 2023-11-09Metallic Disc Coupling Design
- 2023-11-08Types Of Metallic Disc Couplings
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Factory
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Advantages
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Manufacturing Enterprise
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Manufacturer
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Catalogue
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Supplier
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Size Chart
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Couplings Company
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Price
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Applications
- 2023-11-08Metallic Disc Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-08Disadvantages Of Metallic Disc Couplings