Lamina Couplings
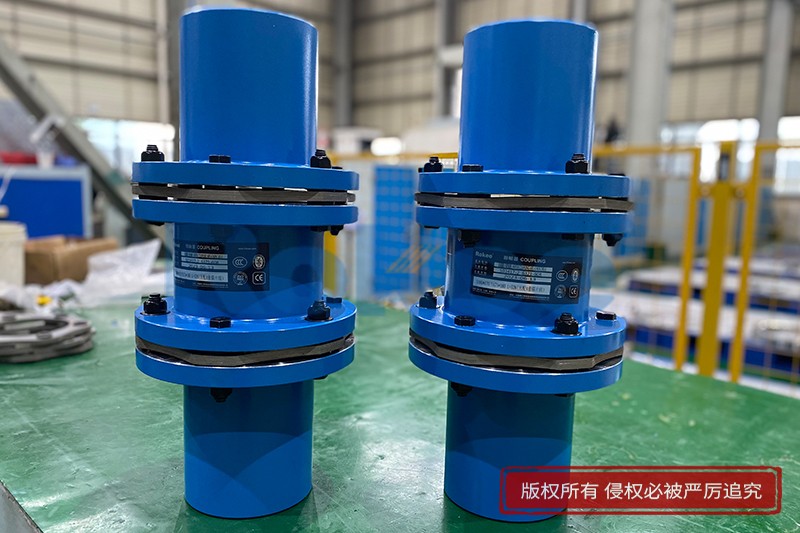

Rokee® is Lamina Couplings Supplier from China, Support Customization and Export, due to excellent quality, complete technical services and superior cost performance, Rokee® Lamina Couplings have been serving more than 60 countries and regions in the world, effectively operating in many corners of the world.
Rokee's Lamina Coupling is a high-quality product developed independently on basis of combination of advanced products from Europe and Japan, etc. Steel Lamina Coupling has smaller size, larger torque of the same model, more reasonable proportioning size, large compensation scope, light weight and small rotational inertia. With modularized design, it’s easy for assembly, maintenance and replacement. Its performance far exceeds the one of JM series product. It’s widely applied in the fields of fan systems, turboset and other pumps, etc.
-

JMI Diaphragm Coupling
JMI metal diaphragm coupling adopts the single-piece design, suitable for short distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at one end has a counterbore, facilitating the fixing of the shaft end. -

JMII Diaphragm Coupling
JMII metal diaphragm coupling also adopts the single-piece design but has no counterbore, suitable for short distance transmission, with more compact structure. -

JMIIJ Diaphragm Coupling
JMIIJ metal diaphragm coupling is designed with intermediate shaft, suitable for long distance transmission. Besides, the semi-coupling sleeve at both ends have no counterbore. -
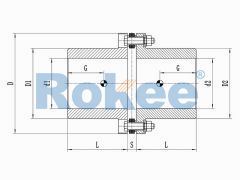
RLA Standard Single Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications, but cannot compensate for radial deviation. -
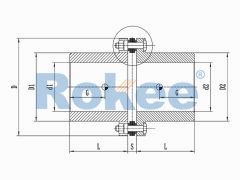
RLM Small Single Diaphragm Coupling
The RLM standard single section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working situations with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm, and cannot compensate for radial errors. -
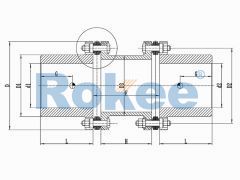
RLMD Small Double Diaphragm Coupling
The RLMD standard double section small metal diaphragm coupling is suitable for various industrial process pumps and small torque working occasions with a working speed not exceeding 5000rpm. -
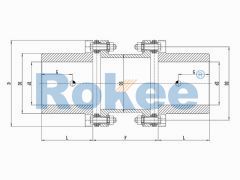
RLAD Standard Double Diaphragm Coupling
The classic design of metal flexible diaphragm couplings is a reliable choice for medium to low speed applications. -
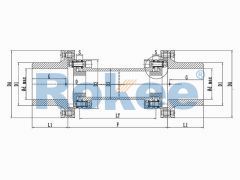
RLAT Super Long Wheelbase Diaphragm Coupling
Adopting an intermediate shaft design, suitable for ultra long shaft spacing power transmission applications. -
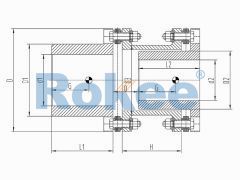
RLAR Single Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
Single side shaft sleeve reverse installation design, suitable for occasions with limited shaft head distance. -
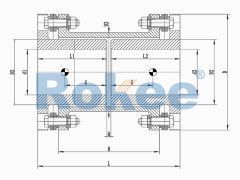
RLARD Double Shaft Sleeve Reverse-mounting Diaphragm Coupling
The double-sided shaft sleeve reverse installation design is also applicable in situations where the distance from the shaft head is limited or the additional bending moment is smaller. -
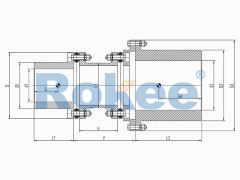
RLAF Large & Small Shaft Mounted Diaphragm Coupling
The size difference design of the bilateral shaft sleeve is suitable for situations where the diameter difference between the two ends of the shaft is significant. -
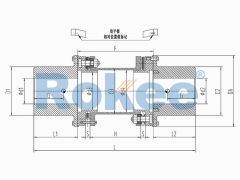
RLQA No Flange Quick Installation Metal Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for various industrial process pumps, fans, and other medium to low speed applications, with a maximum speed generally not exceeding 25000 rpm. It meets the requirements of API610/ISO14691 and is one of the first products for API applications. -
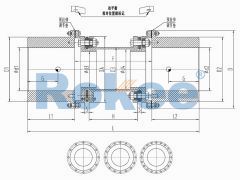
RLQF Flange Type Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications, with a maximum speed of up to 35000rpm. -
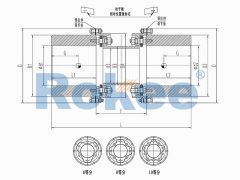
RLQU Improved Flange Quick Installation Diaphragm Coupling
The improved RLQF has smaller additional bending moments and better performance. Suitable for drum pressure fans, turbine compressors, and other high speed applications. -
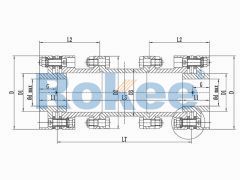
RLHD High Speed Diaphragm Coupling
Suitable for higher speed applications, it also adopts a flexible component integrated assembly design, with a maximum speed of up to 42000rpm.
In the realm of mechanical power transmission, the efficiency, precision, and reliability of component connection directly determine the overall performance of industrial equipment. Among the various coupling devices designed to bridge rotating shafts, lamina coupling has emerged as a critical solution, particularly in scenarios requiring high precision, low maintenance, and resistance to harsh operating conditions. Also known as diaphragm coupling, this type of flexible coupling utilizes thin, elastic metal sheets (laminae) to transmit torque while compensating for axial, radial, and angular misalignments between shafts. Unlike rigid couplings that demand strict alignment or elastomeric couplings that rely on rubber or plastic components, lamina coupling offers unique advantages such as no backlash, high torque density, and compatibility with high-temperature and high-speed environments.
The fundamental design concept of lamina coupling revolves around balancing torque transmission efficiency with the ability to accommodate shaft misalignments. At its core, the coupling consists of three main components: two shaft hubs (also called flanges) that connect to the driving and driven shafts, and a set of laminae (diaphragm packs) that link the two hubs. The laminae are the key functional elements, designed to be thin enough to exhibit elastic deformation under load, yet strong enough to withstand the transmitted torque without permanent damage. The design of the laminae varies depending on the application requirements, with common configurations including single-diaphragm, double-diaphragm, and multi-diaphragm structures. Single-diaphragm designs are simpler and more cost-effective, suitable for light to medium torque applications with moderate misalignment. Double-diaphragm designs, which incorporate two sets of laminae separated by a spacer, offer enhanced misalignment compensation capabilities, particularly for angular and axial displacements, making them ideal for high-precision machinery. Multi-diaphragm structures, with three or more lamina packs, further improve flexibility and torque distribution, catering to heavy-duty industrial applications.
Another critical aspect of lamina coupling design is the arrangement of the laminae. Typically, the laminae are attached to the hubs using bolts or rivets, with the bolt holes distributed in a circular pattern to ensure uniform torque transmission. The shape of the laminae also plays a significant role in their performance. Common shapes include circular, rectangular, and petal-shaped (lobed) designs. Circular laminae are the most straightforward, providing balanced flexibility and strength. Rectangular laminae offer higher radial stiffness, making them suitable for applications with significant radial loads. Petal-shaped laminae, with cutouts or lobes around the circumference, enhance elastic deformation capacity, allowing for greater misalignment compensation while reducing stress concentration. Additionally, the thickness of the laminae is carefully calculated based on the maximum torque, rotational speed, and misalignment requirements. Thicker laminae can transmit higher torque but offer lower flexibility, while thinner laminae provide better misalignment compensation but have lower torque capacity. Engineers must strike a precise balance between these factors during the design process to ensure optimal performance.
The working mechanism of lamina coupling is rooted in the elastic deformation of the laminae. When torque is applied to the driving shaft, the torque is transmitted through the driving hub to the laminae. The laminae, due to their elastic properties, deform slightly to accommodate any misalignment between the driving and driven shafts. As the torque is transferred to the driven hub, the laminae return to their original shape once the load is removed, ensuring no permanent deformation. This elastic deformation capability allows the coupling to compensate for three types of misalignments: axial (axial movement of shafts), radial (offset between shaft centers), and angular (tilt between shafts). Axial misalignment compensation is achieved through the axial stretching or compressing of the laminae, while radial misalignment is accommodated by the bending of the laminae. Angular misalignment is compensated for by the combined bending and twisting of the laminae. Importantly, this compensation occurs without generating backlash, a critical advantage in precision applications where even minimal play can lead to positioning errors or vibration.
Unlike elastomeric couplings that use rubber bushings or flexible sleeves, lamina coupling has no sliding or rolling parts, and thus requires no lubrication. This not only reduces maintenance costs but also eliminates the risk of lubricant leakage, which can contaminate the working environment and damage other components. The absence of lubrication also makes lamina coupling suitable for applications in clean rooms, food processing, and pharmaceutical industries, where hygiene and contamination control are paramount. Additionally, the all-metal construction of lamina coupling ensures high temperature resistance. Unlike elastomeric components that degrade at temperatures above 120°C, lamina couplings made from high-temperature alloys can operate reliably at temperatures exceeding 300°C, making them suitable for use in engines, turbines, and other high-temperature equipment.
Material selection is a decisive factor in the performance and durability of lamina coupling. The laminae, in particular, must be fabricated from materials with excellent elastic properties, high tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance. The most commonly used materials for laminae include stainless steel, titanium alloy, and nickel-based superalloys. Stainless steel, such as 304 or 316 grade, is widely used in general industrial applications due to its good balance of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. It is cost-effective and suitable for temperatures up to 250°C, making it ideal for machinery in automotive, textile, and general manufacturing industries. Titanium alloy is chosen for high-performance applications where weight reduction and high strength are critical, such as aerospace and military equipment. Titanium alloy offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to stainless steel, along with excellent corrosion resistance and fatigue performance, but comes at a higher cost. Nickel-based superalloys, such as Inconel, are used in extreme environments involving high temperatures, high pressure, and corrosive media. These alloys can withstand temperatures above 600°C and are resistant to oxidation and chemical attack, making them suitable for gas turbines, jet engines, and offshore oil drilling equipment.
The hubs of lamina coupling are typically made from carbon steel, alloy steel, or aluminum alloy. Carbon steel is used for general-purpose applications due to its high strength and low cost, while alloy steel is preferred for heavy-duty applications requiring higher torque capacity and wear resistance. Aluminum alloy is selected for lightweight applications, such as in aerospace and automotive components, where reducing overall weight is a priority. The material of the hubs must be compatible with the laminae to ensure reliable attachment and uniform torque distribution. In some cases, surface treatments such as galvanizing or anodizing are applied to the hubs to enhance corrosion resistance, particularly in outdoor or humid environments.
Lamina coupling finds extensive applications across a wide range of industries, driven by its unique combination of precision, reliability, and low maintenance. One of the most prominent application areas is the aerospace industry. In aircraft engines, lamina coupling is used to connect the turbine shaft to the compressor shaft, where high rotational speeds (up to 30,000 rpm), high temperatures, and strict precision requirements are common. The no-backlash and high-temperature resistance characteristics of lamina coupling ensure smooth power transmission and prevent engine vibration, which is critical for flight safety. Additionally, in aerospace actuators and control systems, lamina coupling is used to transmit torque between motors and gears, ensuring precise positioning and response.
The automotive industry is another major user of lamina coupling. In high-performance vehicles, such as racing cars and luxury sports cars, lamina coupling is used in the powertrain to connect the engine to the transmission. The high torque density and low inertia of lamina coupling allow for efficient power transfer, improving acceleration and overall vehicle performance. Additionally, in electric vehicles (EVs), lamina coupling is used to connect the electric motor to the drive axle, where its compact design and high efficiency contribute to the vehicle’s range and performance. Unlike traditional couplings, lamina coupling’s no-lubrication requirement also aligns with the EV industry’s focus on reducing maintenance and environmental impact.
In the industrial machinery sector, lamina coupling is widely used in machine tools, such as CNC milling machines, lathes, and grinding machines. These applications require high precision in torque transmission to ensure accurate machining of workpieces. The no-backlash feature of lamina coupling eliminates positioning errors caused by play, while its ability to compensate for shaft misalignment ensures stable operation even at high spindle speeds. Additionally, in industrial robots, lamina coupling is used in the joint actuators to transmit torque between motors and reducers, enabling precise and smooth movement of the robot arm. The compact size and low weight of lamina coupling also make it suitable for robotic applications where space is limited.
Other application areas of lamina coupling include the energy sector, where it is used in wind turbines, gas turbines, and steam turbines. In wind turbines, lamina coupling connects the gearbox to the generator, transmitting high torque while compensating for misalignments caused by wind load variations. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel or nickel-based lamina coupling makes it suitable for offshore wind farms, where exposure to saltwater and harsh weather conditions is a challenge. In the oil and gas industry, lamina coupling is used in drilling rigs, pumps, and compressors, where it withstands high temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive media. The no-lubrication requirement also reduces the risk of contamination in oil and gas processing facilities.
Despite its numerous advantages, lamina coupling also has certain limitations that need to be considered in practical applications. One of the main limitations is its relatively low damping capacity. Unlike elastomeric couplings that can absorb vibration and shock through the deformation of rubber components, lamina coupling’s all-metal construction provides minimal damping, making it less suitable for applications with significant shock loads or high vibration. In such cases, additional damping components may need to be installed, increasing the complexity and cost of the system. Another limitation is the higher initial cost compared to traditional rigid or elastomeric couplings. The precision manufacturing required for the laminae and hubs, along with the use of high-quality materials, makes lamina coupling more expensive, which may be a barrier for small-scale or low-cost applications.
Looking ahead, the development of lamina coupling is expected to focus on several key directions to address its limitations and expand its application scope. One of the main trends is the adoption of advanced materials and manufacturing technologies to improve performance and reduce costs. For example, the use of composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP), in lamina production could further reduce weight while maintaining high strength and flexibility. CFRP laminae offer excellent corrosion resistance, high fatigue strength, and lower density compared to metal, making them suitable for aerospace and automotive applications where weight reduction is critical. Additionally, additive manufacturing (3D printing) technologies can be used to produce complex lamina shapes with precise dimensions, reducing manufacturing time and cost. 3D printing also allows for the customization of lamina designs to meet specific application requirements, such as enhanced misalignment compensation or torque capacity.
Another development trend is the integration of smart monitoring technologies into lamina coupling. With the rise of Industry 4.0, there is an increasing demand for real-time monitoring of component performance to enable predictive maintenance. By embedding sensors, such as strain gauges or temperature sensors, into the laminae, engineers can monitor torque, temperature, and deformation in real time. This data can be transmitted to a central control system, allowing for early detection of potential failures, such as lamina fatigue or hub loosening. Predictive maintenance not only reduces downtime but also extends the service life of the coupling and the entire equipment system. Additionally, the use of digital twins—virtual replicas of physical couplings—can simulate the performance of lamina coupling under different operating conditions, enabling optimized design and maintenance strategies.
Furthermore, the development of lamina coupling for extreme environments is another important direction. With the expansion of industrial activities into harsh environments, such as deep-sea exploration, space exploration, and high-temperature nuclear power plants, there is a need for couplings that can withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and radiation. Research is ongoing to develop lamina coupling using advanced alloys and composite materials that can operate reliably in these environments. For example, in space applications, lamina coupling must withstand vacuum, extreme temperature fluctuations, and radiation, requiring materials with high thermal stability and radiation resistance.
In conclusion, lamina coupling has established itself as a vital component in modern mechanical power transmission systems, offering unique advantages such as high precision, no backlash, high-temperature resistance, and low maintenance. Its design, which relies on elastic metal laminae to transmit torque and compensate for shaft misalignments, makes it suitable for a wide range of applications across aerospace, automotive, industrial machinery, energy, and oil and gas industries. While it has limitations in terms of damping capacity and initial cost, ongoing advancements in materials, manufacturing technologies, and smart monitoring are expected to address these issues and expand its application scope. As industrial equipment continues to evolve toward higher precision, higher efficiency, and more extreme operating conditions, lamina coupling will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in ensuring the reliability and performance of these systems. The continuous innovation in lamina coupling design and technology will not only meet the current demands of various industries but also pave the way for new applications in the future.
« Lamina Couplings » Post Date: 2023/9/1
URL: https://www.rokeecoupling.com/en/tags/lamina-couplings.html
- 2023-11-02Lamina Couplings Wholesale
- 2023-11-02Types of Lamina Couplings
- 2023-11-02Lamina Couplings Supply
- 2023-11-02Lamina Couplings Supplier
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Structural Diagram
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Specifications
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Size Chart
- 2023-11-02Purpose of Lamina Couplings
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Price
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Parts
- 2023-11-02Model of Lamina Coupling
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Manufacturer
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Make
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling For Sale
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Factory
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Effect
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Drawing
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Disadvantages
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Design
- 2023-11-02Customized Lamina Couplings
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Company
- 2023-11-02Lamina Couplings Catalogue
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Application
- 2023-11-02Lamina Coupling Advantages